Electric Circuit-Definition, Parts, Types, And Precautions
An electric circuit or electrical circuit is a path for the flow of electric current or electricity. A wire is used to establish a relationship between the load and the source of voltage. An ON / off switch and a fuse are used in between the source and load.
What is an Electric Circuit?
There is an electric circuit that can transmit electric current. An electric circuit includes an electrical device that gives energy to the charged particles constituting the current, such as a battery or an AC generator; devices that use current, such as lamps, electric motors, or computers, and the connecting wires or transmission lines. The two basic laws that describe the performance of electric circuits are Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s rules.
Electric Circuit Parts
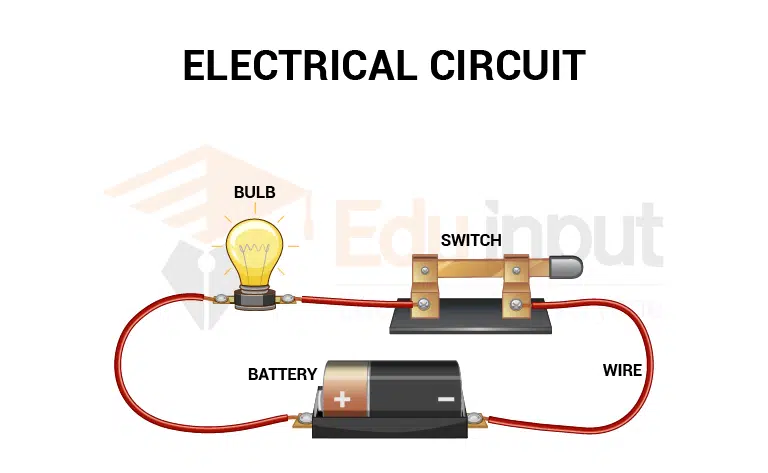
It is important to know about the basics of an electric circuit. There is a source, a switch, a load, and a conductor in a simple electric circuit. Some of the functions of these parts are listed.
● Cell:
It can be used as a source of electric current.
● Load:
There is a component called a Resistor. It’s a light bulb, which glows when the circuit is turned on.
● Conductors:
The wires are made of copper and have no insulation. One end of the wire carries the current from the power source to the load while the other carries it from the power source to the load.
● Switch:
A part of the circuit that controls the supply of current. It’s used to close or open the circuit.
Types of Electric Circuits
These are the basic types of an electric circuit.
Series Electric Circuits
Each device in the series circuit is linked up one after the other in a single large loop. Different devices have different voltages, but the same current flows through them. The whole circuit fails if any one of the devices in the series is broken. One loop of wire connected to a battery is all that is needed for three light bulbs to be connected in a series. The whole circuit doesn’t work if one light bulb is taken out.
Parallel Electric Circuits
In parallel circuits, different devices are arranged so that a single source is able to supply voltage to separate loops of wire. The voltage in every device across the circuit is the same, but in general, different devices are going to see different currents. Even if the other ones don’t work, each device is still going to work. Modern Christmas tree lights are done in parallel circuits so that even if a single light burns out, the whole strand doesn’t have.
Close Circuit
When load works on its own in a circuit, it is called a Close Circuit or Closed Circuit. The value of the current flow is dependent on the load.
Open Circuit
When there is a faulty electrical wire or electronic component in a circuit or a switch is closed, it is called an open circuit. In the diagram below, you can see that the Bulb isn’t glowing because the switch is off or there is a fault with the electrical wire.
Short Circuit
A short circuit is when the two points of a voltage source in a circuit get close to each other. Under this situation, the maximum current starts to flow. Shorting in the load causes the conducting electrical wires to get joint, which causes the short circuit.
Precautions while using Electric Circuits
- Good quality wires with proper insulation and thickness should be used for household wiring. Plugs, switches, and sockets can be used for better use of electrical appliances if they have an ISI mark on them.
- It is recommended that the wires are completely insulated.
- Before starting any work on the electric circuit, you should switch off the main supply.
- First, switch off the main supply if there is a short circuit. Try to insulate the person who has received a shock. Don’t touch him directly.
- You need to take precautions while earthing or installing a fuse for the household electric circuits.





Leave a Reply