Erbium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Erbium is a chemical element with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. It is a rare earth element that is silvery-white in appearance and soft in texture. Erbium has a high melting point and is relatively stable in air.
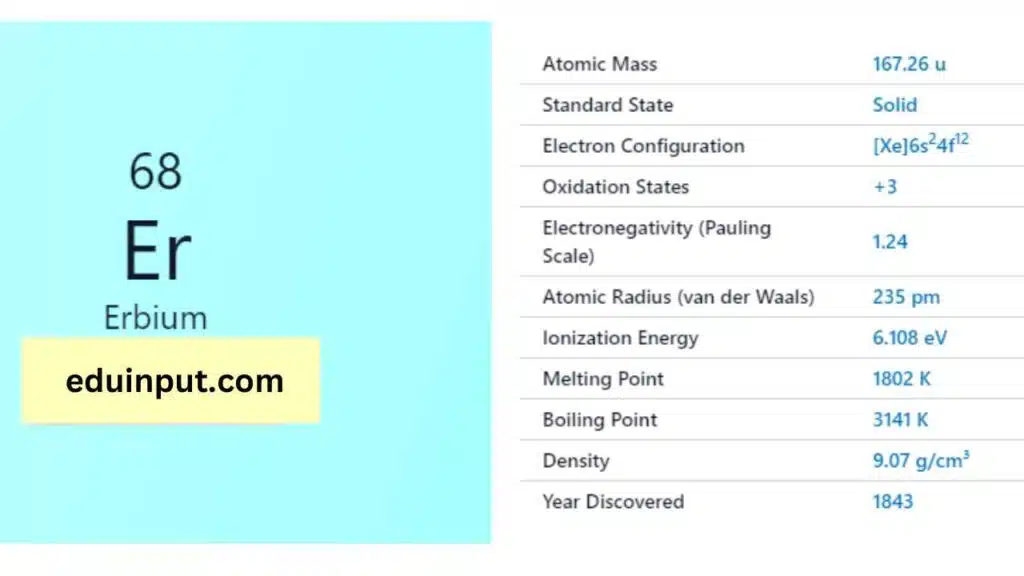
| Property | Value |
| Name | Erbium |
| Symbol | Er |
| Atomic number | 68 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Block in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | |
| Group name | Lanthanoid |
| Period in periodic table | 6 (lanthanoid) |
| Block in periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.30.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-52-0 |
Discovery
Erbium was first discovered in 1842 by Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander. He was able to isolate a new oxide from a sample of the mineral gadolinite. Mosander named the oxide “erbia” after the village of Ytterby in Sweden where the gadolinite was found.
Physical Properties
Erbium is a soft, malleable metal that is silver-white in color. It has a melting point of 1,529°C and a boiling point of 2,860°C. Erbium is paramagnetic, which means it is weakly attracted to a magnetic field.
Chemical Properties
Erbium is a rare earth element that is found in the earth’s crust. It is not found in its pure form in nature but is usually found in minerals such as xenotime, euxenite, and gadolinite. Erbium is not very reactive and does not readily react with water or oxygen. It reacts slowly with dilute acids and quickly with concentrated acids.
Facts
- Erbium is used in nuclear reactors as a neutron absorber.
- Erbium-doped fibers are used in telecommunications to amplify signals in fiber optic cables.
- Erbium is used in metallurgy to improve the workability of alloys.
- Erbium has a pink color that is used in glass and ceramics.
Applications
Erbium is used in a variety of applications such as:
- Nuclear reactors
- Fiber optic telecommunications
- Metallurgy
- Glass and ceramics
Erbium is a rare earth element that has a variety of applications in different fields. It is a relatively stable element that is not very reactive, making it useful in different industries. Its discovery and properties have contributed to the advancement of science and technology.







Leave a Reply