25 Examples of Abiotic Factors in Ecosystem
Abiotic factors are the non-living components of an ecosystem. The abiotic factors of an ecosystem include sunlight (light), water (wetness), temperature (hotness), soil (dirt), wind (blow), precipitation (rain), salinity (salty), pH (acidic), altitude (high), and topography (shape).
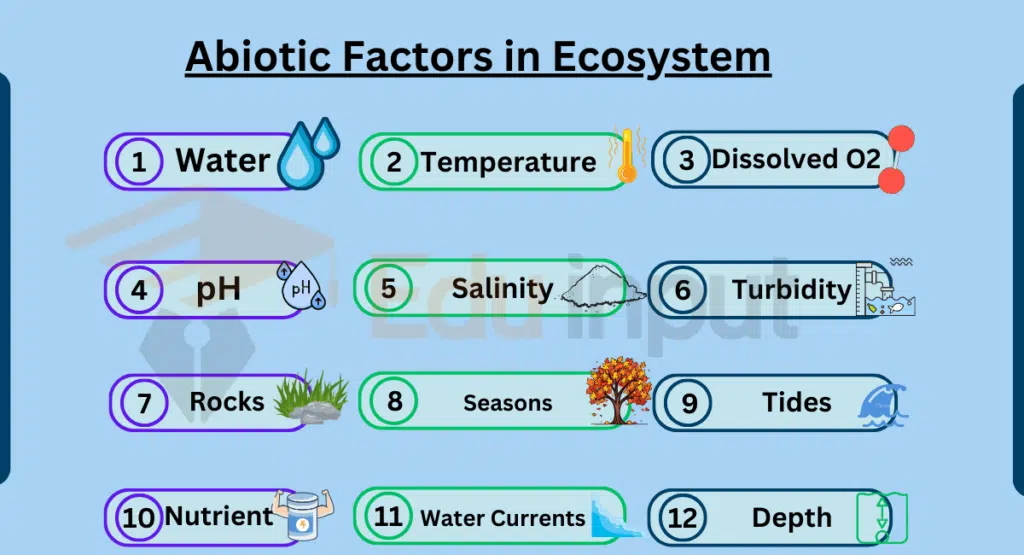
Examples of Abiotic Factors in Ecosystem
Here are examples of abiotic factors in an ecosystem:
1. Sunlight
The amount of sunlight an ecosystem receives affects the types of plants that can grow there.
2. Water
Water is essential for all life. The amount of water available, as well as its quality, can affect the types of organisms that can live in an ecosystem.
3. Temperature
Temperature affects the rate of biological processes, such as photosynthesis and respiration.
4. Humidity
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. It can affect the rate of evaporation and condensation, as well as the ability of organisms to breathe.
5. Wind
Wind can disperse seeds and pollen, and it can also help to distribute heat and moisture.
6. Soil
The type of soil affects the availability of nutrients and water for plants. It can also affect the pH of the environment, which can affect the types of organisms that can live there.
7. Rocks
Rocks provide a habitat for some organisms, and they can also affect the drainage and water retention of the soil.
8. Elevation
Elevation affects the temperature, precipitation, and amount of sunlight an ecosystem receives.
9. Latitude
Latitude affects the amount of sunlight an ecosystem receives.
10. Salinity
Salinity is the amount of salt in water. It can affect the types of organisms that can live in an ecosystem.
11. pH
pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline an environment is. It can affect the availability of nutrients for plants and animals.
12. Dissolved oxygen
Dissolved oxygen is the amount of oxygen dissolved in water. It is essential for the respiration of aquatic organisms.
13. Nutrients
Nutrients are essential for plant and animal growth. They can be found in the soil, water, and air.
14. Pollution
Pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the environment. It can affect the health of organisms and the ability of ecosystems to function.
15. Fire
Fire can be a natural or human-caused disturbance that can affect the structure and composition of an ecosystem.
16. Volcanic activity
Volcanic activity can release ash, gases, and other materials into the environment. These can affect the climate and the availability of nutrients for plants and animals.
17. Earthquakes
Earthquakes can cause physical disturbances to the environment, such as landslides and tsunamis. These can affect the distribution of organisms in an ecosystem.
18. Tides
Tides are the regular rise and fall of the ocean’s surface. They can affect the distribution of organisms in coastal ecosystems.
19. Currents
Currents are the movement of water in the ocean. They can affect the distribution of organisms and the amount of nutrients available in an ecosystem.
20. Precipitation
Precipitation is the water that falls from the sky as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. It is essential for the water cycle and for the growth of plants.
21. Landforms
Landforms are the physical features of the Earth’s surface, such as mountains, valleys, and plains. They can affect the distribution of organisms and the amount of sunlight and water available in an ecosystem.
22. Climate
Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. It is affected by factors such as latitude, elevation, and proximity to the ocean.
23. Seasons
Seasons are the regular changes in weather conditions that occur over the course of a year. They are caused by the Earth’s tilt on its axis.
24. Biological succession
Biological succession is the process by which an ecosystem changes over time. It is driven by the interactions between organisms and the abiotic factors in their environment.
25. Human activities
Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change, can affect the abiotic factors in an ecosystem. This can have a negative impact on the health of the ecosystem and the organisms that live there.



Leave a Reply