15 Examples of Biotic factors in an Ecosystem
Biotic factors are all the living factors present in an ecosystem. They vary in different biomes. Plants, animals, bacteria, insects, algae, fungi, and viruses are the examples of biotic factors.
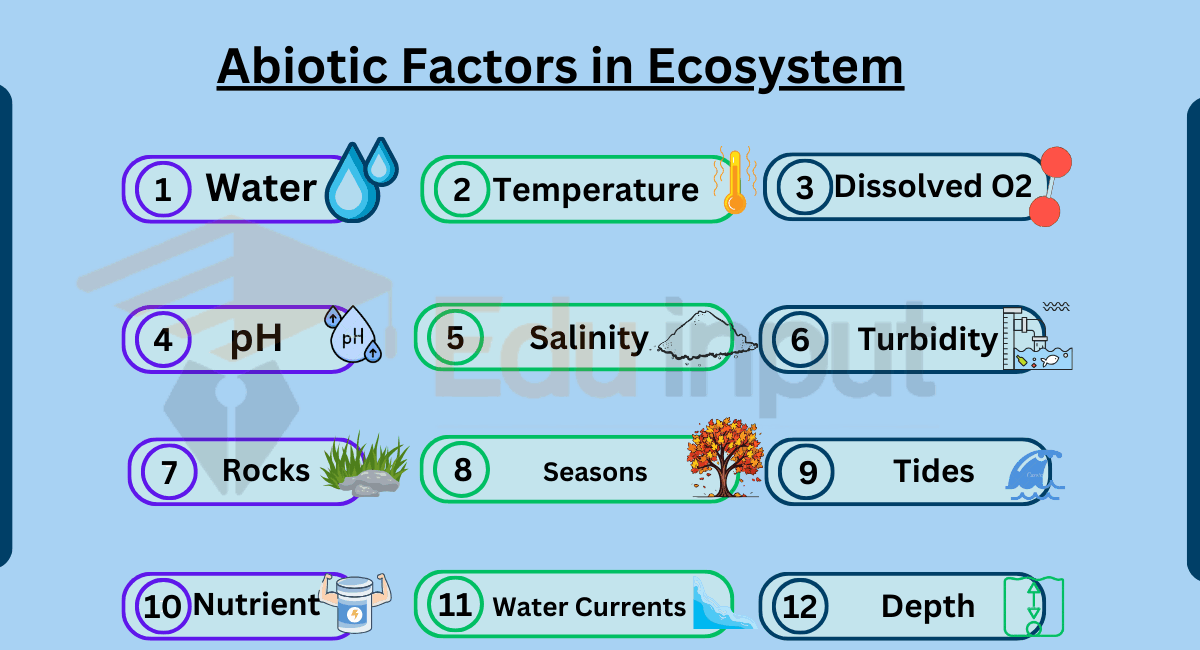
Also learn about Abiotic factors in an ecosystm
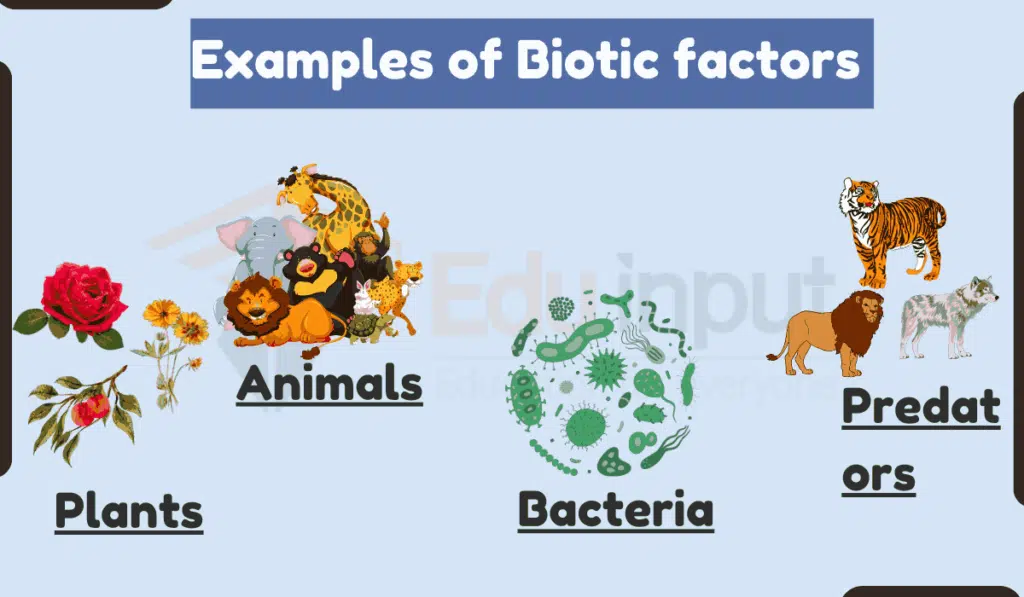
Examples of Biotic factors
here are 15 examples of biotic factors present in an ecosystem. These biotic factors collectively contribute to the complexity and stability of ecosystems by interacting with each other and their physical environments.
1. Plants
Plants are essential biotic factors in ecosystems. They provide oxygen, food, and habitats for various organisms.
2. Animals
Animals like herbivores, cornivores, mammals, insects all are one of the most important biotic factors in an ecosystem.
3. Fungi
Fungi, like mushrooms and molds are examples of biotic factors in certain biomes. They help decompose organic matter and form symbiotic relationships with plants.
4. Bacteria
Bacteria are important living factor that are involved in nutrient cycling, soil health, and various biological processes within organisms.
5. Protists
Protists are example of biotic factor in aquatic ecosystem. Protists, as algae and amoebas, serve as primary producers and are important in aquatic ecosystems.
6. Viruses
Viruses can impact the health and population dynamics of many organisms, including humans.
7. Decomposers
Decomposers like earthworms and carrion-eating insects break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients.
8. Predators
Predators regulate prey populations, contributing to the overall balance of ecosystems.
9. Prey
Prey species are essential in supporting predator populations and shaping their behaviors.
10. Mutualistic Symbionts
Mutually beneficial relationships exist between organisms, such as bees and flowering plants, which rely on each other for survival.
11. Parasites
Parasitic organisms can negatively impact host species, influencing their behaviors and health.
12. Herbivores
Herbivores feed on plants, influencing plant populations and distribution.
13. Omnivores
Omnivores are organisms that consume both plants and animals, playing diverse roles in food webs.
14. Scavengers
Scavengers help clean ecosystems by consuming dead animals and preventing the spread of disease.
15. Detritivores
Detritivores, like woodlice and dung beetles, feed on decaying organic matter, further aiding in nutrient recycling.



Leave a Reply