Feedback Amplifier and Transistor Oscillator
The oscillator in a feedback amplifier and transistor oscillator produces an amplified output signal without consuming any input signals. An oscillator operates in a repeated manner, with amplified input and output producing feedback and persistent activities.
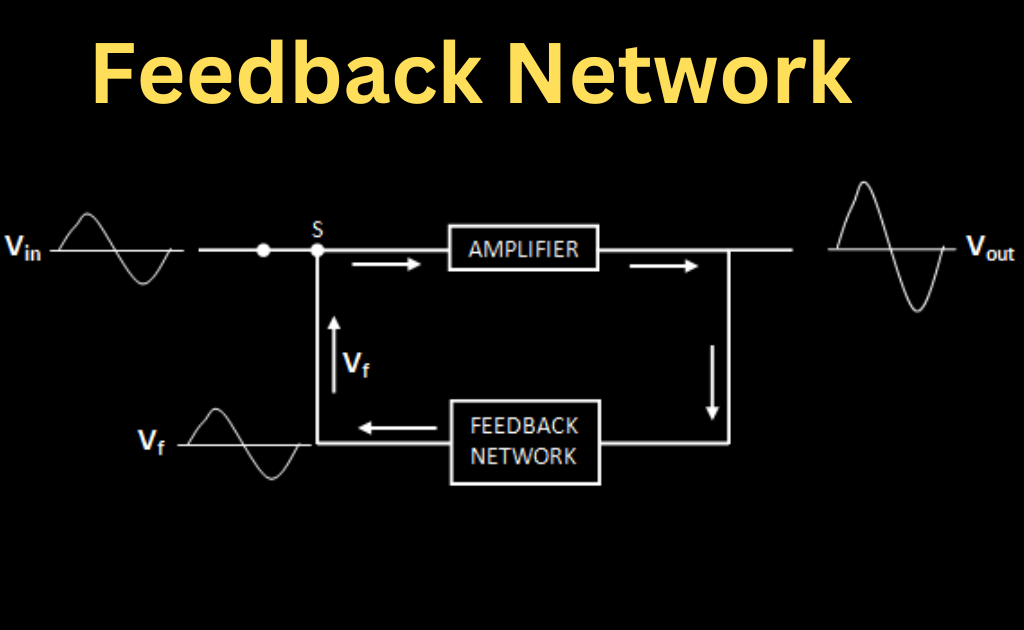
In electrical equipment, this guarantees uninterrupted information signal flow back and forth.
Types of Feedback Amplifiers
Feedback refers to the ability of the output signal to return to the input in an oscillator’s operation. Feedback amplifiers come in two varieties:
Positive Feedback Amplifier
Positive, regenerative, or direct feedback are terms used to describe this form of feedback when it is in phase with the input signal and increases the effective input to the circuit. Although it enhances gain, it also increases distortion and undermines gain stability.
Negative Feedback Amplifier
A negative-feedback amplifier, also known as a feedback amplifier, is an electronic amplifier that reduces the amount of its output from its input so that negative feedback opposes the original signal.
This applied negative feedback can enhance the amplifier’s performance (gain stability, linearity, frequency response, step response), and less sensitivity to parameter variations brought on by manufacturing or the environment.
These benefits are the reason why negative feedback is used in many amplifiers and control systems.
Types of Transistor Oscillators
There are some common types of transistor oscillators.
Armstrong oscillator
US engineer Edwin Armstrong and other Australian engineer Alexander Meissner created the Armstrong oscillator. The oscillator is also known as the Meissner oscillator since each of them separately created it.
Its usage of a tickling coil gives it a distinctive quality, which is why it is occasionally referred to as a tickler oscillator. A capacitor and an inductor work together to create oscillations in this electrical oscillator.
Optoelectronic Oscillator
The idea behind the optoelectronic oscillator, commonly referred to as OEO, is to convert light energy into microwave signals. In addition to a number of additional characteristics that aren’t often seen in simple electronic oscillators, the optoelectronic oscillator is noted for its stability and high-quality factor.
This kind of oscillator, known for operating at high speed, also includes photonic components. An optoelectronic circuit that can modify optical continuous wave signals has been identified.
Wien Bridge Oscillator
Four resistors and two capacitors make up the bridge circuit of a Wein bridge oscillator. It generates sine waves with a wide variety of frequencies. In 1891, Max Wein developed and was given credit for the Wien bridge oscillator, which measures impedances.
Now that we have examined and grasped the operation of the feedback amplifier and transistor oscillator, we can also understand the function of other oscillations, such as the Colpitts oscillator, the Hartley oscillator, and the Wien bridge oscillator.
The positive feedback obtained to achieve repeated and long-term signal processing is one of the elements that never change.
Colpitts oscillator
A modified oscillator tank circuit is made up of two capacitors and one inductor. Its connection in series can be established, allowing the inductor to be positioned next to the capacitors in parallel.
The Colpitt oscillator, which bears the name of physicist Edwin Colpitts, was created in 1918. It promotes preferred frequency stability as compared to the Hartley oscillator’s operating principle.

 written by
written by 




Leave a Reply