Hafnium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Hf’ and atomic number 72. It is a rare and valuable metal that is known for its unique properties, such as its high melting point, corrosion resistance, and ability to absorb neutrons. Hafnium is primarily used in the aerospace and nuclear industries and is often found in association with zirconium.
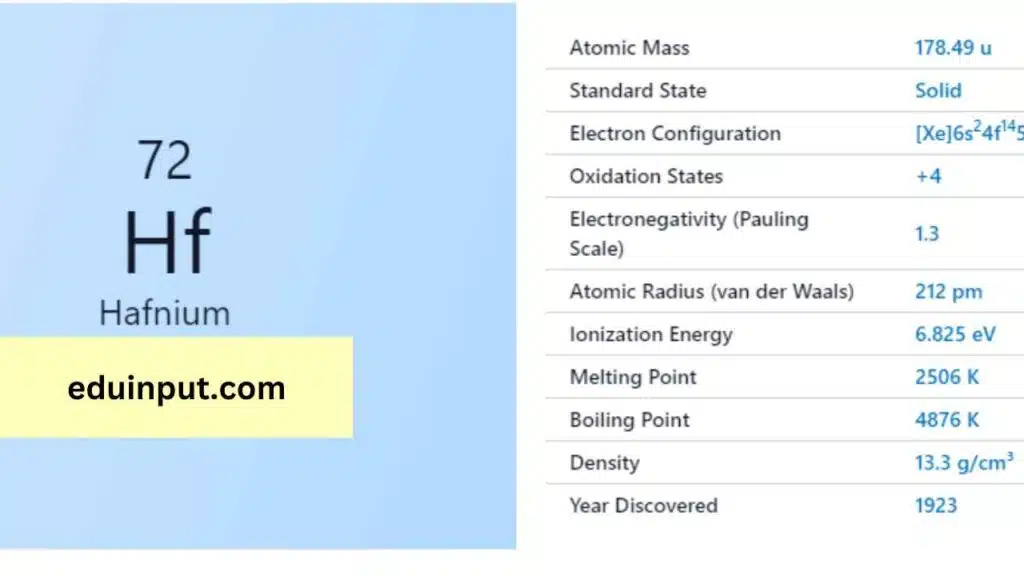
| Property | Value |
| Name | Hafnium |
| Symbol | Hf |
| Atomic number | 72 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 178.49 |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Grey steel |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 4 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Block in the periodic table | 6 |
| Block in periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.10.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-58-6 |
Discovery
Hafnium was discovered in 1923 by the Danish physicist Niels Bohr and his team, who were studying the properties of x-rays emitted by atomic nuclei. They discovered that the x-rays emitted by hafnium atoms were different from those emitted by any other element, leading to the discovery of the new element.
Physical Properties
Hafnium is a dense, silvery metal that is highly resistant to corrosion. It has a density of 13.31 g/cm3, a melting point of 2,233°C, and a boiling point of 4,603°C. Hafnium is also known for its ability to absorb neutrons, making it a valuable material for nuclear applications.
Chemical Properties
Hafnium is a highly reactive metal that readily forms compounds with other elements. It is also highly resistant to corrosion, due to the formation of a stable oxide layer on its surface. Hafnium is also known for its ability to absorb neutrons, making it useful for nuclear applications.
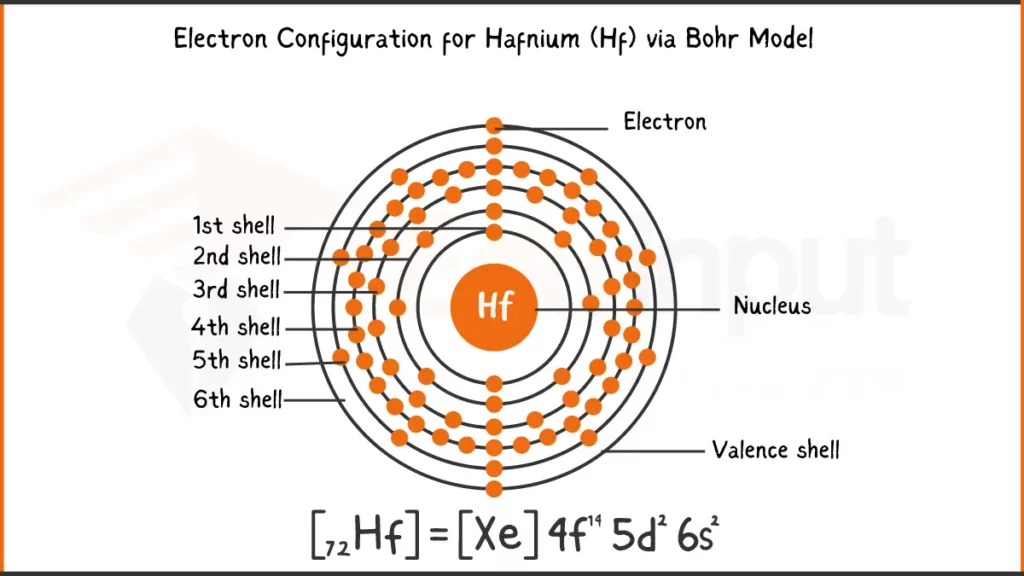
Electronic Configuration of Hafnium
Hafnium (Hf) has 72 electrons. Its ground state electron configuration is: [Xe] 4f¹⁴ 5d² 6s² or 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 4d¹⁰ 5s² 5p⁶ 4f¹⁴ 5d² 6s².
Electronic Configuration of Hafnium via Bohr Model
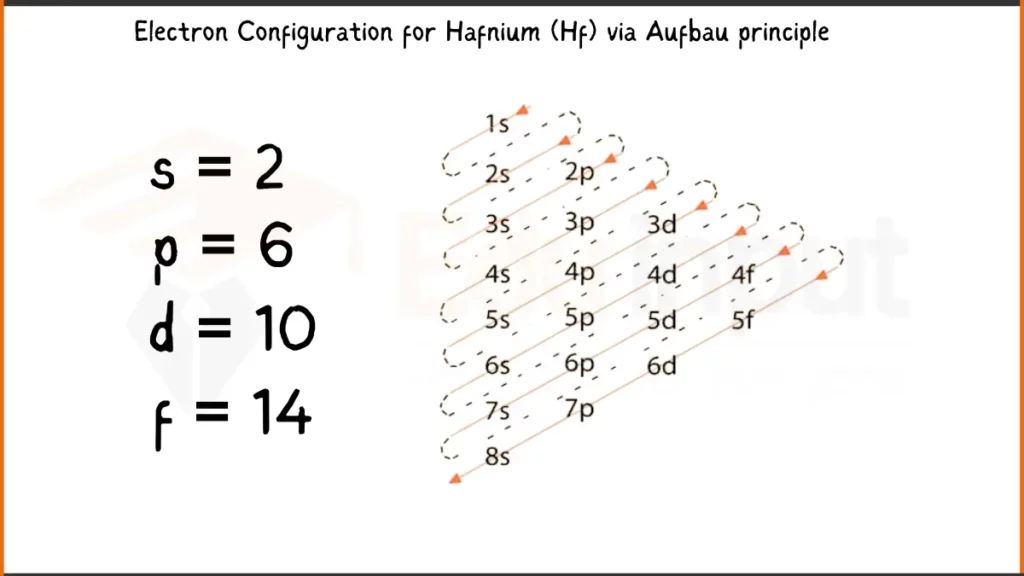
Electronic Configuration of Hafnium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Hafnium is a rare and valuable metal that is primarily found in association with zirconium.
- Hafnium is often used in the aerospace industry to make high-temperature alloys and other components that require strength and durability.
- Hafnium is also used in the nuclear industry, where it is used as a neutron absorber in nuclear reactors.
Applications
Hafnium has a wide range of applications in various industries, including aerospace and nuclear. Some of the major applications of hafnium include:
- Aerospace: Hafnium is used in the aerospace industry to make high-temperature alloys and other components that require strength and durability. It is also used in the production of rocket nozzles and other components that require resistance to heat and corrosion.
- Nuclear: Hafnium is used in the nuclear industry as a neutron absorber in nuclear reactors. It is also used in the production of control rods, which are used to control the rate of nuclear reactions in reactors.
- Other Applications: Hafnium is also used in other applications such as plasma cutting tips, electrical contacts, and jewelry. Its high melting point and corrosion resistance make it a valuable material for a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
Hafnium is a rare and valuable metal with unique properties that make it useful in various industries. Its ability to absorb neutrons, high melting point, and corrosion resistance make it an important material for the aerospace and nuclear industries. As technology continues to advance, the potential uses of hafnium may expand, making it an important element for the future.






Leave a Reply