Is Bacteria Prokaryote or Eukaryote?
Bacteria are prokaryotes because they lack a nucleus, organelles, linear DNA, and other complex cellular features. Their unicellular organization and means of replication further align them with other prokaryotic microbes. [source]
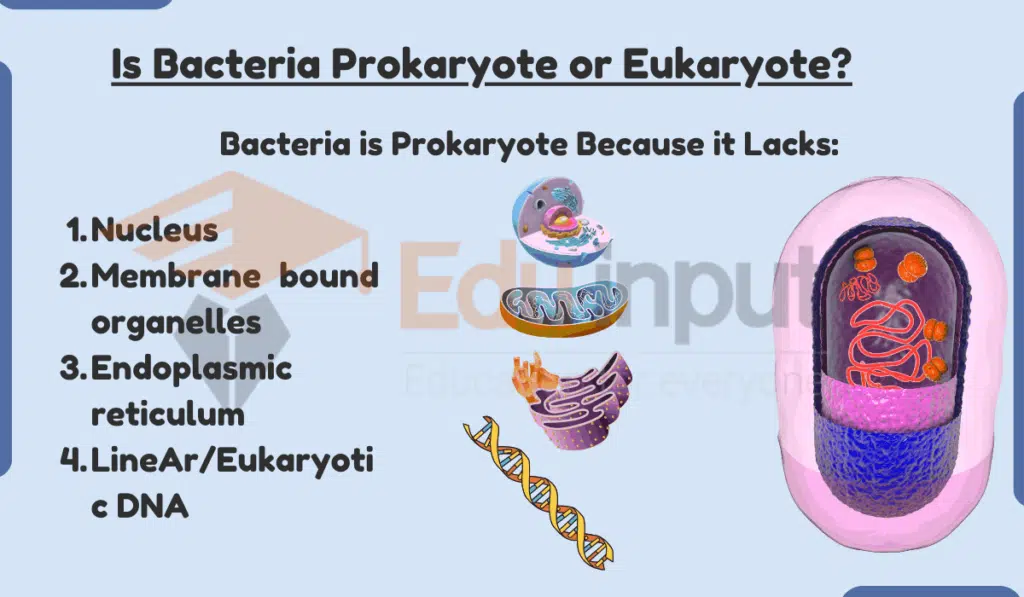
Why Bacteria is Prokaryote?
Here are the reasons why bacteria are characterized as prokaryotes:
1. Lack of Nucleus
Bacteria lack a nucleus. Unlike eukaryotic cells, bacterial cells do not have a nucleus that houses their genetic material. Instead, the bacterial DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm. This lack of nuclear membrane is a defining characteristic of prokaryotes.
2. Lack of Organelles
Bacteria lack organelles. Organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus are hallmarks of eukaryotic cells. Bacterial cells do not contain membrane-bound organelles. They have simpler internal structures compared to eukaryotes.
3. Genetic material
Bacteria have a circular DNA chromosome. Prokaryotic genetic material consists of a single circular DNA chromosome, whereas eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes.
4. Reproduction
Bacteria reproduce asexually. Prokaryotes like bacteria reproduce through binary fission, whereby a cell copies its DNA and splits into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotes use more complex forms of asexual and sexual reproduction.
Bacteria have a simple cell structure. Overall, bacteria consist of a simple cell structure with no compartments or advanced features. This simplicity places them in the prokaryotic domain versus the more complex eukaryotes.

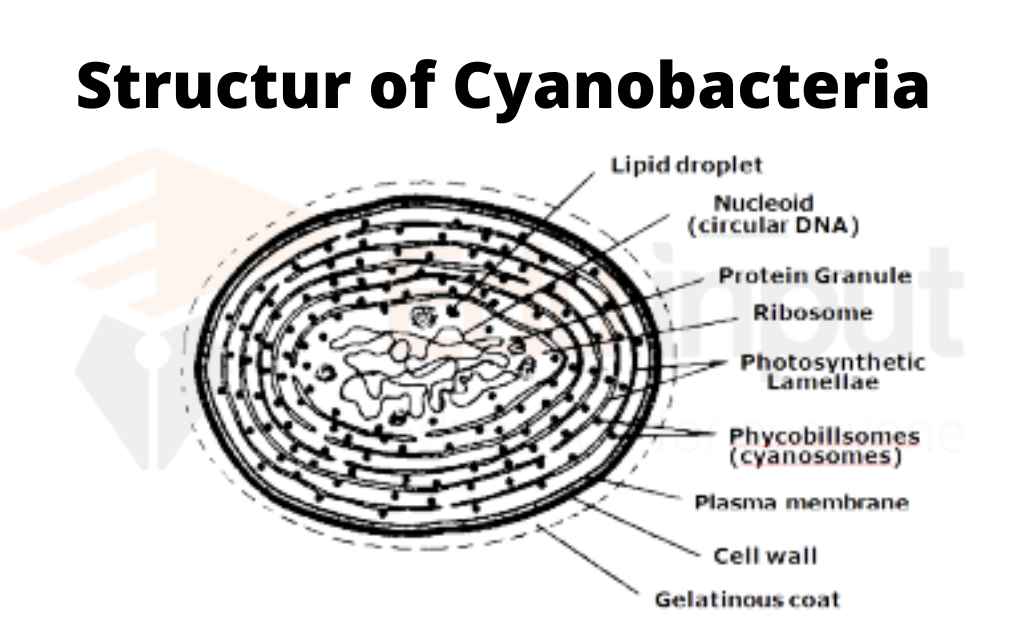




Leave a Reply