Lead-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Lead, denoted by the symbol ‘Pb’ and possessing the atomic number 82, is a versatile chemical element with a rich history and diverse properties that have made it an integral part of human civilization.
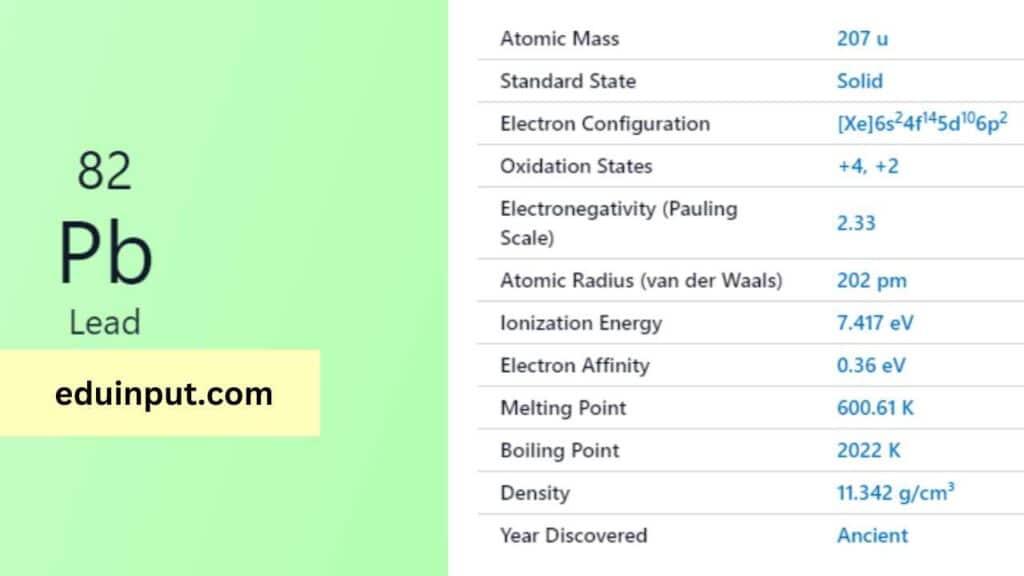
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Lead |
| Symbol | Pb |
| Atomic number | 82 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 207.2 |
| Period in the periodic table | 6 |
| Group in the periodic table | 14 (Carbon group) |
| Block in the periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.18.4 |
Discovery
Lead has a long and storied history, with its use dating back thousands of years. It was known to the ancient Romans and Greeks, who used it for various purposes, including plumbing, coins, and writing tablets. Its Latin name, “plumbum,” is the origin of the chemical symbol ‘Pb.’
Physical Properties
Lead is a heavy, bluish-gray metal at room temperature. It is one of the densest common elements, with a density of approximately 11.34 g/cm³. Lead has a relatively low melting point of 327.5°C and a boiling point of 1,749°C. It is also malleable and a poor conductor of electricity.
Chemical Properties
Lead exhibits various chemical properties. It is relatively unreactive in moist air but reacts slowly with atmospheric oxygen to form a thin layer of lead oxide, which protects the metal from further corrosion. Lead can form compounds with a wide range of elements, resulting in various applications.
Facts
- Lead has four stable isotopes: Pb-204, Pb-206, Pb-207, and Pb-208, with Pb-206 being the most abundant.
- The use of lead in various applications, such as lead-based paint and leaded gasoline, has raised significant environmental and health concerns due to its toxicity.
Applications
Lead has been used in a wide range of applications over the centuries:
- Plumbing: Lead pipes were commonly used in plumbing systems due to lead’s malleability and corrosion resistance.
- Ammunition: Lead is used in bullets and shotgun pellets because of its high density.
- Batteries: Lead-acid batteries are still widely used in vehicles and backup power systems.
- Radiation Shielding: Due to its high density, lead is employed in radiation shielding in medical and industrial applications.
- Historical Artifacts: Lead has been used in historical artifacts, such as statues and stained glass.





Leave a Reply