Monocot & Discot Root Cross-Section Diagram
February 18, 2024
Monocot Root Cross-Section
- Epidermis: The outermost layer of the monocot plant’s root, protecting it from the environment.
- Cortex: The tissue between the epidermis and the vascular tissue, storing starch and providing support.
- Endodermis: A single layer of cells surrounding the vascular tissue, regulating water and nutrient transport.
- Pericycle: The layer outside the vascular tissue, giving rise to lateral roots.
- Vascular tissue: Located in the center of the root, containing xylem (transports water and minerals up) and phloem (transports sugars down). The xylem and phloem are scattered throughout the vascular tissue, not arranged in a ring like in dicots.
- Root hairs: Tiny projections from the epidermis that increase the surface area for water and nutrient absorption.
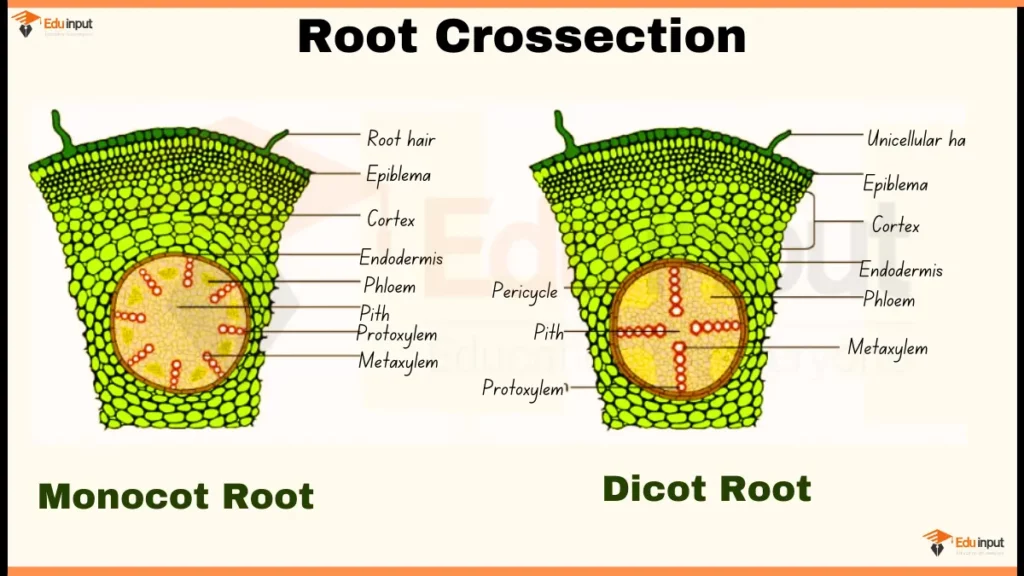
Dicot Root Cross-Section
- Epidermis: The outermost layer of the root, protecting it from the environment.
- Cortex: The tissue between the epidermis and the vascular tissue, storing starch and providing support.
- Endodermis: A single layer of cells surrounding the vascular tissue, regulating water and nutrient transport.
- Pericycle: The layer outside the vascular tissue, giving rise to lateral roots.
- Vascular tissue: Located in the center of the root, arranged in a ring with xylem in the center and phloem around the outside. The xylem transports water and minerals up, and the phloem transports sugars down.
- Root hairs: Tiny projections from the epidermis that increase the surface area for water and nutrient absorption.
Also Check
File Under:



Leave a Reply