Tin-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a silvery-white, soft, malleable, ductile metal that is not easily oxidized in air. Tin is widely used for coating other metals to prevent corrosion and for making alloys, such as bronze.
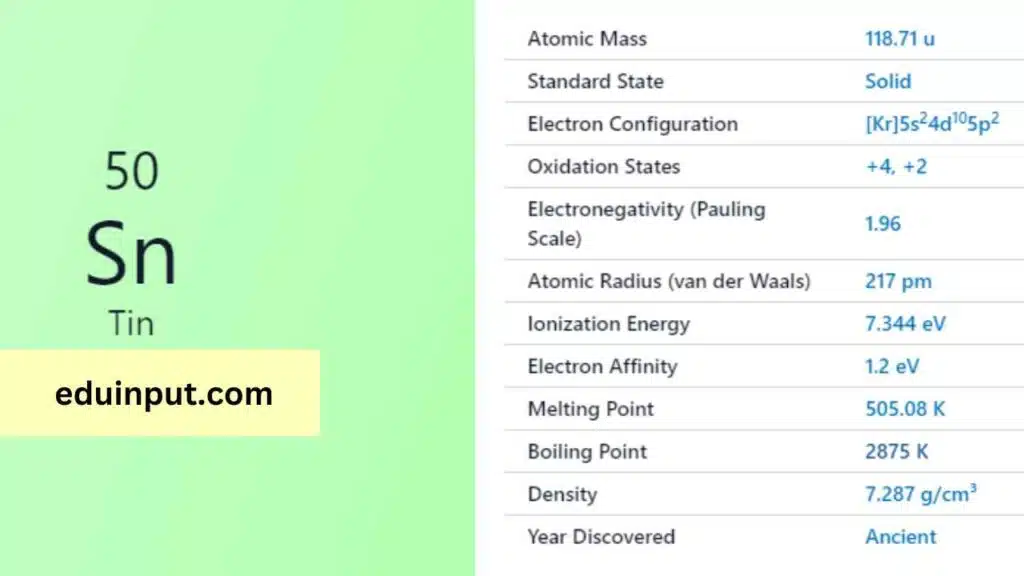
| Property | Value |
| Name | Tin |
| Symbol | Sn |
| Atomic number | 50 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Block in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery lustrous grey |
| Classification | Metallic |
| The group in the periodic table | 14 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Group in the periodic table | 5 |
| Period in the periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.18.4 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-31-5 |
Discovery
Tin has been known since ancient times. The earliest evidence of tin was found in the Tigris-Euphrates valley in Mesopotamia, where a bronze object made of copper and tin was found dating back to about 3000 BC.
Physical Properties
Tin is a silvery-white metal that is soft, malleable, ductile, and highly crystalline. It has a melting point of 231.9°C and a boiling point of 2,270°C. Tin has a density of 7.31 g/cm³, which is lower than that of most metals.
Chemical Properties
Tin is a highly reactive metal and readily reacts with oxygen to form tin oxide. It also reacts with hydrochloric acid to form tin chloride and hydrogen gas. Tin has a valence of +2 and +4 and forms compound with oxygen, halogens, and sulfur. It is a relatively non-toxic element and has no known biological function.
Facts
- The Latin name for tin is stannum, which is where its chemical symbol, Sn, comes from.
- Tin has ten stable isotopes, the most of any element.
- The world’s largest producer of tin is China, followed by Indonesia and Peru.
- Tin has been used for thousands of years to make bronze, which is an alloy of copper and tin.
Applications
Tin is widely used in many applications, including:
- Coating other metals to prevent corrosion
- Making alloys such as bronze and pewter
- Soldering electronic components
- Making tinplate for food packaging
- Making organ pipes
- Adding to glass to create a reflective surface (mirrors)
- Adding to some dental materials.
Tin is an important element with a long history of use. Its physical and chemical properties make it valuable for many applications, from making alloys to coating other metals to prevent corrosion.






Leave a Reply