Transcription-Synthesis of RNA | DNA Transcription
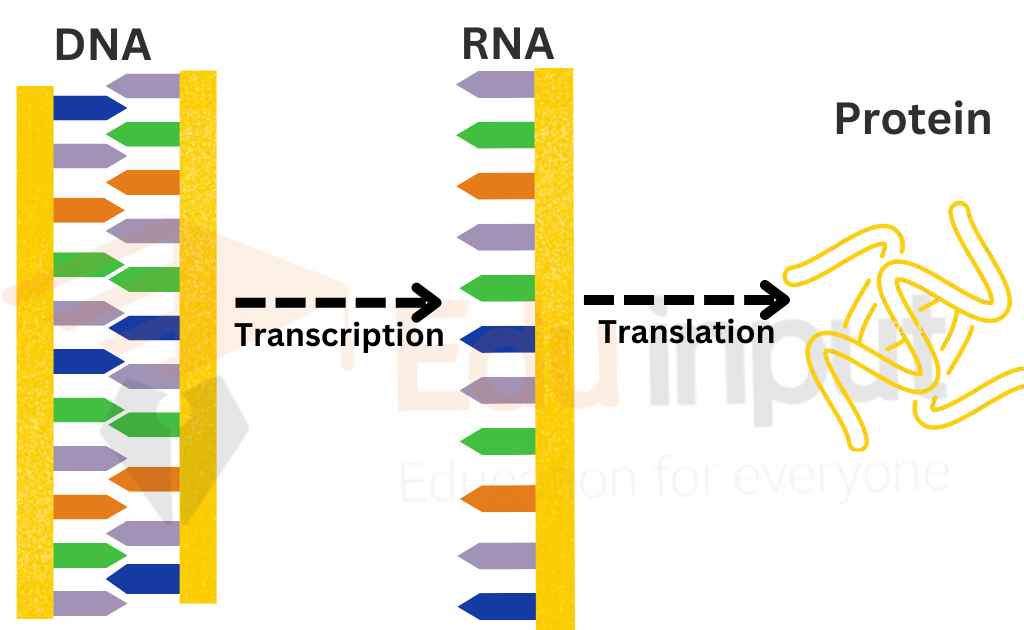
Transcription is the process of creating mRNA from a DNA template. It is the process of converting genetic information into RNA (ribonucleic acid), which is then translated into proteins.
RNA is a type of nucleic acid found in cells. It plays a role in regulating gene expression and is involved in protein production. Splicing is the process of removing introns from pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcripts. Editing is the process of modifying or correcting errors in the transcriptome. These two processes are important for gene expression and regulation.
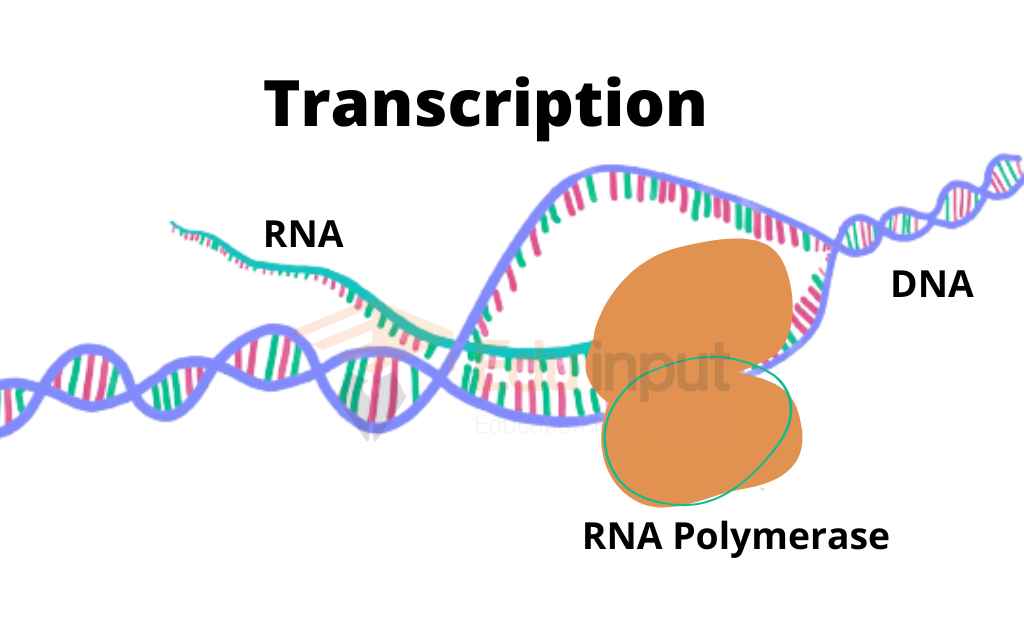
An enzyme RNA polymerase produces RNA copy according to the DNA sequence. This RNA is formed from the gene. Only one strand of DNA is transcribed.
DNA Strands
There are two types of strands in DNA: coding and non-coding.
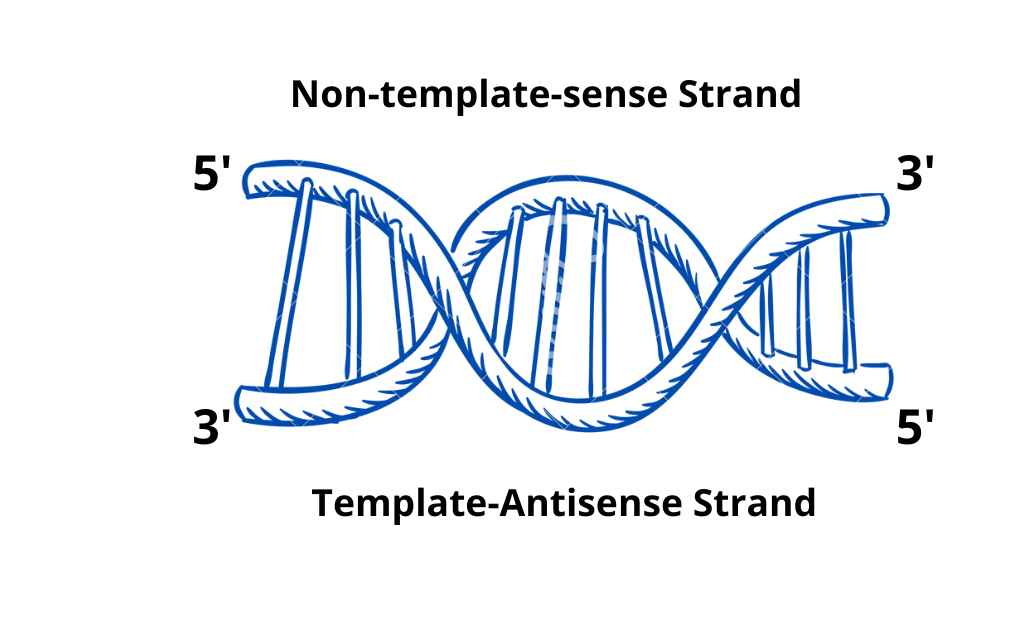
Template Strand Or The Antisense Strand:
The strand transcribed during transcription is called the template strand. It is the template strand of DNA, That is to be transcribed.
Coding Strand Or The Sense Strand:
It is a complementary strand of template or antisense codon. It carries translatable code.
RNA polymerase enzymes synthesize RNA from the 5′-3′ direction. Prokaryotes only have one type of RNA polymerase, which is responsible for the synthesis of all three types of RNAs.
Types of RNA Polymerase
Eukaryotes have three types of RNA polymerases.
These are;
- RNA polymerase I: It synthesizes rRNA
- RNA polymerase II: It synthesizes mRNA.
- RNA polymerase III: It synthesizes tRNA
Steps Of Transcription (Synthesis Of RNA)
Following steps are involved in the synthesis of RNA;
Binding of RNA Polymerase:
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter on the DNA template strand. The promoter is the RNA polymerase binding site. Transcription starts the promoter. There are two binding sites within the promoter of prokaryotes.
These are:
TTGACA Sequence: These are also called 35-sequence.
TATAAT sequence: These are also called 10- sequences. These sequences have an affinity for RNA polymerase.
In eukaryotes, these sites are at -25 and -70 sites. RNA polymerase has one subunit called the sigma factor. It is responsible for the correct initiation of the transcription process. The sigma factor is released at the start of transcription. Now the remaining part of the enzyme is called core enzymes.
Elongation:
The core enzyme moves over the template strand and completes the transcription of the gene. The DNA strands open up at the place where the enzyme is attached to the template strand, forming a transcription bubble. As the bubble moves down the DNA, it leaves the growing strand protruding from it.
Termination:
The stop sequences are present at the end of the gene. They terminate the synthesis of mRNA. The simplest stop signal is a series of GC base pairs followed by a series of AT base pairs. The RNA formed in this region forms a GC hairpin (U shaped). This hairpin is followed by four or more U ribonucleotides. The hairpin stops the synthesis of RNA polymerase.
Transport Of Newly Formed mRNA:
The pathway for the transport of newly synthesized RNA might be different in eukaryotes and prokaryotes;
In Prokaryotes:
The newly synthesized mRNA is directly released into the cytoplasm in bacteria. It is converted into a polypeptide chain in the cytoplasm.
In Eukaryotes
The mRNA in eukaryotes has to travel from inside the nucleus to ribosomes outside the cytoplasm. Therefore, eukaryotic mRNA is modified in several ways. These modifications help it in its journey cap and a tail is added. Thus the molecule remains stable during the long journey to the ribosome. The caps and tails save the mRNA from the action of a variety of nucleases and phosphatase enzymes.
Cap: It is in the form of 7 methyl GTP. It is linked to the 5′ end of mRNA.
Tail: It is in the form of a poly A tail. It is linked to the 3′ end of the RNA.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What is transcription?
Transcription is the process of synthesis of RNA from DNA sequences. It is the process of converting genetic information into RNA (ribonucleic acid), which is then translated into proteins.
What are the 4 steps of DNA transcription?
The following steps are involved in transcription;
Binding of RNA Polymerase (Initiation)
Elongation
Termination
Transport Of Newly Formed mRNA
Where does the process of DNA transcription occur?
DNA transcription occurs in the cell nucleus, Where RNA is synthesized from a template strand of DNA.
What is the end product of transcription?
RNA is the end product of transcription, which is then used in translation.
Which enzyme is involved in transcription?
RNA Polymerase is involved in transcription. It needs double-stranded DNA as a substrate.



Leave a Reply