Dependent, Independent, and Constant Variables in Diffusion Lab
Variables in a diffusion lab are the factors that can affect the rate of diffusion.
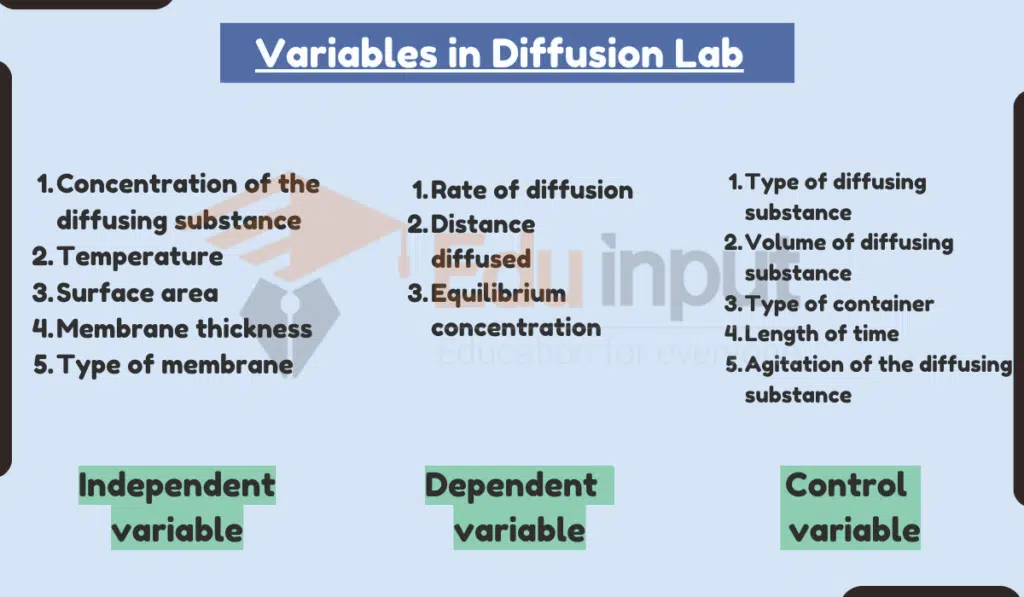
Variables in Diffusion Lab
There are three main types of variables in a diffusion lab:
1. Independent variable
The variable that is manipulated by the experimenter. This is the variable that the experimenter is interested in seeing how it affects the dependent variable.
Examples
- Concentration of the diffusing substance
- Temperature
- Surface area
- Membrane thickness
- Type of membrane
2. Dependent variable
The variable that is measured by the experimenter. This is the variable that the experimenter expects to change as a result of changes in the independent variable.
Examples
- Rate of diffusion
- Distance diffused
- Equilibrium concentration
Control variables
All other variables that are kept constant in the experiment. This is important to ensure that the changes in the dependent variable are due to the independent variable and not to any other factors.
Examples
- Type of diffusing substance
- Volume of diffusing substance
- Type of container
- Length of time
- Agitation of the diffusing substance
Example of Diffusion Lab
Here is an example of a diffusion lab:
Hypothesis: Increasing the temperature of the diffusing substance will increase the rate of diffusion.
Independent variable: Temperature
Dependent variable: Rate of diffusion
Control variables
- Type of diffusing substance
- Concentration of the diffusing substance
- Surface area
- Membrane thickness
- Type of membrane
- Volume of diffusing substance
- Type of container
- Length of time
- Agitation of the diffusing substance
Procedure
- Set up two diffusion chambers.
- Fill one diffusion chamber with the diffusing substance at room temperature.
- Fill the other diffusion chamber with the diffusing substance at a higher temperature.
- Place both diffusion chambers in the same container.
- After a certain amount of time, measure the amount of the diffusing substance that has diffused into the container.
Results: The diffusion chamber with the higher temperature will have more of the diffusing substance diffuse into the container than the diffusion chamber with the lower temperature.
Conclusion: The results of the experiment support the hypothesis that increasing the temperature of the diffusing substance will increase the rate of diffusion.





Leave a Reply