Variables in Mathematics
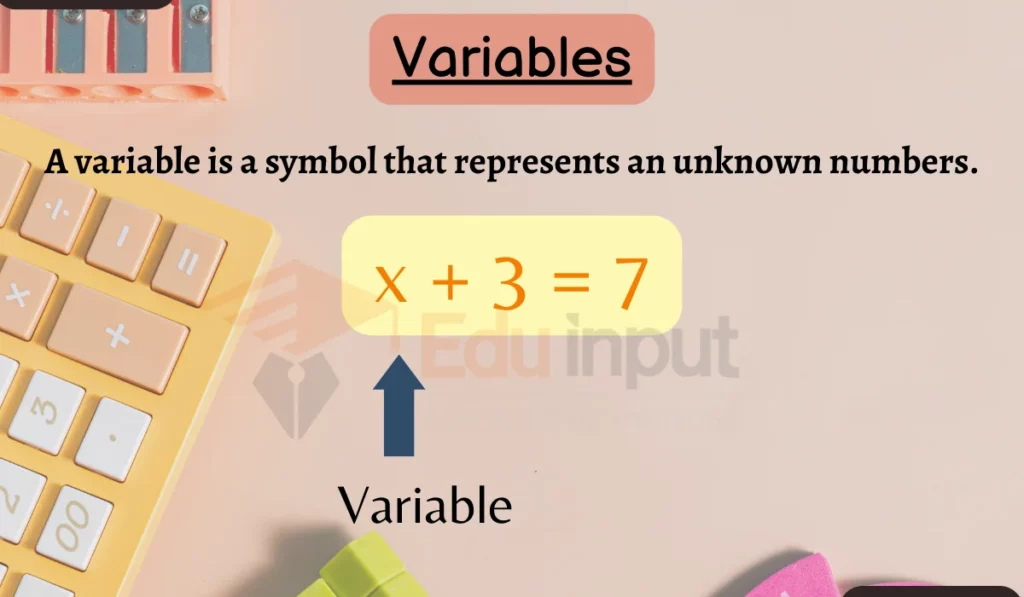
In mathematics, a variable is a symbol that represents an unknown or changing value. Variables are commonly represented by letters like x, y or n. They’re like the puzzle pieces that help us solve mathematical mysteries.
In this article, we will understanding the concept of variables in mathematics.
Parts of Equation
Equations in Mathematics are formed of different parts. They are:
1: Variable
2: Constant
3: Coefficient
4: Operators
5: Term
Example
In equation, 2x + 3 = 7
x is a variable
2 is a coefficient of x
3 , 7 are constants
and + is operator.
Examples of Variables
1: x in 2x + 3 = 7: Here, ‘x’ is a variable. It represents an unknown number.
2: y in 3y – 5 = 10: Similar to the previous example, ‘y’ is a variable representing an unknown value.
Types of Variables
- Independent variables
- Dependent variables
Independent variables
Represents an input value that influences another value. In y=3x+5, x is the independent variable.
Dependent variables
Represents an output value that depends on an independent variable. In y=3x+5, y is the dependent variable.
Rules for Variables
Variables in math follow certain rules:
- Can only represent single numbers or values, not operations or expressions. For example, x cannot equal x + 1.
- Cannot represent multiple values at the same time. X cannot equal 2 AND 3 simultaneously.
- Are case sensitive. X and x represent different variables.
- Can use any letter, but common conventions are to use letters at the end of the alphabet like x, y, z.
Understanding how to properly use variables helps provide a crucial foundation for algebra, calculus, physics, chemistry, economics, and more advanced fields.





Leave a Reply