Output Devices- Types, and Working Principle
What is an Output Device?
Output devices refer to hardware components used to transmit processed data from a computer to either another device or a user.
The processed data that is given to the user is known as the output. The computer gives us output as a result of any input given to it.
Devices that send data to a computer are inputs, while those that receive and present data are outputs. Think of it like a conversation: inputs “talk” to computer, while outputs “speak” to you.

Why Do We Need Output Devices?
Output devices are essential because they allow computers to communicate with us in ways we understand—through visuals, sounds, and printed information. They make the digital world accessible and interactive. They increase our ability to receive information, make decisions, and use content.
Types of Output Devices
Output Devices devices can be categorized based on their functions:
1. Audio Output Devices
Audio output devices focus on conveying digital sound signals into audible experiences.
Examples
- Speakers (Sound Reproduction):Speaker is an output device that Work on the principle of converting electrical signals into mechanical vibrations, producing sound waves that we can hear.
- Headphones (Personalized Audio): Utilize small speakers close to the ears, providing a direct and personalized audio experience.
- Audio Amplifiers (Sound Enhancement): Amplify weak audio signals to a level suitable for driving speakers, enhancing the overall sound quality.
2. Visual Output Devices
Visual output devices are designed to display digital content visually. It uses a variety of technologies.
Examples
- Monitors (Visual Display): Operate by lighting up individual pixels based on the digital information received, creating a visual representation.
- Projectors (Large-Scale Display): Use light sources and lenses to project enlarged images onto a screen or surface for viewing.
- LED Displays (High-Brightness Visuals): Rely on light-emitting diodes to produce bright and vibrant visuals for digital signage and electronic displays.
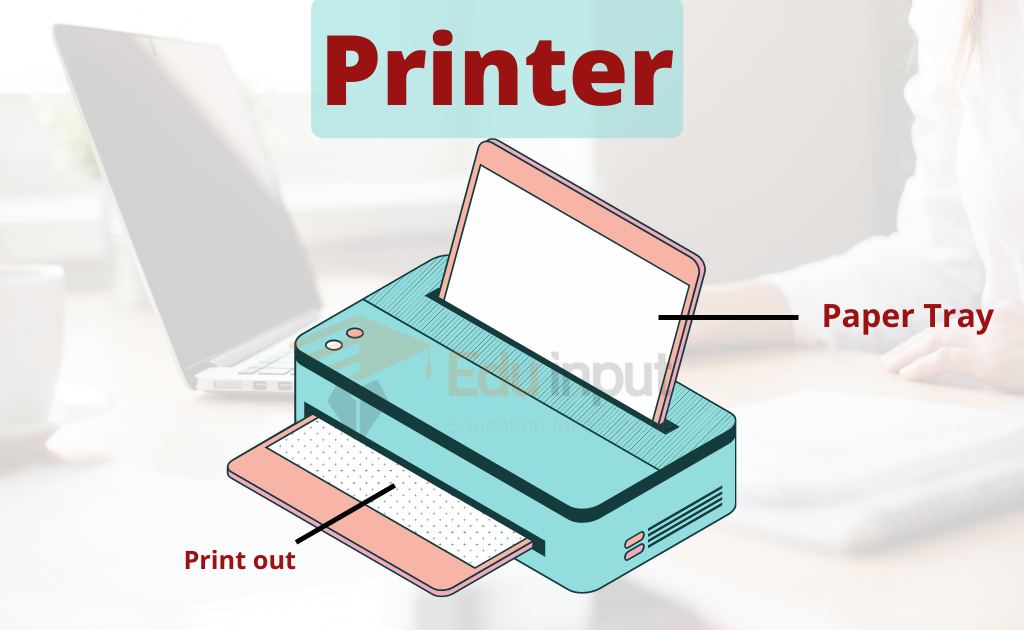
- Printers (Physical Image Reproduction): Apply ink or toner to paper in specific patterns, reproducing digital images and text in a physical format.
- Plotters (Precision Graphic Output): Use pens or other tools to precisely draw or mark on paper, providing detailed graphical output.
3. Sensation Output Devices
Sensation output devices engage the sense of touch and other tactile experiences.
Examples
- Haptic Feedback Devices (Touch Simulation): Employ motors or actuators to create vibrations or forces, simulating the sense of touch for a more immersive experience.
- Braille Embossers (Tactile Reading): Mechanically emboss Braille dots onto paper, allowing users to read information through touch.
- Tactile Feedback Interfaces (Physical Interaction): Utilize various mechanisms to provide physical sensations, enhancing touch interactions on surfaces like touchscreens.
- 3D Printers (Physical Object Creation): Build physical objects layer by layer from digital designs, adding material in a controlled manner.
4. Physical Output Devices
Physical output devices involve the creation of tangible objects based on digital instructions.
Examples
- 3D Printers (Object Fabrication): Operate by depositing material layer by layer, creating three-dimensional objects from digital designs.
- CNC Machines (Precision Manufacturing): Cut or shape materials based on computer-controlled instructions, ensuring high precision and repeatability.
5. Communication Output Devices
Communication output devices facilitate the transmission of digital information.
Examples
- Fax Machines (Document Transmission): Convert digital documents into analog signals for transmission over phone lines, reproducing physical copies at the receiving end.
- LED Status Indicators (System Status Communication): Use lights with different colors and patterns to communicate various system states or conditions.
6. Specialized Output Devices
Specialized output devices cater to specific applications and industries.
Examples
- Air Traffic Control Displays (Aviation Information Presentation): Provide real-time information for air traffic management, aiding controllers in ensuring safe and efficient air travel.
- Barcode Printers (Inventory Labeling): Generate labels with barcodes to facilitate efficient inventory tracking and management.
7. Interactive Output Devices
Interactive output devices promote user engagement and collaboration.
Examples
- Interactive Whiteboards (Collaborative Presentation): Combine display capabilities with touch or pen input, allowing users to interact with and manipulate displayed content.
- Virtual Reality Headsets (Immersive Simulation): Track head and body movements to immerse users in interactive virtual environments.
8. Remote Output Devices
Remote output devices involve the display of content in distant locations.
Examples
- Digital Signage Displays (Remote Content Showcase): Use digital technology to display dynamic content in public spaces, often with remote content management capabilities.
- LED/LCD Billboards (Outdoor Information Display): Employ large-scale LED or LCD technology for outdoor displays, conveying information to a broad audience.
List of Output Devices of Computers
Here are a few examples of output devices:
- Monitor
- Projector
- Head-Mounted Display (HMD)
- Speakers
- Headphones
- Earbuds
- Printers
- Plotters
- 3D Printers
- Braille Displays
- Speech Synthesizers

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply