What is Bus Topology -Types, Components and Working
Bus topology is defined as a computer network layout where all devices are connected to a single central cable, called the backbone or bus. This cable is like a road, and all the data or information travels along this road to reach the devices.
Think of it like a bus route. All bus stops (devices) are connected by one road (the bus). The bus travels along the road and can stop at any point to let passengers (data) on or off.
Types of Bus Topology
- Hybrid Bus Topology: Combines bus with other types, like star or ring. This allows for a more customized network setup based on needs.
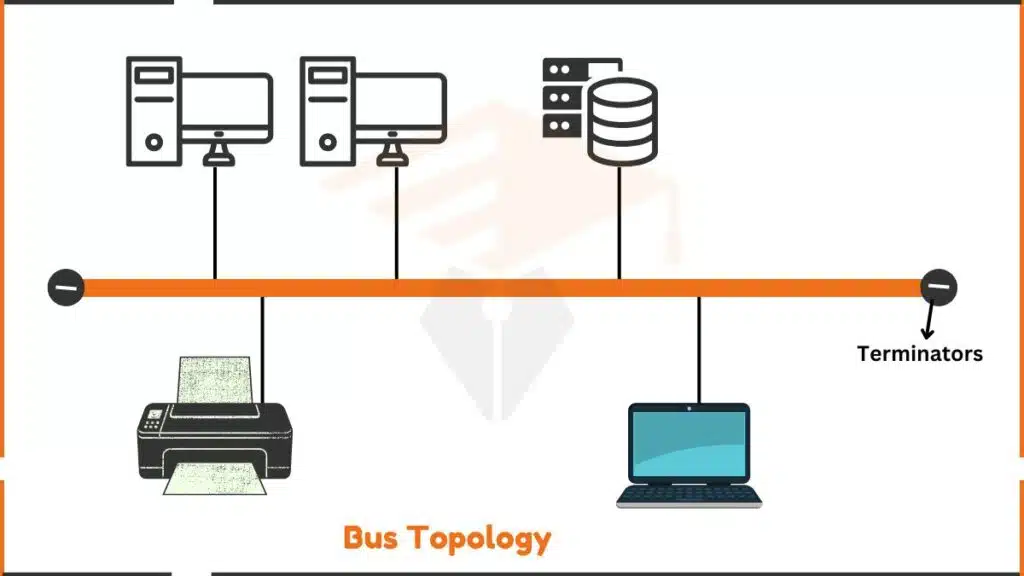
- Linear Bus Topology: All devices connect to one main cable. Terminators at each end stop signals from bouncing back.
- Distributed Bus Topology: Multiple cables are linked to a central backbone. This allows more devices to connect and offers flexibility.
- Collapsed Backbone Bus Topology: A central device (like a hub) connects all devices. It manages data flow, making the network more reliable.
- Dual Bus Topology: Two cables run parallel to each other, allowing data to flow in both directions. This helps reduce network traffic and improves speed.
Components of Bus Topology
- Backbone Cable: The backbone cable is the main wire that connects all devices in the network. It carries data back and forth between the devices.
- Nodes: Nodes are the devices, like computers and printers, that connect to the backbone cable. Each node can send and receive data using the cable.
- Terminators: Terminators are special devices placed at both ends of the backbone cable. They stop signals from bouncing back, which helps keep the network running smoothly.
How Bus Topology Works?
Bus topology connects all devices to a single cable. Data travels along this cable to reach its destination. It’s a simple setup but less reliable than other topologies. If the cable fails, the entire network goes down. While it’s easy to install and maintain, it’s not suitable for large networks due to its limitations in scalability and performance.
FAQs
Who is the father of topology?
The father of topology is Leonhard Euler.
What is the oldest topology?
The oldest topology is point-set topology
Why is topology useful?
Topology is useful for:
Studying Shapes, Solving Problems, Designing Networks, Making Systems Strong



Leave a Reply