What is Mesh Topology -Types, Components and Importance
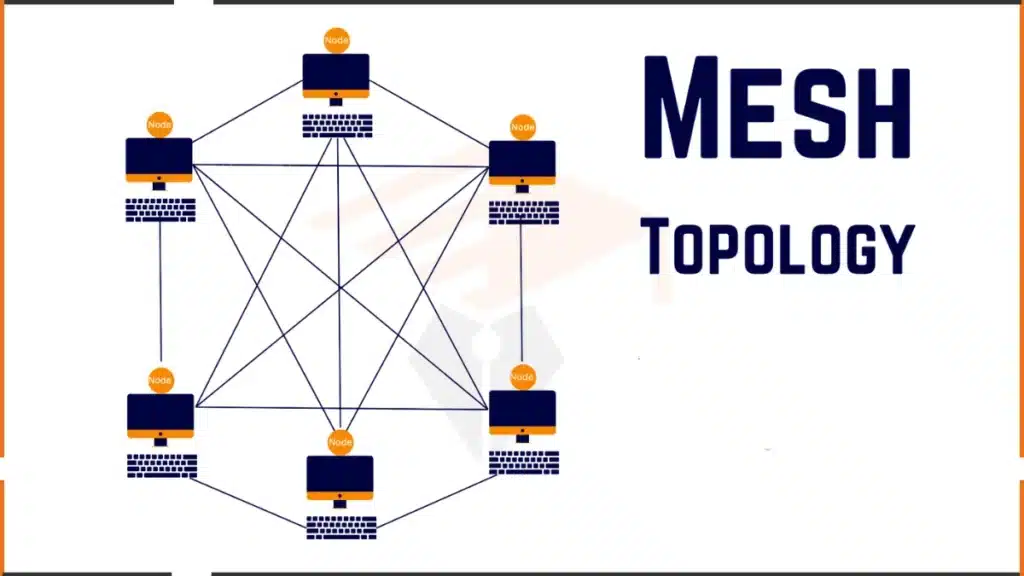
Mesh topology is a type of computer network in which each device connects to multiple other devices. In this setup, every device (called a node) is connected to one or more other devices, creating a web-like structure.
For example, imagine a group of friends holding hands in a circle. Each friend is connected to the ones next to them. In mesh topology, devices are like these friends, and the connections are like their hands.
Also Read: Examples of Mesh Topology in Networking
Why Is It Called Mesh Topology?
The name “mesh topology” comes from the way the network looks. The word “mesh” means a network of interconnected things, like the threads in a net or a spider web.
In this type of network, devices are connected in a way that resembles a mesh or a net. Each device links to others. They create multiple paths for data to travel. This interconnected structure is why it is called “mesh topology.”
There are two main types of mesh topology:
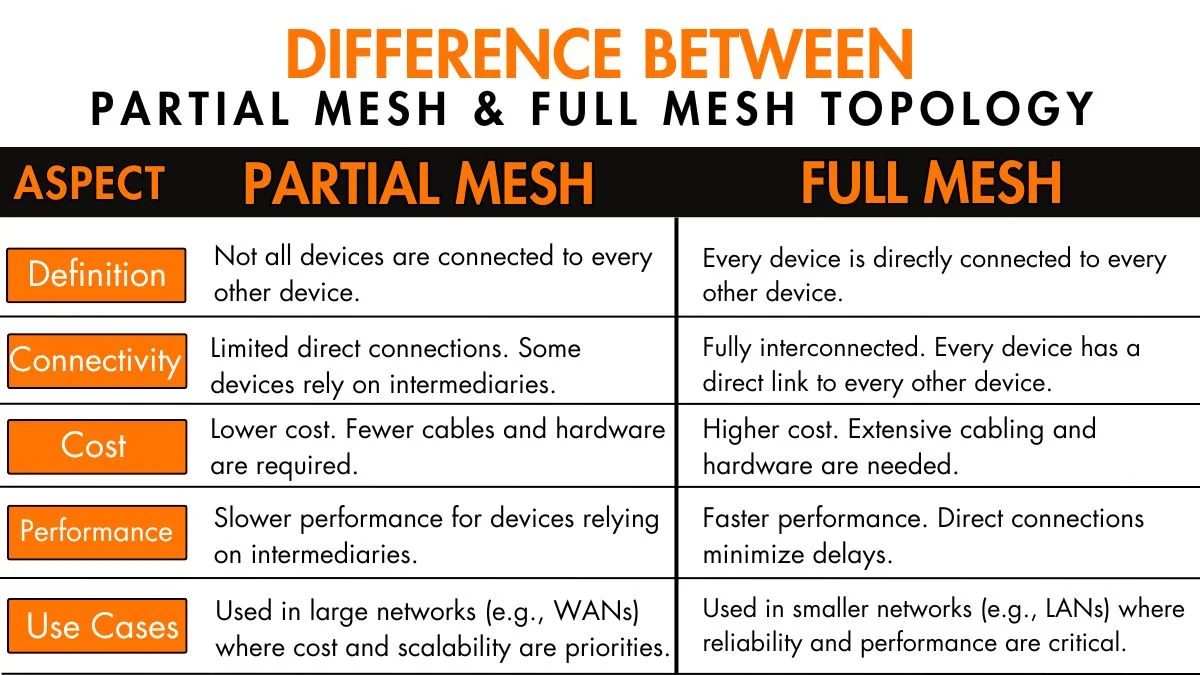
- Full Mesh: Every device is directly connected to every other device. This is like a group where everyone can talk directly to everyone else.
- Partial Mesh: Devices are connected to some devices but not all devices. This is like a group where people talk to a few others, not everyone.
Components of Mesh Topology
The following are the main components of Mesh topology:
1. Nodes
Nodes are the devices in the network. They can be computers, phones, or any device that sends and receives data. In mesh topology, each node connects to multiple other nodes. This helps data find another path if one connection fails.
2. Links (Connections)
Links are the connections between nodes. They allow data to travel from one device to another. Each node has many links in a mesh topology. This makes the network reliable. Links can be wired (cables) or wireless (Wi-Fi).
3. Routers
Routers help direct data through the network. They find the best path for data to reach its destination. In mesh networks, routers make sure data flows smoothly, even if some connections fail.
4. Switches
Switches connect several devices within a minor part of the network. They manage data flow, especially when many devices are active. Switches keep local areas of the network organized and reduce traffic.
5. Cables (for Wired Mesh Networks)
In wired mesh networks, cables connect nodes. Commonly used cables are Ethernet or fiber-optic. These cables provide stable, fast connections, making wired mesh networks solid and reliable.
6. Wireless Access Points (for Wireless Mesh Networks)
Wireless access points (APs) allow nodes to connect without cables. In wireless mesh networks, APs create a Wi-Fi network. They also relay data between nodes, keeping the network flexible and easy to expand.
7. Protocols
Protocols are rules that guide how data moves between nodes. They ensure data follows the best paths and reaches the right place. Protocols keep the network organized and reliable.
8. Network Interface Cards (NICs)
NICs allow devices to connect to the network. Each device needs an NIC to send and receive data. NICs can be wired (for Ethernet) or wireless (for Wi-Fi).
9. Network Software
Mesh networks often use special software to manage connections. This software keeps track of traffic, finds problems, and balances data loads. It helps keep the network stable and efficient.
Features of Mesh Topology
Here are some important features of mesh topology:
Interconnected Devices
In mesh topology, every device connects to one or more devices. This creates a network where devices are linked together like a web.
For example, if Device A wants to send data to Device B, it can send it directly if they are connected. If they are not directly connected, the data can travel through other devices to reach Device B. This interconnected design ensures that data can always find a way to move from one device to another.
Multiple Paths for Data
One of the key features of mesh topology is that data can travel through many paths. Imagine passing a note in class. If you cannot give the note directly to your friend, you can ask someone else to pass it along.
Similarly, in a mesh network, if one path is busy or broken, the data can take another path. This makes the network strong and reliable because there is always a backup route for data to travel.
Reliability
Mesh topology is very reliable because it does not depend on a single path or device. If one device stops working or a connection breaks, the network still works. This is because data can find another path to travel.
For example, if a connection between Device A and Device B fails, the data can go through Device C to reach its destination. This reliability makes mesh topology a good choice for important networks like those used in hospitals or offices.
Scalability
Another feature of mesh topology is scalability. This means it is easy to add new devices to the network. To add a new device, you simply connect it to one or more existing devices. This makes mesh topology a good choice for growing networks.
For example, if you have a smart home system and want to add a new smart light, you can easily connect it to the existing network without disrupting the system.
Self-Healing
Mesh networks have a special feature called self-healing. This means the network can “heal” itself if a connection fails. If one path is broken, the network automatically finds another path for data to travel.
This is like finding a new road if the main road is closed. Self-healing makes mesh networks very strong and reliable, even in situations where connections might fail.
Why Is This Important?
Mesh topology is important because it makes networks reliable. If one device stops working, the network still works. This is useful in places where a strong connection is needed, such as hospitals or offices. It is also used in smart home systems, where many devices need to stay connected.
Also Read:
| How Mesh Topology Works | Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology |
| Differences Between Partial Mesh and Full Mesh Topology |
FAQs
How is mesh working?
A Mesh network works by connecting each device to others so data can find multiple paths to reach its destination.
What is a mesh topology in real life?
A real-life example of mesh topology is Wi-Fi networks in large buildings, where routers connect for better coverage.
What are the characteristics of mesh topology?
Duplicativepaths, Reliable, Scalable, Complex setup and High cost




Leave a Reply