What is Regeneration? -Definition And Examples
Regeneration is a type of asexual reproduction which involves the generation of a new organism from a lost body part. This is because the specialized cells present in the organism can differentiate and grow into a new individual. Organisms like hydra and planaria exhibit regeneration.
Types of Regeneration
There are two types of regeneration:
- Reparative regeneration
- Restorative Regeneration
Examples of Regeneration
Here are some examples of Regeneration in different organisms.
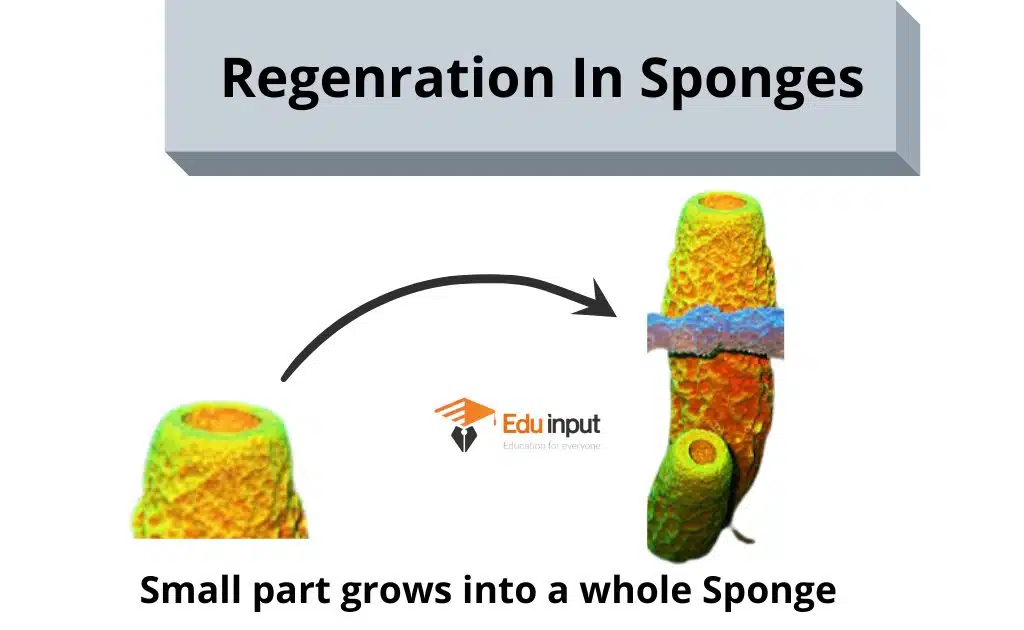
Regeneration in sponges:
Sponges have simple organization. So sponges possess great power of regeneration. The sponges replace the parts lost during injury by regeneration. Any piece of the body is capable of growing into a complete sponge. The process of regeneration is very slow. It requires months or years for complete development.
Regeneration in lobsters
If a lobster loses its pincer claw. A new claw regenerates.

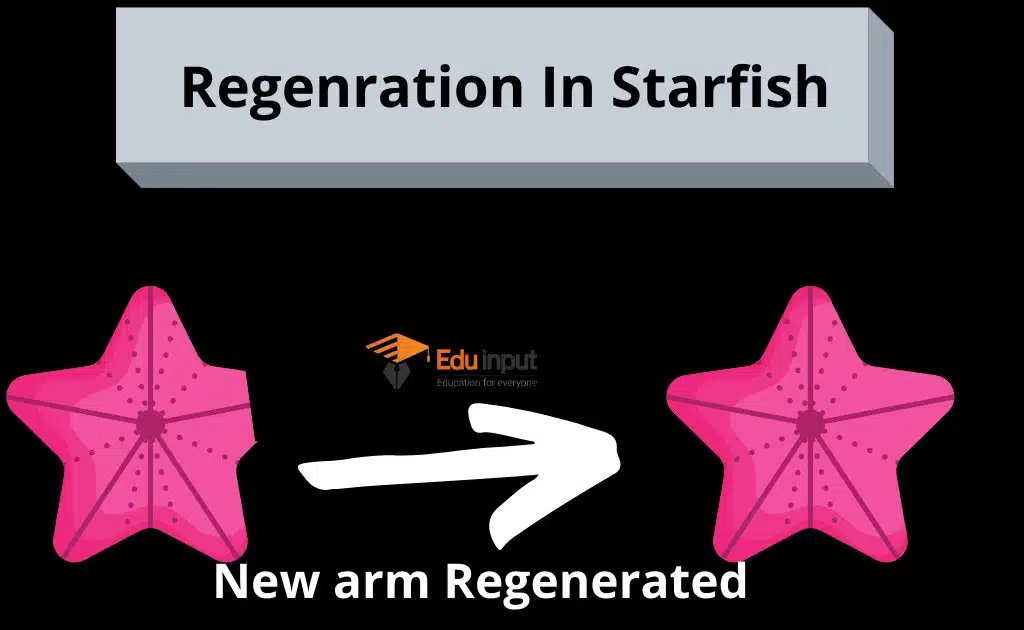
Regeneration In starfish
Sometimes starfish break off portions of their arms into pieces and the central disc completely lost the arm. The individual regenerates the arm. In some cases, the arm can also develop.
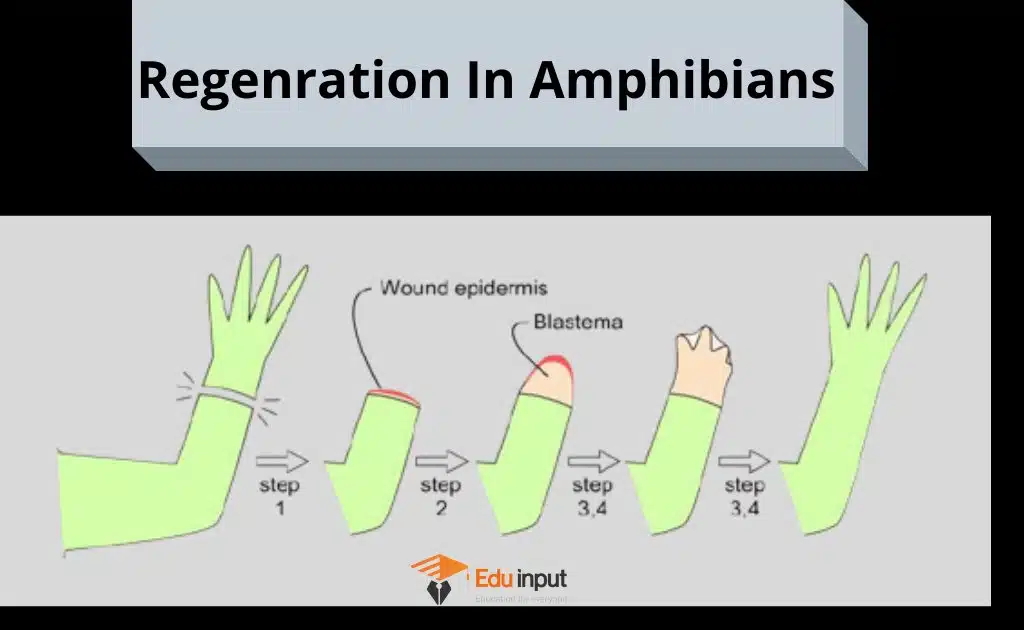
Regeneration in Amphibians
Salamanders can regenerate their limbs are regenerated throughout life. But they more rapidly regenerated w amphibian is young and small. The other parts of the body also have considerable regeneration capacity e.g. Tail in the larva of amphibians.
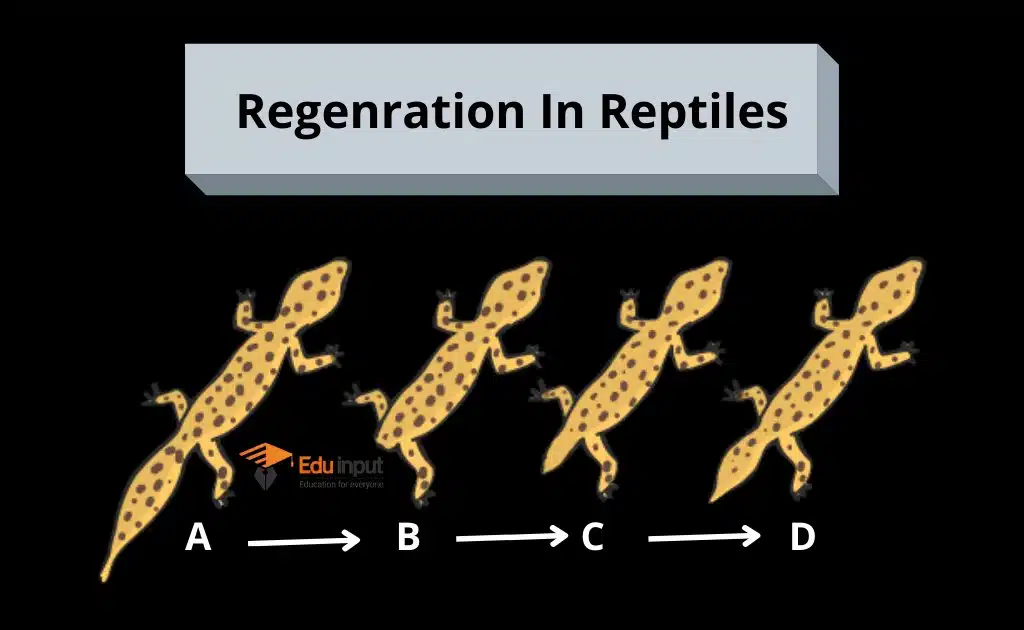
Regeneration in Reptiles
Lizards can also regenerate their tail. For example, Lizard can easily discard its tail. It has special features of its tail and regenerates its tail.
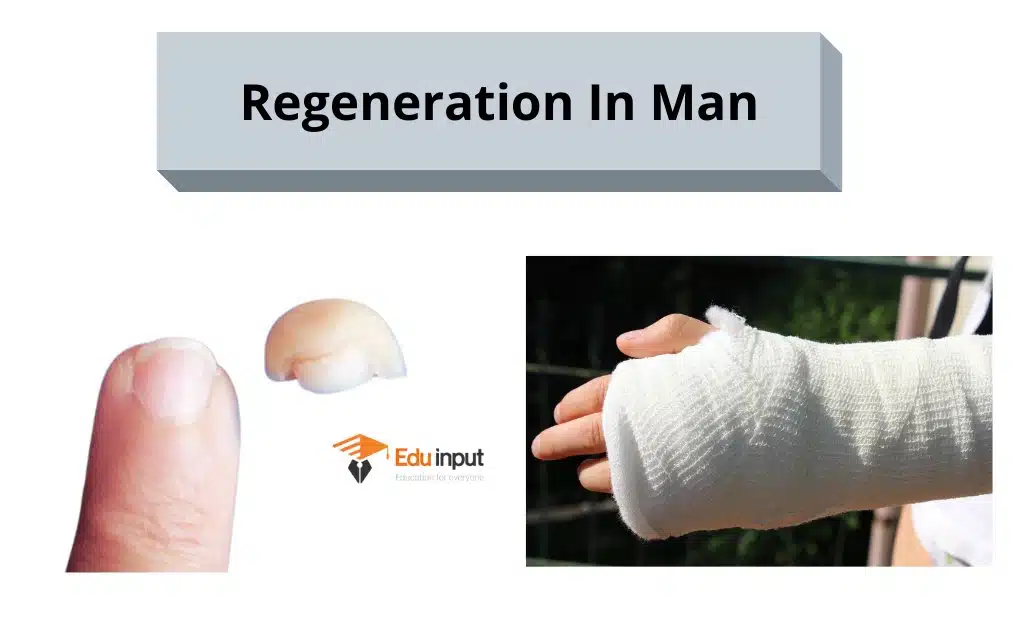
Regeneration in Man
Healing of fractures and repair of skin are some examples of regeneration in man.
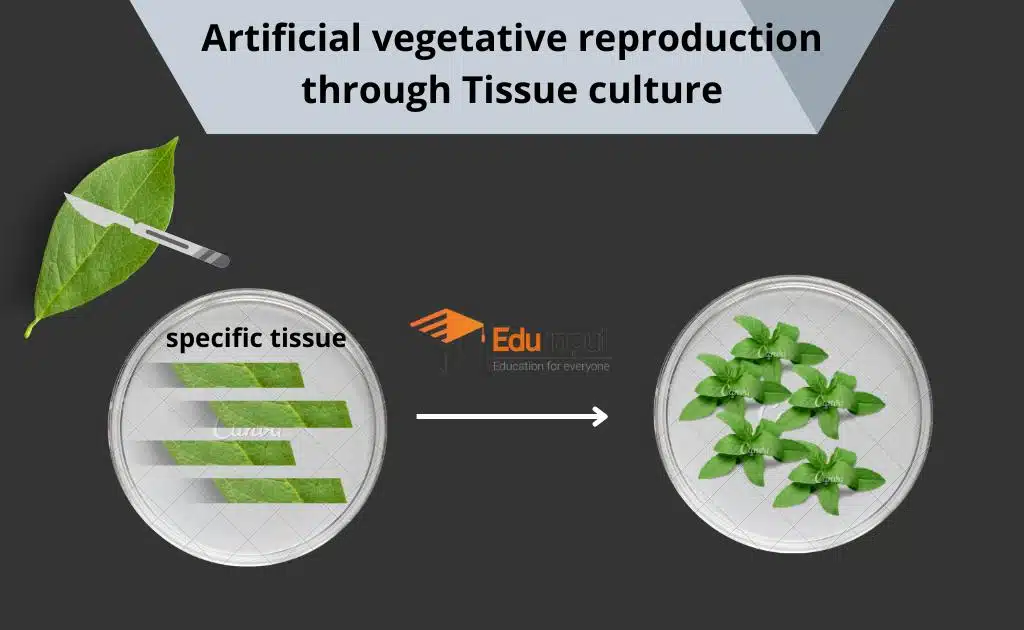
Regeneration in plants
Regeneration is the basis of plant propagation ( Almost any part or even very small fragments of a plant can be regenerated example, a piece of stem or leaf or a single tissue cell can develop into a full p part of the stem with a few leaves taken from plants. It is planted in soil for a complete plant. It is done by vegetative propagation.
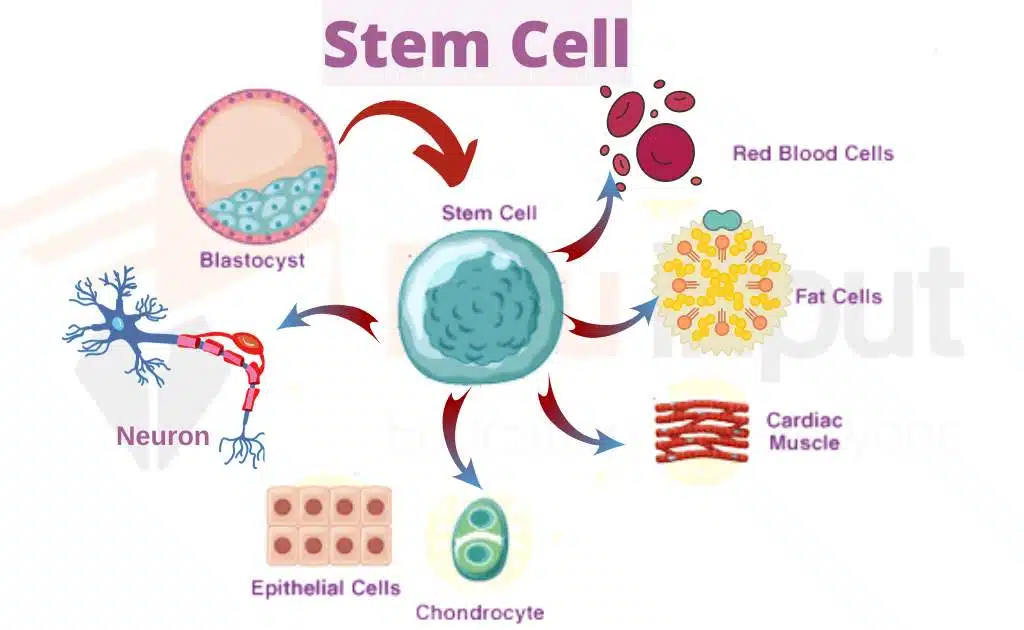
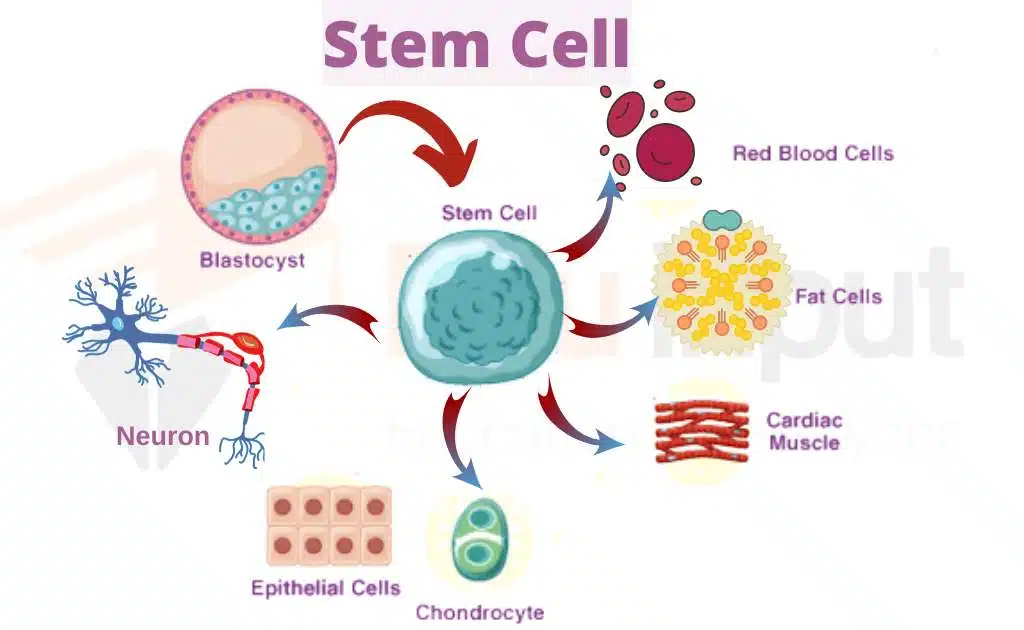
Mechanism of regeneration
Regeneration is the development and formation of the missing organ in adult an So development some embryological processes are repeated during regeneration. There are two types of processes of regeneration:
Presence of undifferentiated cells
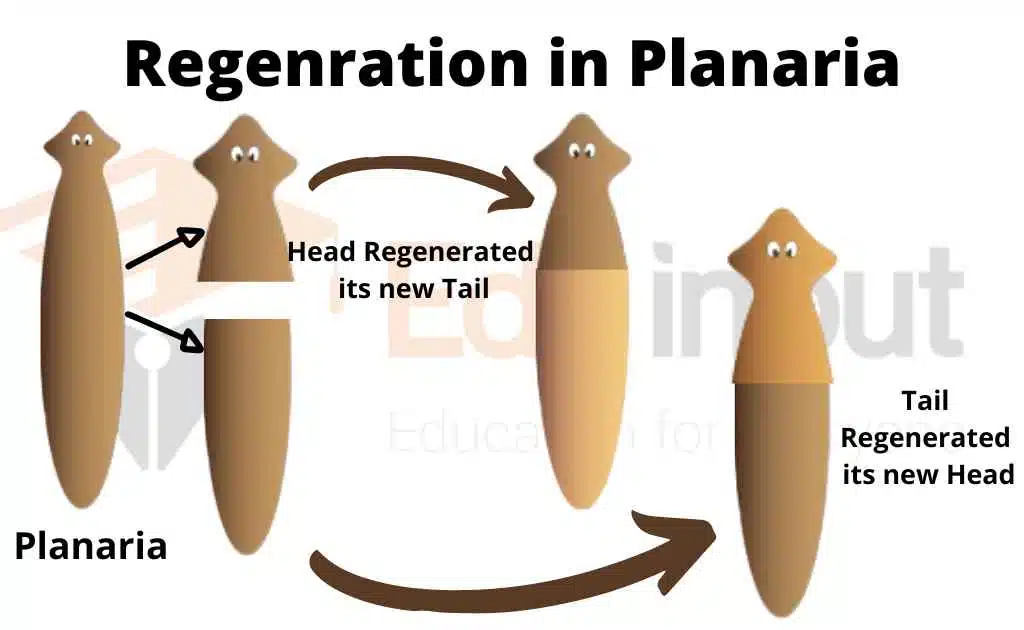
Some organism retains undifferentiated cells. The missing part of the body is replaced by the differentiation of these cells during regeneration. Unspecialized cells or undifferentiated cells are present in organisms like flatworms and Planaria. These cells are called neoblasts. Neoblasts are always present in the body of an adult. They migrate to the site of amputation. Where they are differentiated into specialized cell types.
Formation of dedifferentiated cells
There is another mechanism of regeneration in other organisms like salamanders or newts. In these animals the specialized cell in the stump of an amputated limb are dedifferentiated (become specialized). Then these dedifferentiated cells are differentiated into different types of cells and regenerate the organ.
Related FAQs
What is Regeneration?
Regeneration is a type of asexual reproduction which involves the generation of a new organism from a lost body part.
How do organisms regenerate lost parts through regeneration?
Some organism like flatworms and Planaria retains undifferentiated cells. These cells are called neoblasts. Neoblasts are always present in the body of an adult. They migrate to the site of amputation. Where they are differentiated into specialized cell types.
What are the types of regeneration?
There are two types of regeneration:
Reparative regeneration
Restorative Regeneration



Leave a Reply