What is Sentence? – Structure, and Types According To Function and Structure
A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought. It consists of a subject and a predicate, which work together to form a meaningful unit of communication.
What is Sentence in English?
A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought. It helps us share ideas, ask questions, give commands, or express feelings. If you’re wondering what is a sentence, it simply means a complete unit of meaning made up of words. A common definition of sentence with example would be: “She is happy.” This short sentence clearly expresses a full idea.
When we ask what the sentence is, we are referring to a structured group of words that makes sense and stands alone. The sentence definition is tied to communication—it must make a complete statement. There are different types of sentences, including declarative (statements), interrogative (questions), imperative (commands), and exclamatory (strong emotions).
Here’s another definition of sentence: it is the basic unit of language that conveys meaning. You can also define sentence by saying it’s a collection of words that begins with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, question mark, or exclamation point.
To give a clearer picture of a sentence, consider this: “The sun rises in the east.” This is not just a sentence but also an informative statement. Learning what is sentence structure is key to good communication. Understanding the definition of sentence helps improve both writing and speaking skills.

Structure of Sentence
The structure of a sentence refers to how its parts are arranged to express a complete thought. Every sentence has key elements such as a subject and a verb, and sometimes includes objects, phrases, or clauses. These parts work together to make the sentence clear and meaningful.
Parts of Sentence
Here are the basic parts that make up the structure of a sentence:
1. Subject
The subject is the person, place, thing, or idea that does something in the sentence. It’s usually a noun or pronoun.
- Example: The cat chased the mouse.
(The subject is The cat)
2. Verb
The verb shows what the subject is doing or the state it is in. It tells us the action or condition.
- Example: The cat chased the mouse.
(The verb is chased)
3. Object
The object receives the action of the verb. It tells us what or who is affected by the action. There are two types:
- Direct object – directly receives the action.
- Indirect object – receives the result of the action.
- Example: The cat chased the mouse.
(The mouse is the object)
4. Prepositional Phrase
A prepositional phrase adds more detail to a sentence. It starts with a preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun.
- Example: The cat sat on the mat.
(on the mat is the prepositional phrase)
5. Clause
A clause is a group of words with a subject and a verb. It can be:
- Independent clause – Can stand alone as a sentence.
- Dependent clause – Cannot stand alone; needs more information.
- Example of a dependent clause: Although it was late
- Example of an independent clause: She smiled.
Sentence Structure Examples
Understanding different sentence structure examples helps in writing clearly. Here are a few types:
Simple Sentence
Has one independent clause.
- Example: She runs every morning.
Compound Sentence
Has two independent clauses joined by a conjunction.
- Example: She runs every morning, and he goes to the gym.
Complex Sentence
Has one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
- Example: Although it was raining, they played outside.
Imperative Sentence Structure
An imperative sentence gives a command, request, or instruction. The subject (you) is often hidden.
- Structure: [Verb] + [Object/Details]
- Example: Close the door.
(You is the hidden subject)
Exclamatory Sentence Structure
An exclamatory sentence shows strong emotion like surprise or excitement. It ends with an exclamation mark (!)
- Structure: [What/How] + [subject] + [verb] + !
- Example: What a beautiful day!
Types of Sentences According to Function
Sentence types and functions play an important role in how we communicate. There are four main types of sentences based on function: Declarative, Interrogative, Imperative, and Exclamatory. These are also known as the functional types of sentences because each serves a different purpose.
Understanding the types of functional sentences helps improve both writing and speaking skills. Let’s explore each type with examples and understand how they work in the overall structure of a sentence.
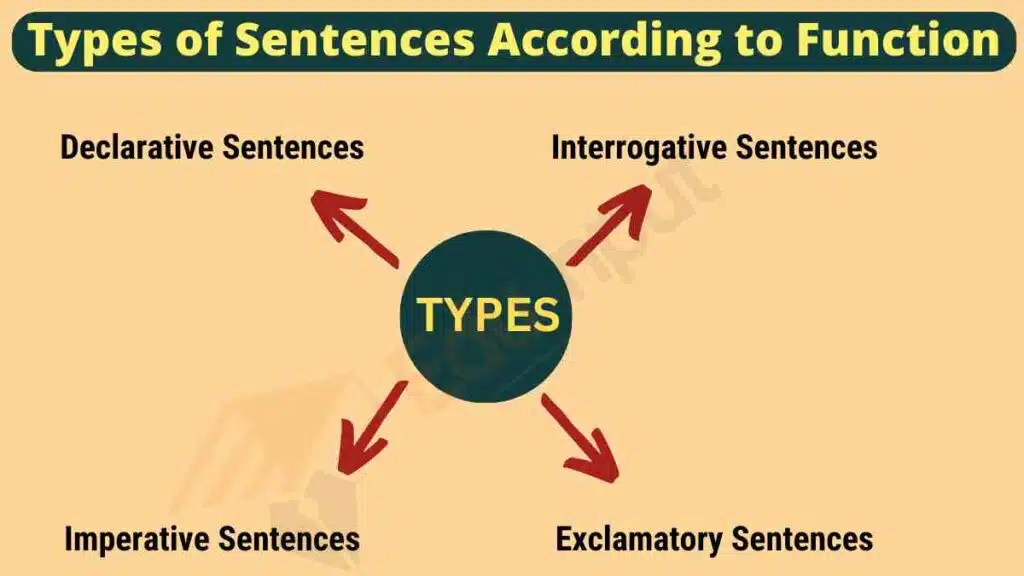
1. Declarative Sentences
Declarative sentences are used to make statements, give facts, or express opinions. These are the most common types of sentences according to function. They always end with a period (.) and are neutral in tone.
Examples
- The sun rises in the east. (Fact)
- I enjoy reading books. (Opinion)
- Today is Monday. (Information)
These types of sentences based on function typically follow a clear structure of a sentence with a subject and a verb.
2. Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences are used to ask questions. They are designed to gather information and always end with a question mark (?).
Examples
- What time is it? (Asking for time)
- Where do you live? (Asking for location)
- Do you like pizza? (Yes/No question)
Among all types of functional sentences, these help open conversations and clarify doubts.
3. Imperative Sentences
Imperative sentences give commands, make requests, or offer advice. These functional types of sentences may end with a period (.) or an exclamation mark (!) depending on the tone or urgency.
Examples
- Please pass the salt. (Request)
- Be quiet! (Command)
- Study hard for the test. (Advice)
In the imperative sentence structure, the subject is often implied (usually “you”).
4. Exclamatory Sentences
Exclamatory sentences show strong emotions like excitement, surprise, or anger. These types of sentences according to purpose always end with an exclamation mark (!) to show emotion and emphasis.
Examples
- Wow, that’s amazing! (Excitement)
- I can’t believe it! (Surprise)
- What a beautiful sunset! (Admiration)
These sentence types and functions are expressive and add emotion to everyday language.
Types of Sentences According to Structure
Sentences are grouped into types of sentences on the basis of structure depending on how their clauses are arranged. These kinds of sentences according to structure help express ideas in different ways—from simple to more complex thoughts. Understanding these forms improves both writing and communication skills.
Here are the main types of sentences according to structure, along with clear sentence structure examples for each:
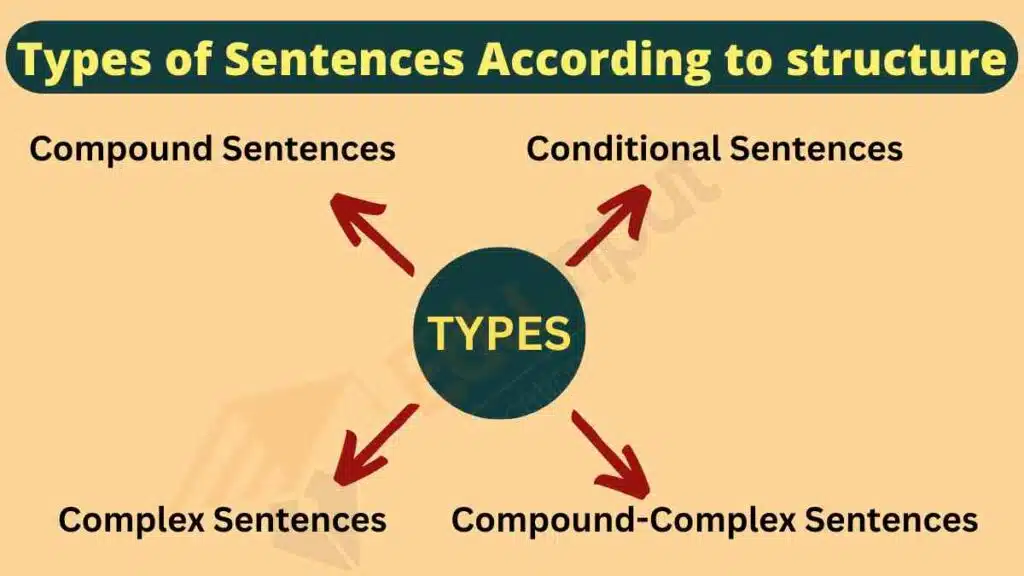
Conditional Sentences
Conditional sentences express a condition and its possible outcome. These follow a specific conditional sentence structure that usually includes an “if” clause and a main clause. They are commonly divided into four types:
- Zero Conditional (general truths)
- First Conditional (real future possibilities)
- Second Conditional (unreal or hypothetical situations)
- Third Conditional (imaginary past situations)
Examples of Conditional Sentences
- If it rains, we will stay indoors. (First Conditional)
- I would buy that car if I had enough money. (Second Conditional)
- If you study hard, you will pass the exam. (First Conditional)
These types of sentence structure with examples show how we talk about conditions and results.
Compound Sentences
A compound sentence consists of two or more independent clauses joined by coordinating conjunctions such as “and,” “but,” or “so.” This sentence structure is useful when you want to connect related ideas.
Examples of Compound Sentences
- I wanted to go to the party, but I had to work late.
- She loves to dance, and he enjoys playing the guitar.
These are simple sentence structure examples that combine two complete thoughts into one sentence.
Complex Sentences
A complex sentence includes one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. The dependent clause cannot stand alone and depends on the main clause for meaning. These sentences help show cause and effect, time relationships, and contrast.
Examples of Complex Sentences
- Although it was raining, we decided to go for a walk.
- She couldn’t attend the concert because she had a prior commitment.
Among the types of sentence structure with examples, complex sentences are essential for expressing deeper relationships between ideas.
Compound-Complex Sentences
Compound-complex sentences are the most advanced types of sentences according to structure. They include two or more independent clauses and at least one dependent clause. This structure allows you to express layered ideas clearly.
Examples of Compound-Complex Sentences
- I went to the store and bought some groceries, but I forgot to buy milk because it slipped my mind.
- After he finished his presentation, she asked a few questions, and the audience applauded his efforts.
These types of sentence structure with examples show how multiple actions and conditions can be joined for clarity and detail.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Can a sentence have more than one subject?
Yes, a sentence can have multiple subjects, especially in compound or complex sentences. Each subject contributes to the overall meaning of the sentence.
Are all imperative sentences considered commands?
Not all imperative sentences are commands. They can also express requests, invitations, or suggestions, depending on the context and tone.
Can a declarative sentence end with an exclamation mark?
No, a declarative sentence typically ends with a period. Exclamation marks are reserved for exclamatory sentences that express strong emotions or intensity.
Are all conditional sentences hypothetical?
Not necessarily. While conditional sentences often present hypothetical situations, they can also express real or factual conditions and their results.
What is the purpose of using compound-complex sentences?
Compound-complex sentences allow for the expression of complex ideas and relationships by combining multiple independent and dependent clauses.
External References: Paragraph rewriter: It helps you improve your existing sentences and structure to look more professional.





Leave a Reply