What is Star Topology -Types, Components and Working
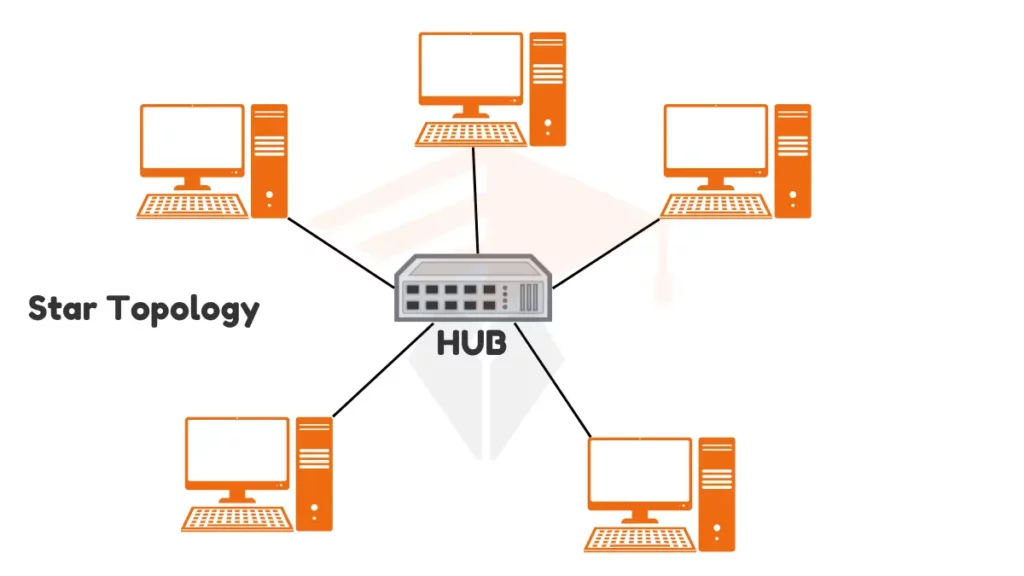
Star topology is a computer network configuration where all devices connect to a central point. This central point can be a hub or a switch. The devices connected to the hub are called peripheral nodes.
Each peripheral node has its dedicated connection to the hub. The network’s layout resembles a star, with lines (cables) extending from the central hub to each device. This structure helps keep the network organized and easy to manage.
Types of Star Topology
Star topology can be divided into two main types:
1. Passive Star Topology:
In passive star topology, the hub does not process data. It simply acts as a connection point for devices. This type is cheaper and easier to set up. But may not perform as well in large networks. Passive hubs do not amplify or regenerate signals, which means that signal strength may weaken over long distances
2. Active Star Topology:
In active star topology, the central hub has its power supply and can process data. This hub type is more powerful and can manage more significant amounts of data. It improves network performance by allowing the hub to handle data traffic efficiently. Active hubs can also regenerate signals, which helps maintain strong connections over longer distances.
Components of Star Topology
the following are the components of star topology
1. Peripheral Nodes:
Peripheral nodes are the devices connected to the hub. These can include computers, printers, scanners, and other devices that need to connect to the network. Each device has a cable connecting it to the central hub. This individual connection allows each device to communicate directly with the hub, ensuring fast and reliable data transfer.
2. Central Node:
The central node, or hub, is the heart of the network. It acts as a control center for data communication. When one device wants to send data to another, it first sends that data to the hub. The hub then forwards the data to the appropriate device. The central hub helps manage the flow of information and ensures that data is sent to the right place. It can be a simple device with advanced features to improve network performance.
How Star Topology Works?
In star topology, when a device wants to send data to another device, it sends it to the hub first. The hub then processes this data and sends it to the correct destination, helping ensure that data travels quickly and efficiently.
Star topology also helps reduce data collisions. A data collision occurs when two devices try to send data at the same time. In a star network, all data passes through the central hub, which helps coordinate the communication. The hub manages the data flow, so it is easier to avoid collisions and keep the network running smoothly. This feature is essential in busy networks where many devices are communicating at the same time.
Examples of Star Topology
Let’s look at an example to understand this better:
Real-world Applications
Star topology is commonly used in various settings. For example, many schools use it to connect computers in a lab, allowing students to access shared resources like printers and files easily. Offices often use star topology to connect computers and printers, enabling employees to work together efficiently. Hospitals also use this setup to connect medical devices and computers, allowing for quick communication and data sharing among healthcare professionals.
FAQs
What are the three importance of stars?
They emit light and energy, guiding navigation and timekeeping
What is the purpose of a star?
The purpose of a star is to:
Emit light, Produce energy, Guide Navigation
What are the main advantages of a star network?
Easy setup, Good performance, Simple troubleshooting, Reliable




Leave a Reply