What is Urea Cycle? (History, Reactions, Enzymes, and Steps)
The urea cycle is a metabolic pathway that facilitates the conversion of toxic ammonia into urea that is a less harmful waste product.
It involves a series of enzymatic reactions. It occurs in Liver. Urea is a waste product produced by our bodies during protein metabolism. Urea is a nitrogenous compound found in urine and blood plasma. The urea cycle is responsible for producing urea from amino acids.
Formula Of Urea Cycle
The overall equation of the urea cycle can be written as follows:
NH3 + CO2 + aspartate + 3 ATP + 3 H2O → urea + fumarate + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + AMP + PPi + H2O
History Of Urea Cycle
The Krebs-Henseleit cycle, also known as the urea cycle, is the first metabolic cycle that was discovered by Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit. In more detail, the individual reactions were described by Ratner and Cohen. One of the NH 2 groups is derived from NH3 while the other is derived from aspartate. CO2 is what gives the carbon atom its shape.
Reactions of Urea Cycle
| Step | Reactants | Products | Catalyzed by | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NH3 + HCO3- + 2ATP | carbamoyl phosphate + 2ADP + Pi | CPS1 | mitochondria |
| 2 | carbamoyl phosphate + ornithine | citrulline + Pi | OTC, zinc, biotin | mitochondria |
| 3 | citrulline + aspartate + ATP | argininosuccinate + AMP + PPi | ASS | cytosol |
| 4 | argininosuccinate | arginine + fumarate | ASL | cytosol |
| 5 | arginine + H2O | ornithine + urea | ARG1, manganese | cytosol |
Urea Cycle Enzymes
In the urea cycle, there are five important enzymes involved:
- Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1)that catalyzes the formation of carbamoyl phosphate
- Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) that is responsible for the conversion of carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine into citrulline
- Argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS1) facilitates the synthesis of argininosuccinate
- Argininosuccinate lyase (ASL) catalyzes the breakdown of argininosuccinate into arginine and fumarate
- Arginase 1 (ARG1) is the final enzyme in the urea cycle and is responsible for the conversion of arginine into urea and ornithine
Stages of Urea Cycle
Urea cycle completes in two stages, Because enzymes needed for urea cycle are present in mitochondria, and some in cytosol of the cytoplasm. That’s why these two stages are known as mitochondrial and cytosolic stages respectively.
1. Mitochondrial Stage
Mitochondrial stage of urea cycle involves following steps:
- Carbamoyl phosphate synthesis
- Citrulline formation
- Transport of Citrulline to the cytosol
2. Cytosolic Stage
Cytosolic stage of urea cycle involves following steps:
- Argininosuccinate synthesis
- Argininosuccinate breakdown
- Urea production
- Mitochondrial translocation
Steps Of Urea Cycle
Urea synthesis is a five-step cyclic process, with five distinct enzymes. The first two enzymes are present in mitochondria while the rest are localized in the cytosol.
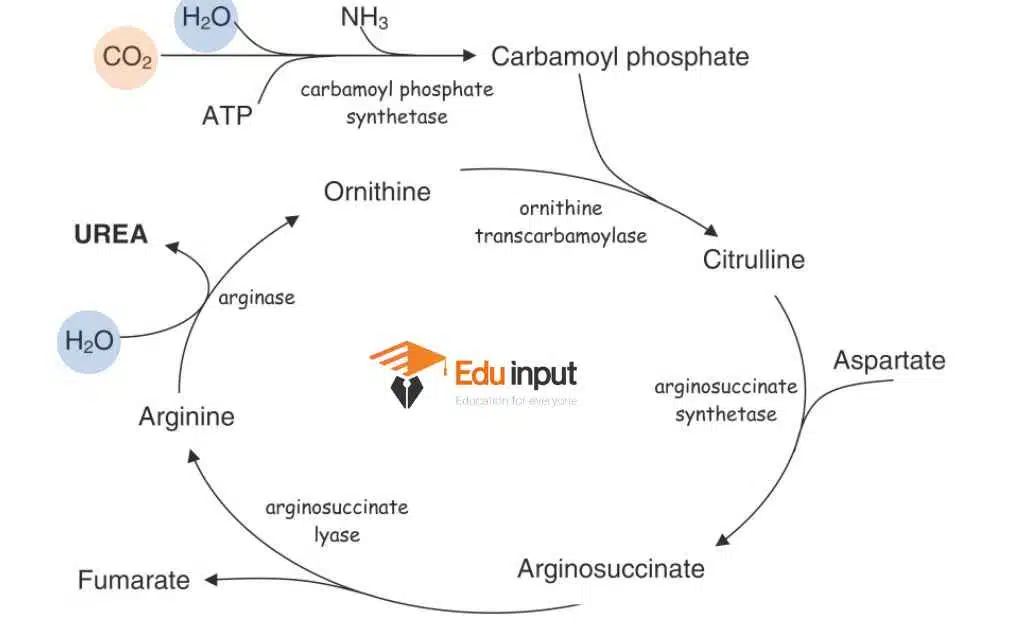
1. Synthesis Of Carbamoyl Phosphate:
The condensation of NH4 + ion with CO2 is the catalyst for the formation of carbamoyl phosphate.
- This step is crucial and determines the overall rate of the urea cycle as it is rate limiting step as it uses two molecules of ATP.
- It involves the conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) and ammonia (NH3) into carbamoyl phosphate using an enzyme called carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I). CPS I requires a special activator called N-acetyl-glutamate (NAG) to function properly.
- NAG is formed from the combination of glutamate and acetyl-CoA with the help of an enzyme called NAG synthase.
- Ammonia provides the first amine group needed to create urea.
- Arginine can increase the production of NAG by upregulating the activity of NAG synthase.
CO+ NH+ 2ATP produces carbamoyl phosphate +2ADP + P
Glutamate + acetyl-CoA NAG : Synthesis of NAG
2. Formation of citrulline:
One of the central reactions in the urea cycle involves the formation of citrulline by combining ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate.
- Ornithine is regenerated from arginine and plays an important role in the urea cycle.
- Citrulline is not found in protein structures due to lacking codons.
- The enzyme ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTC) catalyzes the formation of citrulline by combining carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine.
- Citrulline is then transported from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm using a transport system called ornithine translocase, allowing further progression of the urea cycle.
Carbamoyl phosphate + ornithine citrulline
3. Synthesis Of Arginosuccinate:
Argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS) catalyzes the combination of citrulline and aspartate to produce argininosuccinate, the immediate precursor of arginine.
- Argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS) catalyzes the condensation of citrulline and aspartate to form argininosuccinate, which is the immediate precursor of arginine.
- Argininosuccinate lyase converts L-arginine into L-citrulline and fumarate.
- In the next step, argininosuccinate synthetase combines L-citrulline with aspartate to produce argininosuccinate.
- This reaction incorporates the second amino group of ammonia, resulting in the formation of arginine.
- The formation of argininosuccinate and arginine requires the use of ATP, which is cleaved into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).
- The inorganic phosphate (Pi) is rapidly broken down into inorganic phosphate as a byproduct.
Citrulline + aspartate + ATP argininosuccinate
Oxaloacetate + glutamate aspartate + alpha-ketoglutarate
4. Cleavage Of Arginosuccinate:
Arginosuccinase breaks down arginosuccinate to synthesize arginine and fumarate. Arginine is the immediate precursor for urea.
Fumarate liberated here provides a connecting link with the TCA cycle, gluconeogenesis, etc.
READ How Urea Cycle Is Linked With TCA Cycle?
5. Formation Of Urea:
The last step of the urea cycle involves the conversion of excess ammonia into urea in the mitochondria of liver cells. Urea is then released into the bloodstream, filtered by the kidneys, and ultimately excreted in the urine.
- Arginase catalyzes the hydrolysis of L-arginine into urea and L-ornithine.
- Urea is formed through the conversion of arginine by arginase.
- Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I converts urea back into ammonia.
- Ornithine transcarbamylase allows the recycling of ornithine back into arginine.
Arginine + HO urea + ornithine
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What is Urea cycle?
The cycle which is involved in the conversion of excessive ammonia into urea is known as the urea cycle.
What is another name for the urea cycle?
The urea cycle is also known as the Orthinine cycle.
How many ATPs are used in urea cycle?
4 molecules of ATP are used in the urea cycle.
How many steps are in urea cycle?
There is a series of enzymatic reactions comprising 5 steps.
Where does the urea cycle occur?
The urea cycle primarily takes place in the liver. While the entire cycle doesn’t happen in a single location within the liver, it involves Mitochondria and Cytoplasm.




Leave a Reply