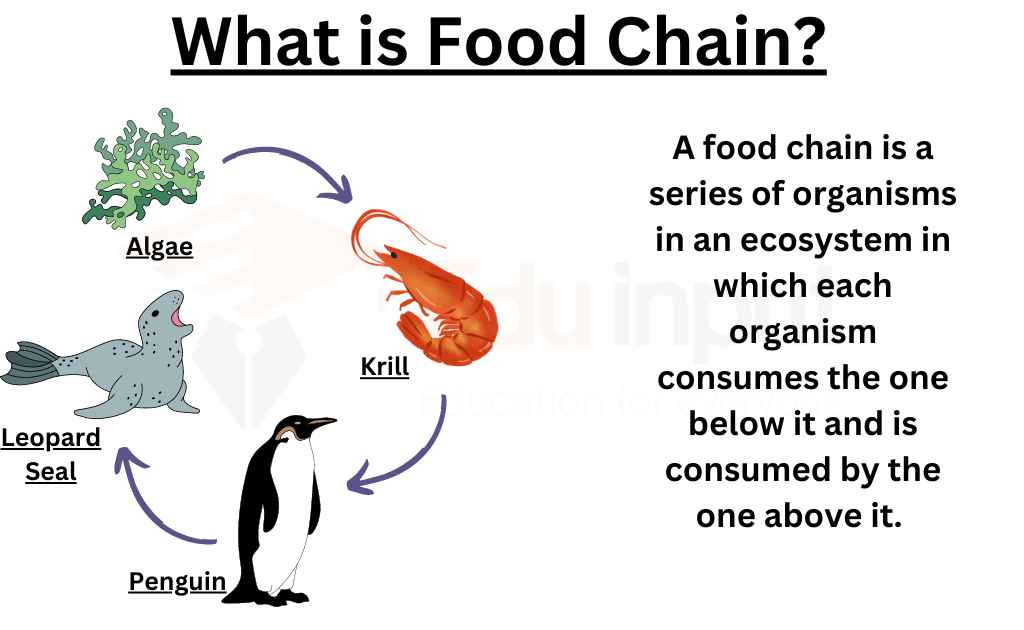
Why Flow Of Energy Is Unidirectional In Food Chain?
The flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional because energy from the sun is passed through autotrophs to herbivores and then to carnivores, but it does not revert back. Therefore, the flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional.
Why Food Chain is Unidirectional?
The sun is the only source of energy for ecosystems, so energy flows in one direction through a food chain. This is because energy cannot be recycled once it’s used by an organism.
When organisms consume food, they convert energy into a form they can use for their bodily functions. Some energy is lost as heat and the rest is used for growth, reproduction, or other activities.
Energy cannot be reused by other organisms when an organism dies. Therefore, energy flows in one direction from producers to consumers and can’t be recycled.
This unidirectional flow is important for transferring energy and nutrients from one organism to another and maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
The energy flow in a food chain typically follows these steps:
- Producers (The first trophic level consists of producers)
- Primary Consumers (The second trophic level includes primary consumers, which are herbivores)
- Secondary Consumers (The third trophic level contains secondary consumers, which are carnivores)
- Tertiary Consumers (The fourth trophic level includes tertiary consumers, which are top predators)
- Decomposers (At each trophic level, energy is lost as heat and waste. The final step in the energy flow is decomposition, where decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down dead organisms and waste into nutrients that can be reused by producers)



Leave a Reply