How Homeostasis Is Affected By pH And Osmosis?
pH and osmosis can disrupt homeostasis by affecting the concentration of fluids and electrolytes in the body.
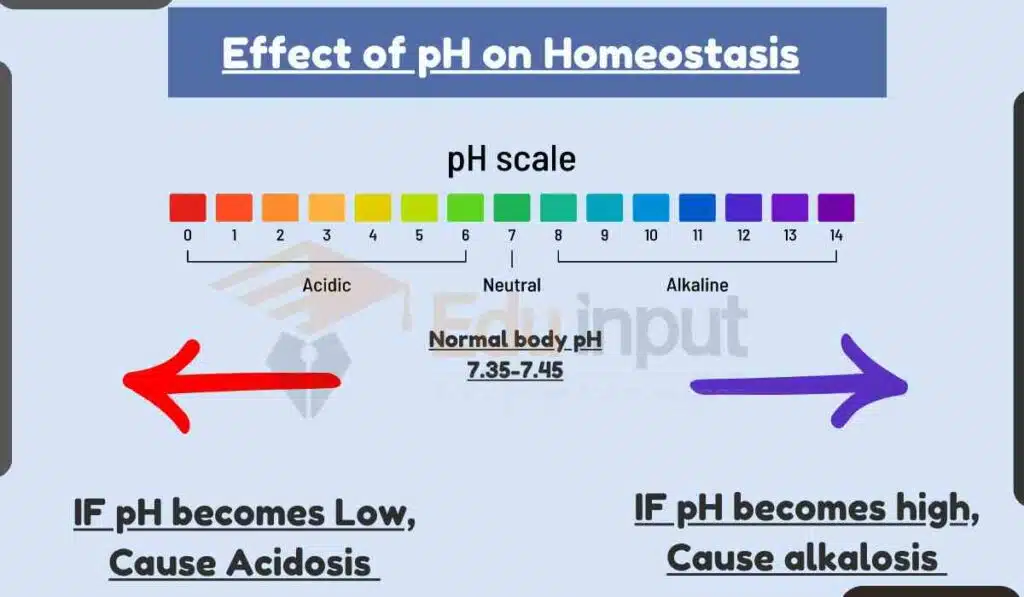
Effect of pH on Homeostasis
The body’s pH is tightly regulated within a narrow range of 7.35 to 7.45. This is because many biological processes are sensitive to pH changes.
For example, enzymes, which are proteins that help the body to function. They work best at a specific pH level. If the pH level changes too much, the enzymes may not work properly. This can lead to problems with digestion, metabolism, and other bodily functions.
The body maintains pH homeostasis through a variety of mechanisms.
For example, the kidneys help to regulate the amount of acid and base in the blood. The lungs also play a role in pH regulation by releasing carbon dioxide, which helps to keep the blood pH alkaline.
When the body’s pH is not maintained within the normal range, it can lead to a condition called acidosis or alkalosis.
Acidosis is a condition in which the blood pH is too low, and alkalosis is a condition in which the blood pH is too high.
Both acidosis and alkalosis can lead to a variety of health problems.
Effect of Osmosis on Homeostasis
Osmosis plays an important role in homeostasis by helping to regulate the amount of water in the body.
If the body loses too much water, the cells can shrink and become damaged. If the body gains too much water, the cells can swell and burst.
The body maintains osmosis homeostasis through a variety of mechanisms.
For example, the kidneys help to regulate the amount of salt in the blood. Salt helps to draw water into the body, so if there is too much salt in the blood, the kidneys will excrete more salt to help lower the water level.
The gastrointestinal tract also plays a role in osmosis homeostasis. When we eat food, the water in the food is absorbed into the bloodstream.
The amount of water that is absorbed depends on the osmolality of the food. Osmolality is a measure of the concentration of dissolved particles in a solution. The higher the osmolality of a solution, the more water it will draw into itself.
When we drink fluids, the water is also absorbed into the bloodstream. The amount of water that is absorbed depends on the osmolality of the fluid.
If we drink a hypotonic fluid, which is a fluid that has a lower osmolality than the blood, water will move from the fluid into the blood.
This can lead to water intoxication, which is a condition in which the body has too much water.
If we drink a hypertonic fluid, which is a fluid that has a higher osmolality than the blood, water will move from the blood into the fluid.
This can lead to dehydration, which is a condition in which the body has too little water.



Leave a Reply