How Does the Respiratory System Maintain Homeostasis?
The respiratory system helps to maintain homeostasis by controlling the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, regulating the pH of the blood, and adjusting the breathing rate to meet the body’s energetic demands.
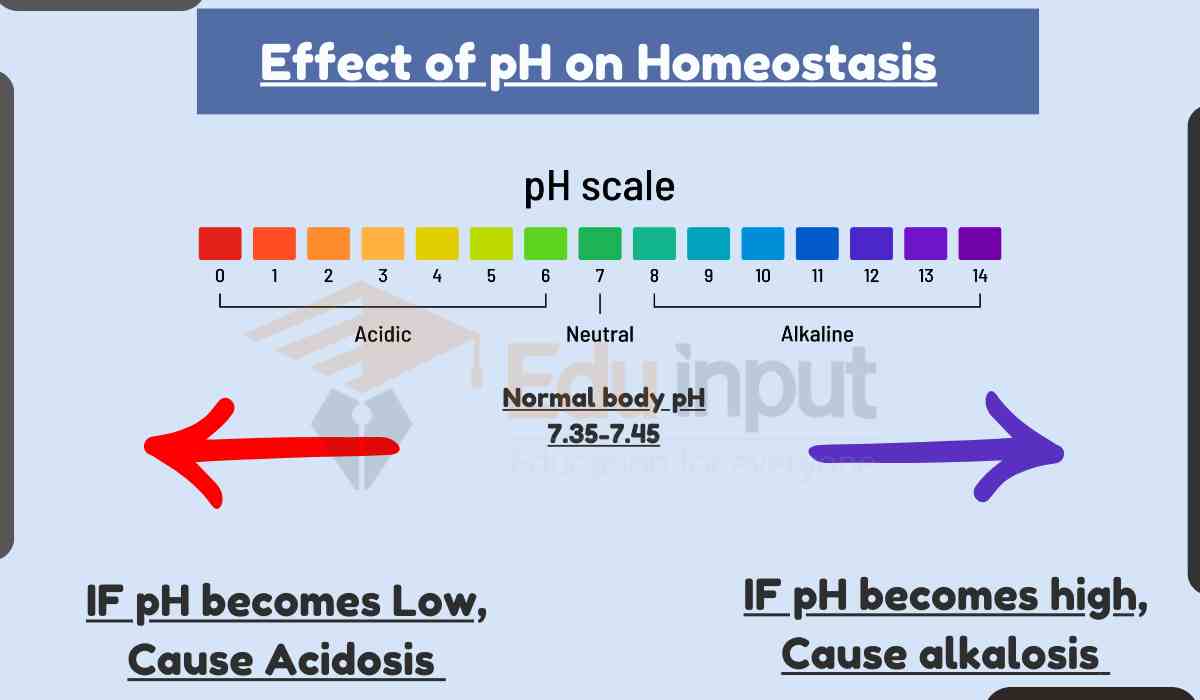
Also learn about How Homeostasis Is Affected By pH And Osmosis?, and How Homeostasis Relates To Both Healthy Body Functions And Disorders?
How Does the Respiratory System Maintain Homeostasis in body?
The respiratory system maintains homeostasis in the body in the following ways:
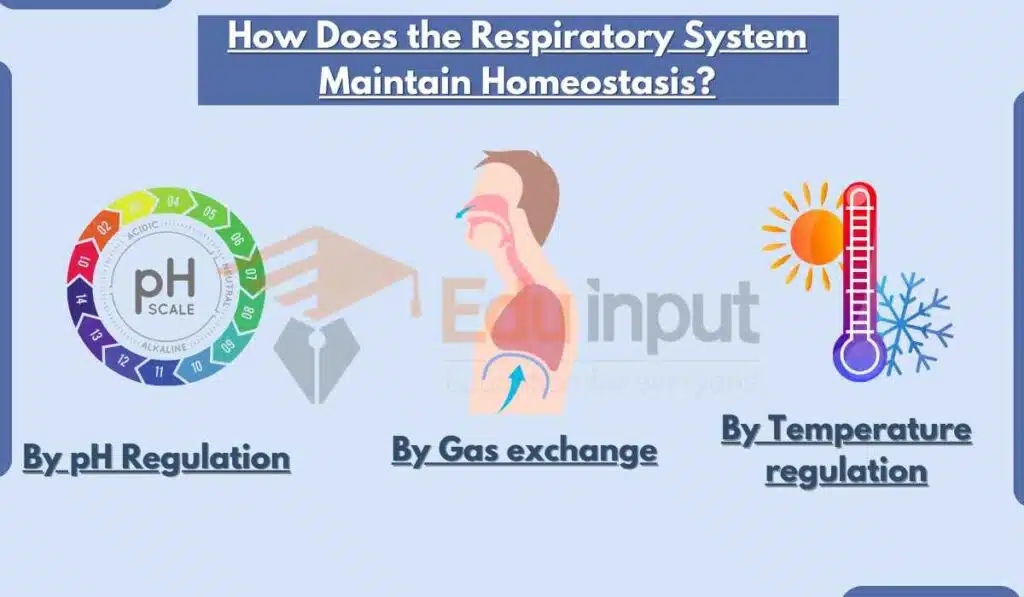
1: Gas exchange
The respiratory system allows oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to leave the bloodstream. This is essential for maintaining the proper levels of these gases in the blood and tissues.
2. pH regulation
The respiratory system helps to regulate the pH of the blood by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Carbon dioxide is an acidic gas, so when levels of carbon dioxide increase, the blood becomes more acidic.
The respiratory system can respond to this by increasing the rate and depth of breathing, which helps to remove carbon dioxide from the blood and restore the blood pH to normal.
3. Temperature regulation
The respiratory system also helps to regulate body temperature. When the body is too hot, the respiratory system can increase the rate and depth of breathing to help cool the body down.
When the body is too cold, the respiratory system can decrease the rate and depth of breathing to help conserve heat.
Examples of How the Respiratory System Maintains Homeostasis
Here are a few examples of how the respiratory system maintains homeostasis in response to specific changes in the body:
1. When you exercise
When you exercise, your muscles need more oxygen to produce energy. The respiratory system responds to this by increasing the rate and depth of breathing, which brings more oxygen into the bloodstream.
2. When you’re at high altitude
At high altitudes, the air is thinner and contains less oxygen. The respiratory system responds to this by increasing the rate and depth of breathing, as well as by increasing the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen.
3. When you have a lung infection
When you have a lung infection, the airways can become inflamed and narrowed. This makes it more difficult for air to flow into and out of the lungs.
The respiratory system responds to this by increasing the rate and depth of breathing, which helps to overcome the resistance in the airways.



Leave a Reply