Bohrium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Bohrium, represented by the symbol ‘Bh’ and having the atomic number 107, is a highly intriguing chemical element. This article highlights its essential properties, historical context, and potential applications.
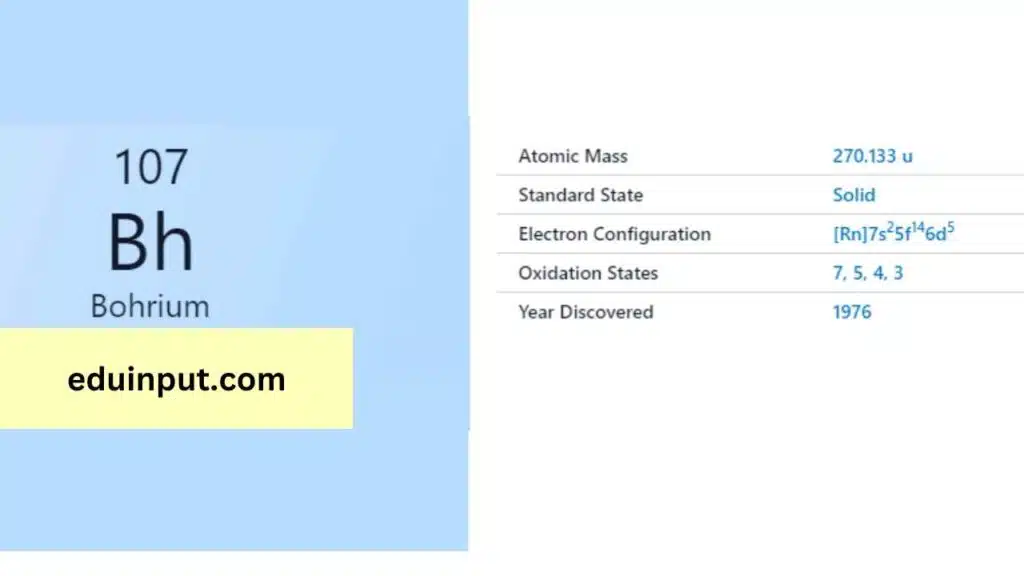
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Bohrium |
| Symbol | Bh |
| Atomic number | 107 |
| Period in the periodic table | 7 |
| Group in the periodic table | 7 (Transition metal) |
| Block in the periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.32.13.2 |
Discovery
Bohrium was first synthesized in 1976 by a team of scientists at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Dubna, Russia. This achievement marked a significant milestone in the creation of superheavy elements.
Physical Properties
As a synthetic element, bohrium’s physical properties are not as well-defined as naturally occurring elements. It is a radioactive element, and its stability and behavior are primarily observed in controlled laboratory conditions.
Chemical Properties
Due to its radioactivity and synthetic nature, the chemical properties of bohrium are not been extensively studied. However, it is classified as a transition metal, which typically means it could exhibit a wide range of oxidation states.
Facts
- Bohrium is named after the Danish physicist Niels Bohr, who significantly contributed to our understanding of atomic structure.
- Its most stable isotope is Bh-270, which has a half-life of approximately 22 milliseconds.
- Given its fleeting existence, bohrium currently has no practical applications.
Applications
Currently, bohrium has no known practical applications outside of scientific research. Its production is challenging and highly resource-intensive, limiting its use to the field of nuclear and particle physics. Scientists study bohrium to further our understanding of the behavior of superheavy elements and their role in the universe.







Leave a Reply