Difference Between Marginal and Parietal Placentation
December 23, 2023
Table of Contents
Key Difference
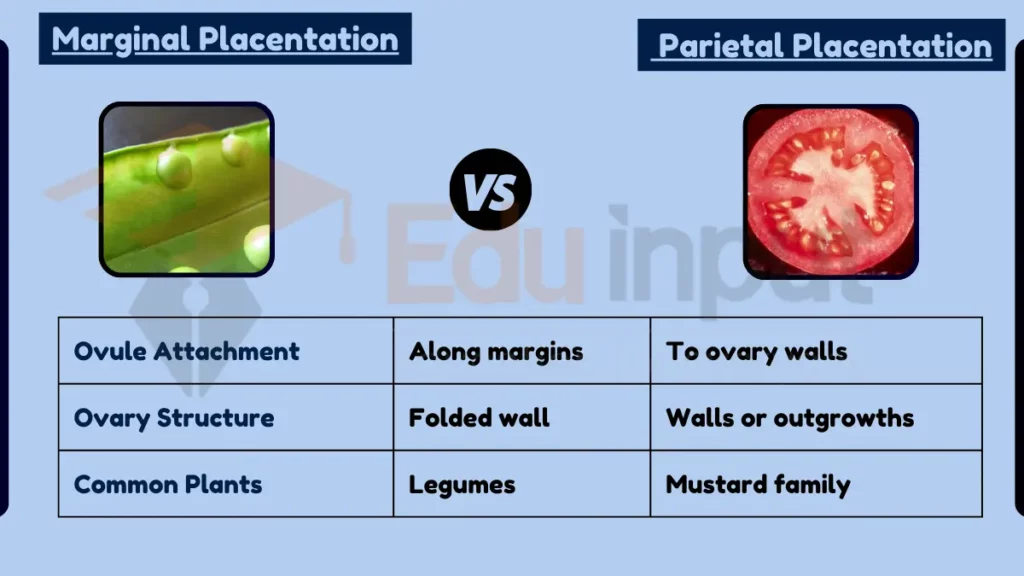
Marginal and parietal placentation are two types of placentation found in plants, differing in the arrangement of ovules within the ovary. Marginal placentation involves ovules attached to the margins of a folded ovary wall, forming a single line. In contrast, parietal placentation features ovules attached to the ovary walls or to outgrowths of the ovary walls, not on a central axis or column.
Comparative Analysis
- Ovule Attachment:
- Marginal Placentation: Ovules attached along the margins of the ovary.
- Parietal Placentation: Ovules attached to the ovary walls.
- Ovary Structure:
- Marginal Placentation: Folded ovary wall.
- Parietal Placentation: Ovary walls or outgrowths from them.
- Common in Plants:
- Marginal Placentation: Common in legumes.
- Parietal Placentation: Seen in mustard and its relatives.
- Seed Arrangement:
- Marginal Placentation: Seeds in a single line.
- Parietal Placentation: Seeds along the ovary walls.
- Developmental Process:
- Both involve the development of ovules, but their positioning in the ovary differs.
Table Summary
| Feature | Marginal Placentation | Parietal Placentation |
|---|---|---|
| Ovule Attachment | Along margins | To ovary walls |
| Ovary Structure | Folded wall | Walls or outgrowths |
| Common Plants | Legumes | Mustard family |
| Seed Arrangement | Single line | Along walls |
| Development | Ovule development | Ovule position variance |
Marginal and parietal placentation differ in the positioning and attachment of ovules within the ovary, influencing the seed arrangement and overall reproductive structure of the plants.
File Under:



Leave a Reply