What Does Sigma (σ) Mean in Different Fields?
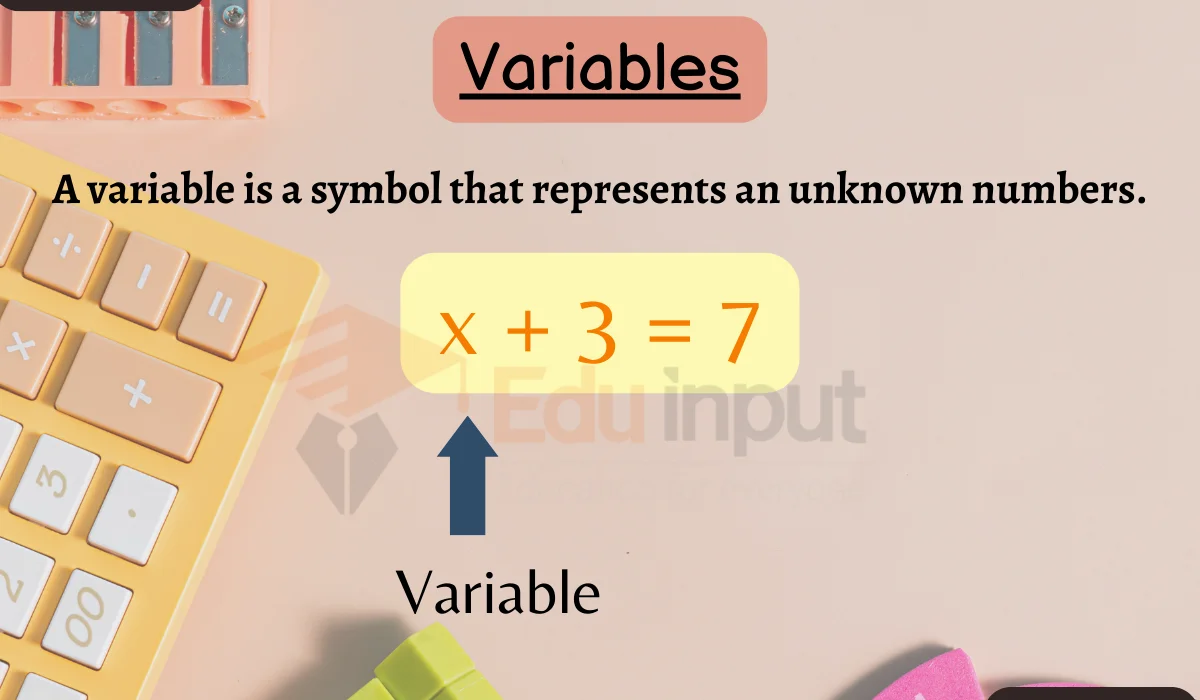
Sigma (σ) is the most commonly used mathematical constant, and it is also called the standard deviation. Sigma is used as a measure of variability and can be used to describe the degree of dispersion or variation of a data set. The term also is used to describe the variability of a sample population.
The use of the Sigma sign in mathematics started with the Greek mathematician, Archimedes. He used the Greek letter Sigma as a symbol to represent the summation symbol in his calculations. Sigma (σ) is widely used in statistical theory and is very important to understand.
What is Sigma(σ)?
σ= standard deviation,
σ is the number that gives the average deviation of the given value from the mean.
This symbol is also used in statistics to represent the variance of the underlying distribution of the data. It can describe as Σd(x-μ).
Used for Symbols of Sigma in different fields
Sigma Symbols are used in many fields.
1. Astronomy
σ = the distance between a planet and the sun
2. Chemistry
σ = the standard deviation of atomic mass
3. Physics
σ = the standard deviation of energy of an electron
4. Biology
σ = the standard deviation of a gene
5. Statistics
σ = the standard deviation of a random variable
6. Mathematics
σ = the standard deviation of a function
7. Economics
σ = the standard deviation of the income of the individuals in a population
8. Engineering
σ = the standard deviation of a product
9. Geography
σ = the standard deviation of elevation
10. Geology
σ = the standard deviation of a geologic time scale
11. Ecology
σ = the standard deviation of a species
12. Geophysics
σ = the standard deviation of an earthquake
13. Meteorology
σ = the standard deviation of temperature
14. Psychology
σ = the standard deviation of a personality trait
15. Sociology
σ = the standard deviation of a social status
16. Law
σ = the standard deviation of a probability
17. Economics
σ = the standard deviation of a stock price
18. Finance
σ = the standard deviation of a financial return
19. Business
σ = the standard deviation of a firm’s profit margin
20. Education
σ = the standard deviation of student performance
21. History
σ = the standard deviation of a culture’s material production
22. Political science
σ = the standard deviation of a political party’s support
23. Physics
σ = the standard deviation of an electron’s velocity
24. Astronomy
σ = the distance from a planet to its host star
25. Chemistry
σ = the standard deviation of an element’s atomic mass
26. Geology
σ = the standard deviation of a geologic time scale
27. Biology
σ = the standard deviation of a gene
28. Physics
σ = the standard deviation of a particle’s energy
29. Economics
σ = the standard deviation of a stock price
What is Sigma in math?
In the world of mathematics, the symbol is used to signify different math processes involving deviations and summation. Discover the concept and definition of sigma and the purposes of the lower case and upper case sigma.
In mathematics, the lower case sigma stands for standard deviation. The upper case sigma is used for the summation notation. Each has its own unique formula, and yes, both the lower case and upper case look vastly different from each other. But they are both the Greek equivalent of it. If you note this the two formulas upper case and lower case that uses these two symbols both start with the letters.
- Σ= upper case sigma is used for the summation notation
- (σ) the lower case sigma stands for standard deviation
What is Upper Case Sigma?
The upper case sigma is used in the summation notation. This particular notation is also called sigma notation.
For example:
1+2+3+4+……+20= Σ20n=1(n)
12+22+32+……+502= Σ50n=1(n2)
What is lower case sigma stands for standard deviation?
The lower case sigma stands for standard deviation .it is denoted by (σ).
σ= standard deviation,
σ is the number that gives the average deviation of the given value from the mean




Leave a Reply