Introduction to Cell Signaling (Cellular Signaling)
Cell signaling is an important aspect of biology that allows cells to communicate with each other and their surroundings. Cell signaling is used by all types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, to coordinate their activities and maintain their functions.
Cellular signaling refers to the communication between cells within our body. This happens through chemical messengers called hormones or neurotransmitters. These chemicals travel from cell to cell via a network of channels called receptors.
Cellular signaling plays a key role in regulating metabolism, growth, development, reproduction, and immunity. In other words, it helps control every aspect of life. Learn more about cellular signaling and its role in health and disease.
Extracellular Signals
Extracellular signals are crucial for a cell’s ability to function properly. These signals can come in many different forms, such as physical agents like mechanical pressure or temperature, or chemical signals like small molecules or peptides.
Extracellular signals can be either hydrophobic or hydrophilic, and each type of signal interacts with the cell in a unique way.
Signaling molecules are responsible for relaying messages between cells, and can travel either short or long distances.
Classification Of Cell Signaling
Signaling can be classified as:
- Autocrine
- Juxtacrine
- Intracrine
- Paracrine
- Endocrine
Synthesis Of Signaling Molecules (Chemical Signal)
Signaling molecules are synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways, and can be released through passive or active transport methods. In some cases, signaling molecules can also be released from cell damage.
Role Of Receptors In Cell Signaling
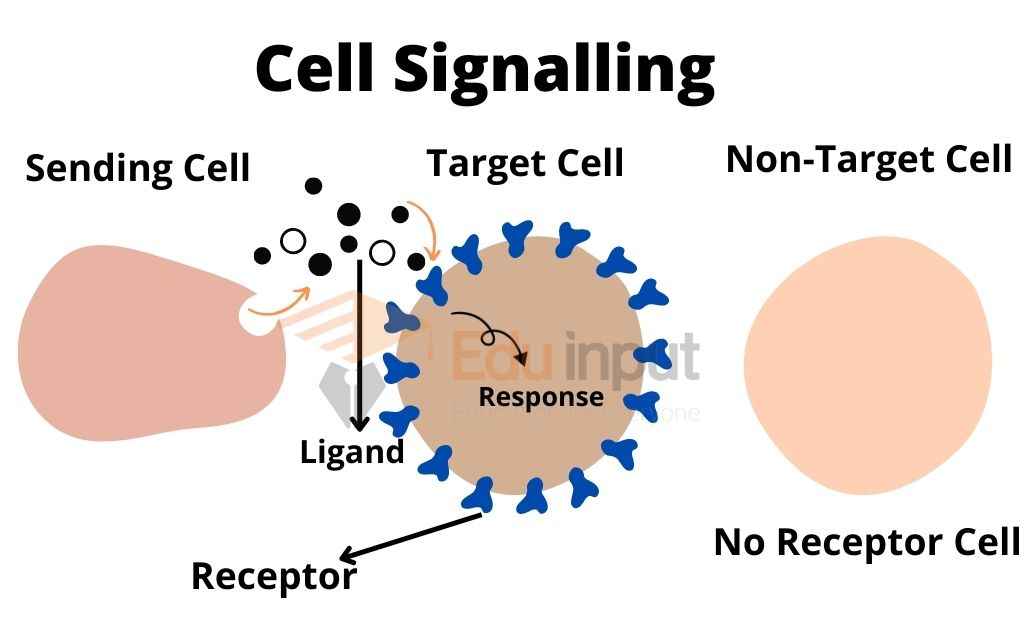
Proteins known as receptors are important for cell signaling. They can be found on the cell surface or within the interior of the cell, and they detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors help to relay information that is essential for the cell to function properly.
Cell surface receptors are important for many cellular processes. They usually bind with extracellular signals (or ligands), which causes a change in the receptor that leads it to initiate an activity, such as opening or closing an ion channel. Some receptors do not have enzymatic or channel-like domains but are instead linked to enzymes or transporters.
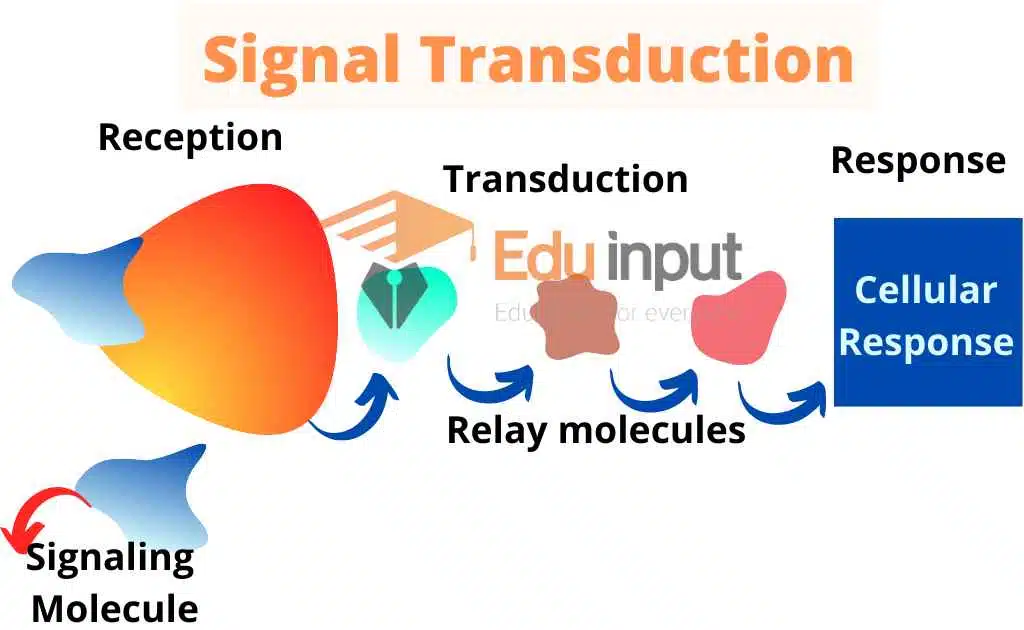
Direct Signaling
- In direct signaling, two cells bind to one another because they have complementary proteins on their surfaces.
- When the proteins bind, this interaction changes the shape of one or both proteins and transmits a signal.
This signaling is especially important in the immune system, where immune cells use cell-surface markers to recognize pathogen-infected cells and the body’s cells.
Importance Of Cell Signaling
Cells are like machines that respond to specific molecules in their environment, and they form the basis of many important functions in the body. If something goes wrong with the signaling interactions between cells, it can lead to problems like cancer, autoimmune diseases, and other disorders.




Leave a Reply