What is Abscisic Acid?-Definition, Structure and Functions
Abscisic acid is a naturally occurring hormone produced by plants. ABA helps regulate many aspects of plant growth and development including seed dormancy, germination, stomatal closure, leaf senescence, fruit ripening, and responses to environmental stresses.
ABA is also involved in regulating the timing of flowering and fruiting in some species of plants. Let’s Learn more about its Discovery, structure and its role in plant biology.
Abscisic Acid (ABA) is an essential plant hormone involved in regulating plant growth and development. While the name suggests involvement in abscission (the shedding of leaves), the role of ABA is much broader.
In addition to being involved in abscission, ABA also acts as a signal molecule in response to environmental stresses such as drought, salinity, cold, heat and nutrient deficiency. ABA is perceived on both the external surface of the cell membrane and within the cell itself.
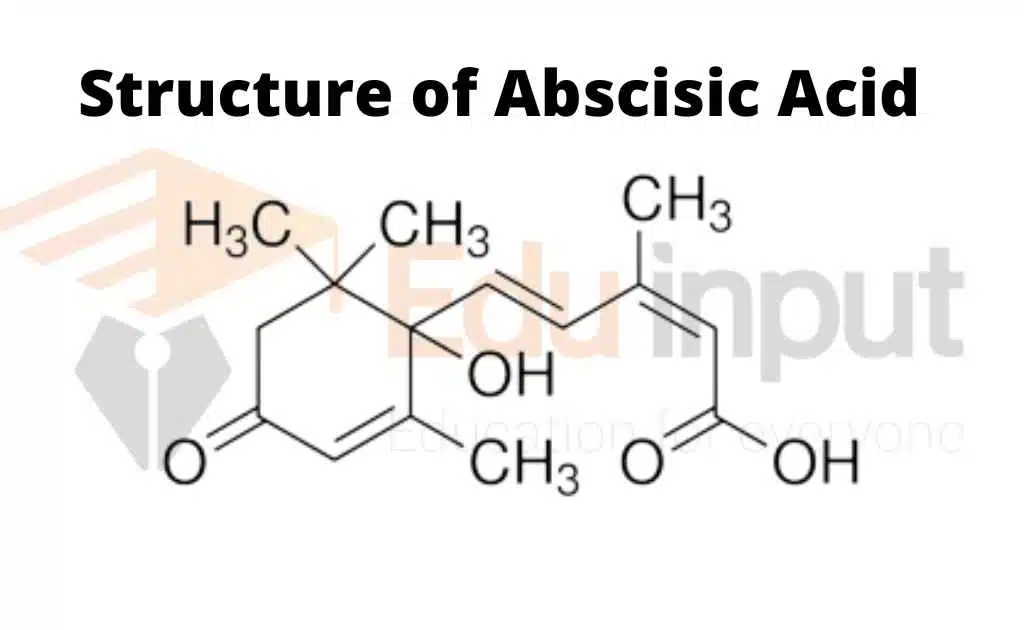
Structure Of Abscisic Acid
Abscisic acid is a plant hormone that is involved in many regulatory functions. Its molecular structure is as follows;
Discovery Of Abscisic Acid
Abscisic Acid (ABA) is a classic plant hormone that was isolated multiple times in various studies. Scientists in the early 1950s identified acidic compounds, referred to as β-inhibiting agents, from plants; they used paper chromatography to separate these compounds and demonstrated that β-inhibiting substances inhibit coleoptile growth in oats.
In early 1960, US researchers isolated an acetic acid compound from young cotton fruit, called “abiscisin II.” Later, UK researchers isolated a substance from sycamore leaves that induced dormancy in seeds, called “drought.”
The chemical structure of Abiscisin II was determined in the mid-1960s and drought was subsequently shown to be identical to Abiscisin II. This compound became known as abscisic acid because of its presumed role in the Abscission of plant parts. Subsequent research revealed that the β-inhibitory agent is also ABA.
Functions Of Abscisic Acid
Abscisic acid is responsible for
- Dormancy of seeds
- Inhibition of seeds
- Stimulates the closure of stomates
- Inhibits shoot growth
- Induces the storage of proteins
- Regulates the balance between intrinsic growth (cell division) and environmental responses (such as leaf expansion).
Abscisic Acid In Humans
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone that helps plants respond to drought stress. Can it also help humans?
The human body produces abscisic acid naturally, but it only occurs at very low levels. In recent years, scientists have discovered that ABA has a wide range of health benefits for humans. It can help reduce inflammation, improve memory, boost energy, and even fight cancer.
ABA is a natural compound found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, beans, and grains. It’s also present in some supplements. However, it’s important to note that ABA isn’t regulated or approved by the FDA. While research shows its potential, more studies are needed before it can be considered safe and effective.




Leave a Reply