Peripheral Nervous System-Definition, Composition and Types
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a type of nervous system that consists of nerves outside of the central nervous system (CNS). These nerves include cranial nerves, spinal nerves, sympathetic nerves, parasympathetic nerves, and sensory nerves.
The PNS is responsible for regulating involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure. It also controls voluntary muscle movement, sensation, and emotions.
Composition Of Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system is composed of sensory neurons and motor neurons. These nerves form ganglia and nerves.
Ganglia: The concentrations of cell bodies of neurons are called ganglia.
Nerves: The bundles of axons or dendrites bounded by connective tissues are called nerves. They may be sensory-motor or mixed nerves depending upon the direction of impulse they conduct.
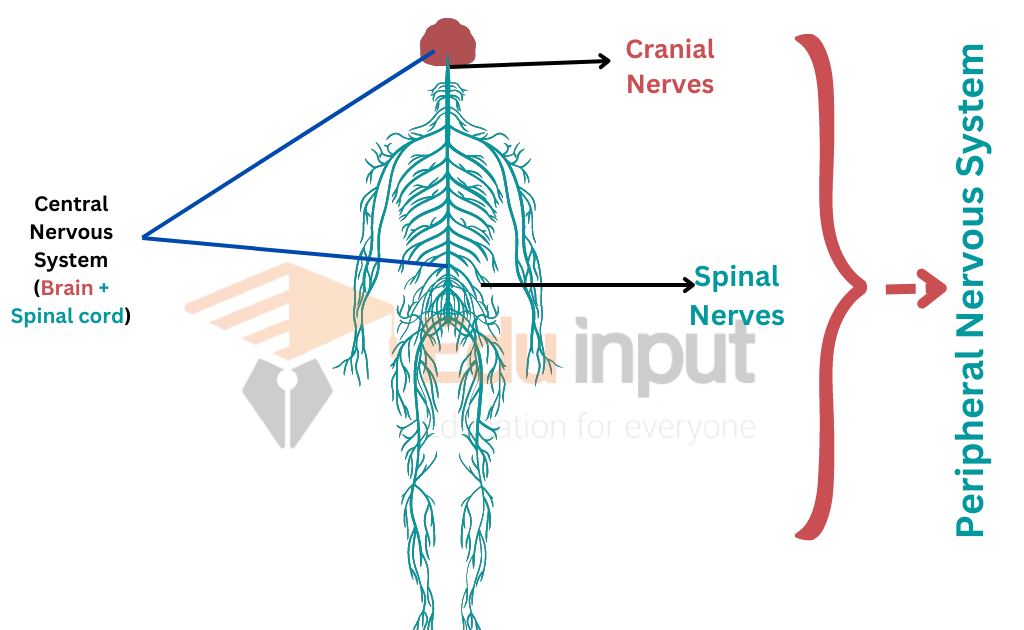
Types of Nerves
There are two groups of nerves in humans:
Cerebral or cranial nerves: The nerves which arise from the brain, or lead to the brain are called cerebral or cranial nerves. There are 12 pairs of cerebral nerves. Some of these nerves are sensory, some motor, and some are mixed.
Spinal nerves: 31 pairs of spinal nerves arise or lead to the spinal cord. All these nerves are mixed. They have fibers of both sensory and motor neurons.
Types Of Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists of sensory neurons, motor neurons, sympathetic neurons, parasympathetic neurons, enteric neurons, and other types of neurons. The central nervous system (CNS), on the other hand, is composed of the brain and spinal cord, which control voluntary movement and sensation.
There are two types of Peripheral nervous system:
Somatic Nervous System
Motor neurons that control voluntary movements form the somatic nervous system. The voluntary movements are under the conscious control of the body. Voluntary movements are caused by skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
Motor neurons that control involuntary responses form the autonomic nervous system. These motor neurons influence the organs, glands, and smooth muscles. The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. These systems function automatically. These systems innervate (connect) all internal organs.
They use two neurons and one ganglion for each impulse.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The system which is stimulated during emergencies or fear is called the sympathetic system. Most nerves of the sympathetic system arise from the middle portion of the spinal cord. These nerves terminate in the ganglia. These ganglia lie near the spinal cord.
This system is important during emergencies. It is associated with fight or flight. The system increases the heartbeat, dilates the branches of blood vessels, and inhibits the function of the digestive tract.
Parasympathetic system
The system which promotes a relaxed state is called the parasympathetic system. It is composed of a few cranial nerves including the vaga (supply heart) nerve and fibers from the bottom portion of the spinal cord. It promotes a relaxed state. It contracts the pupils, promotes digestion of food, and retards the heartbeat.
Functions of Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system performs following functions:
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a network of nerves that connects the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
- The PNS carries information to and from the brain, and it also controls vital processes like heartbeat and breathing. Most of the muscles in the body are controlled by the PNS, which means that it plays a key role in the movement.
- The PNS is made up of nerves that send signals between the CNS and the parts of the body that are not part of the CNS.
Related FAQs
What is Peripheral Nervous System?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a type of nervous system that consists of nerves outside of the central nervous system (CNS). These nerves include cranial nerves, spinal nerves, sympathetic nerves, parasympathetic nerves, and sensory nerves.
What are the types of Peripheral Nervous System?
There are two types of Peripheral nervous system:
Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
What are the functions of Peripheral nervous system?
The PNS is responsible for regulating involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure. It also controls voluntary muscle movement, sensation, and emotions.
What is the difference between CNS and PNS?
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves that come out from the brain and spinal cord.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply