Evolution of the Leaf- Shape, Texture, and Veination
Early vascular land plants did not have true leaves or roots. These plants had small sizes. They had dichotomously branched erect smooth aerial branches. They have subterranean rhizomes. The rhizome is used for anchoring and absorption. Later, the evolution of the leaf took place.
Evolution of the Leaf
Plants evolved their leaves 350 million years ago. There were two stages of evolution;
- Evolution of Microphyll
- Evolution of Megaphyll
Evolution of Microphyll (small leaf)
A small sized leaf with a single undivided vein (vascular supply) is called microphylls. For example leaves of Lycopods (Lycopodium) .
1. Rhynia was a primitive vascular plant. It had a naked stem without leaves.
2. Such plants started forming leaves as small outgrowths. These outgrowths were not supplied with vascular bundles. Therefore, they were not regarded as true leaves.
3. Lycopods were the first plants that formed true leaves and roots.
Evolution of megaphyll (large leaves)
Large leaves with divided veins and veinlets and with expanded leaf blades or lamina are called megaphylls. Such leaves are characteristics of ferns and seed plants.
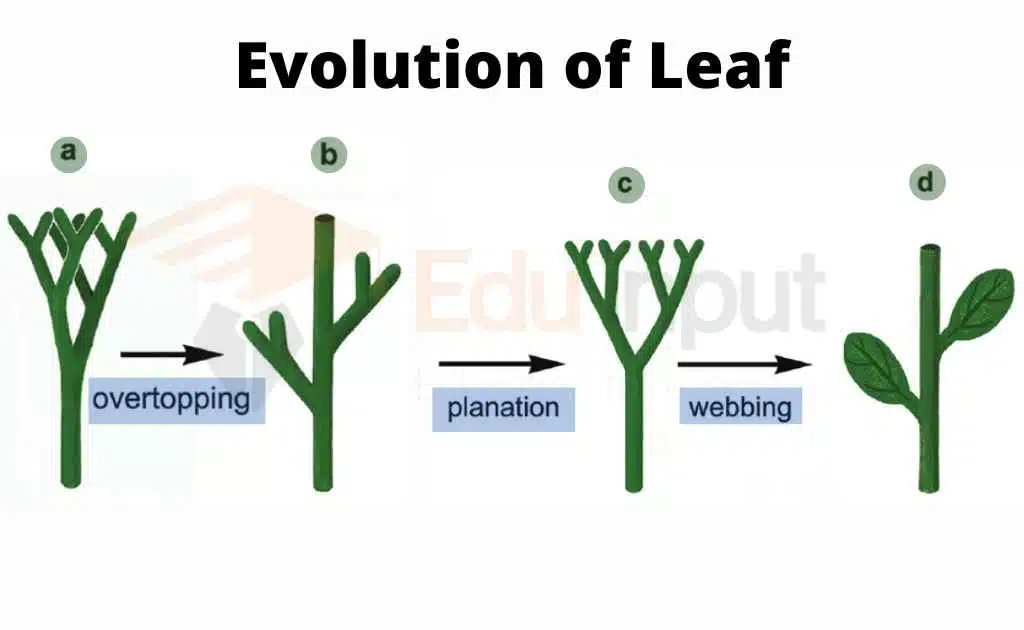
The evolution of megaphylls started from a dichotomous branching system. This evolution took place in some primitive fern like plants approximately 350 million years ago. The process of evolution was very slow and gradual. It was completed in more than 15-20 million years. The evolution of megaphylls took place in the following steps:
1. Overtopping
The unequal development of various branches is called overtopping.
a) There were some unequal branches on the dichotomously branched aerial portion.
b) Some branches remained short. But other branches grew and expanded at a much faster pace. All these branches grew in different planes.
2. Plantation
The arrangement of dichotomous branches in one plane is called planation. It was the second step in the evolution of megaphylis.
3. Fusion or Webbing
The filling of space between dichotomous branches by a sheet of parenchyma cells is called fusion or webbing. Parenchyma connected these branches and formed a flat lamina or leaf blade. This structure has many dichotomously branched veins. After some time, vascular strands fused. They form a net or reticulate venation pattern.
Leaf Shape
Leaf shape is determined by the angle at which the leaf blade is attached to the stem. Leaves are classified as simple (flat) or compound (folded). Simple leaves have parallel veins running down their length. Compound leaves have cross-veins that run perpendicular to the length of the leaf. There are three basic types of compound leaves: palmately lobed, pinnately lobed, and ternately lobed.
Leaf Texture
The texture of a leaf refers to its surface. Leaves can be smooth or rough. Smooth leaves are those that have no bumps or ridges on them. Rough leaves have small bumps or ridges on their surfaces. Smooth leaves are often shiny. Rough leaves are often dull.
Leaf Vein Structure
Vein structure refers to the pattern of veins on the leaf. There are four basic vein structures: reticulate, palmate, cordate, and suborbicular. Reticulate leaves have many small veins radiating out from the center of the leaf.
Palmate leaves have larger veins radiating out from a central point. Cordate leaves have a heart-shaped appearance. Suborbicular leaves have a circular arrangement of veins around the edge of the leaf.
Leaf Margin
A leaf margin is the edge of the leaf where the leaf meets the stem. There are three types of margins: entire, serrated, and dentate. The entire leaves do not have any teeth along the edges. Serrated leaves have teeth along the edges. Dentate leaves have teeth along both sides of the leaf.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
From where do plant leaves originate?
Leaves of plants originate from the shoot apex.
What is Leaf?
The leaf is a plant organ, which originates from shoots. It helps in photosynthesis, and sometimes stores the waste material of plants.
Is a leaf an organ?
The leaf is the most important organ of the plant body, as it absorbs light, which is then used in photosynthesis.
How have plant leaves evolved?
Leaves firstly evolved Microphyll and then Megaphyll, which is the modern plant leaves.




Leave a Reply