Aluminum-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Aluminum is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. It is the most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust and the third most abundant element after oxygen and silicon. It is a reactive metal and has a silvery-white appearance.
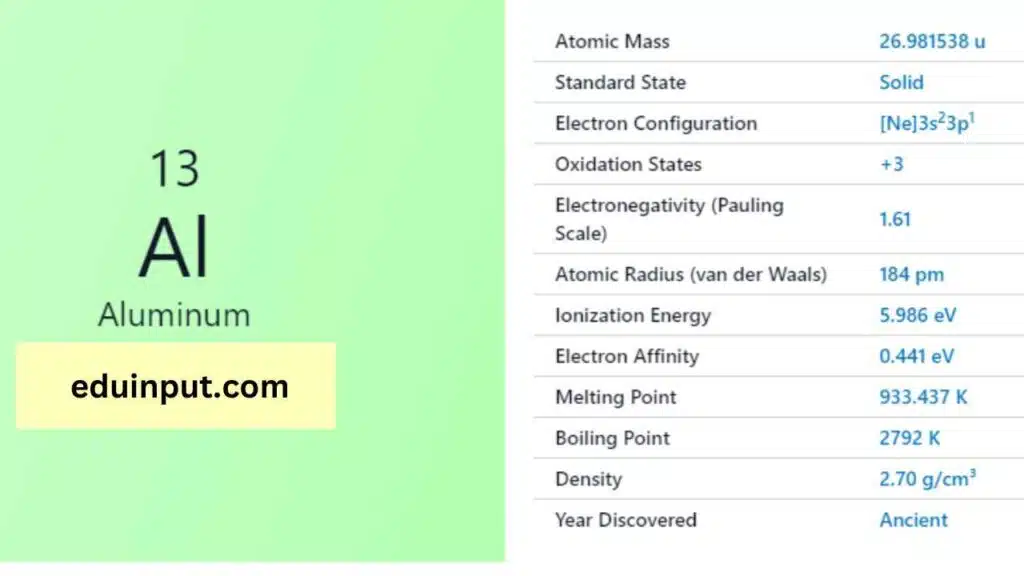
| Property | Value |
| Name | Aluminium |
| Symbol | Al |
| Atomic number | 13 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Group in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | 13 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Block in the periodic table | 3 |
| Block in periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.3 |
| CAS Registry | 7429-90-5 |
Discovery
Aluminum was first discovered by Danish physicist and chemist Hans Christian Ørsted in 1825. However, the first isolation of aluminum was done by German chemist Friedrich Wöhler in 1827 using a process involving the reduction of aluminum chloride with potassium.
Physical Properties
Aluminum has a density of 2.7 g/cm³ and a melting point of 660.32°C. It is a good conductor of heat and electricity and has a low density, making it useful for a variety of applications.
Chemical Properties
Aluminum is a reactive metal and forms a thin layer of oxide on its surface when exposed to air, which protects the metal from further corrosion. It reacts with acids to release hydrogen gas and can also react with bases to form aluminate.
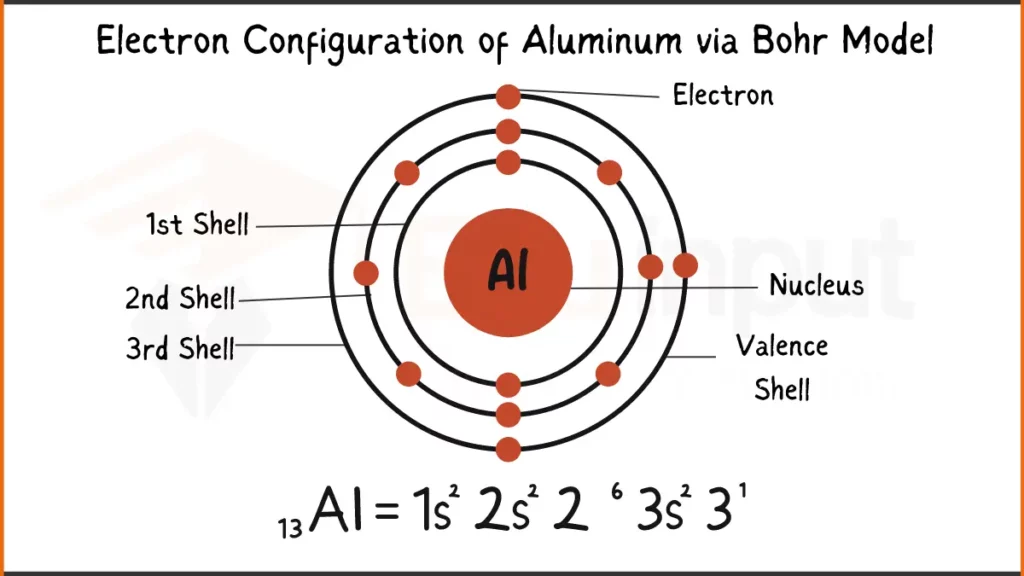
Electron Configuration of Aluminum
Aluminum (Al) packs 13 electrons. Its configuration is either 1s²2s²2p⁶3s² showing subshell filling or [Ne]3s².
Electron Configuration of Aluminum Via Bohr Model
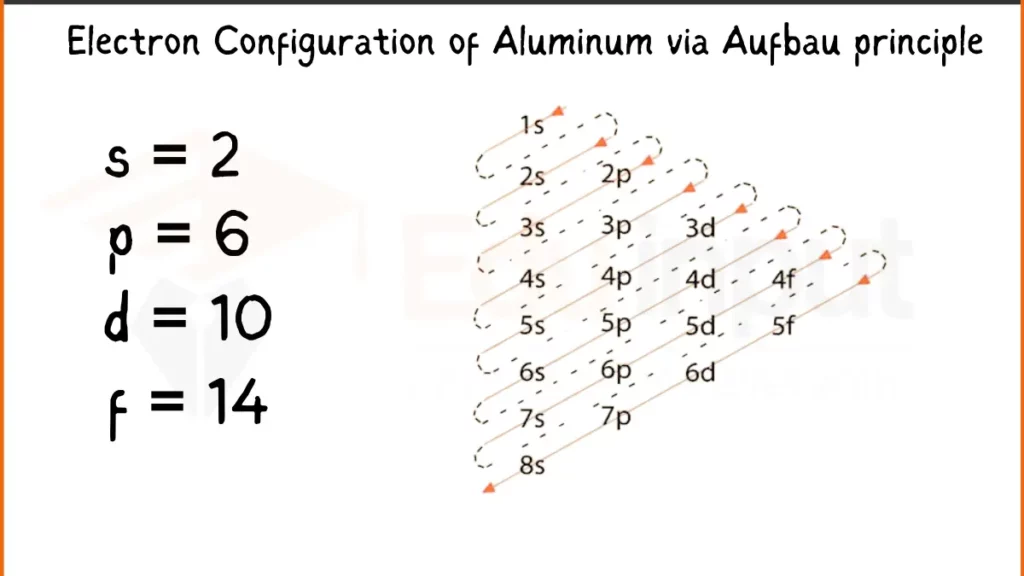
Electron Configuration of Aluminum Via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Aluminum is the third most abundant element on Earth.
- It is the most widely used non-ferrous metal.
- It is a good reflector of both visible light and heat.
Applications
Aluminum is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Construction: due to its low density and high strength-to-weight ratio, aluminum is used in the construction of airplanes, cars, buildings, and bridges.
- Packaging: aluminum is used in packaging for food and beverages due to its ability to keep food fresh and its recyclability.
- Electrical conductivity: aluminum is a good conductor of electricity and is used in wiring, power lines, and electrical components.
- Reflectivity: aluminum’s reflective properties make it useful in mirrors, reflective coatings, and solar panels.






Leave a Reply