Antimony-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
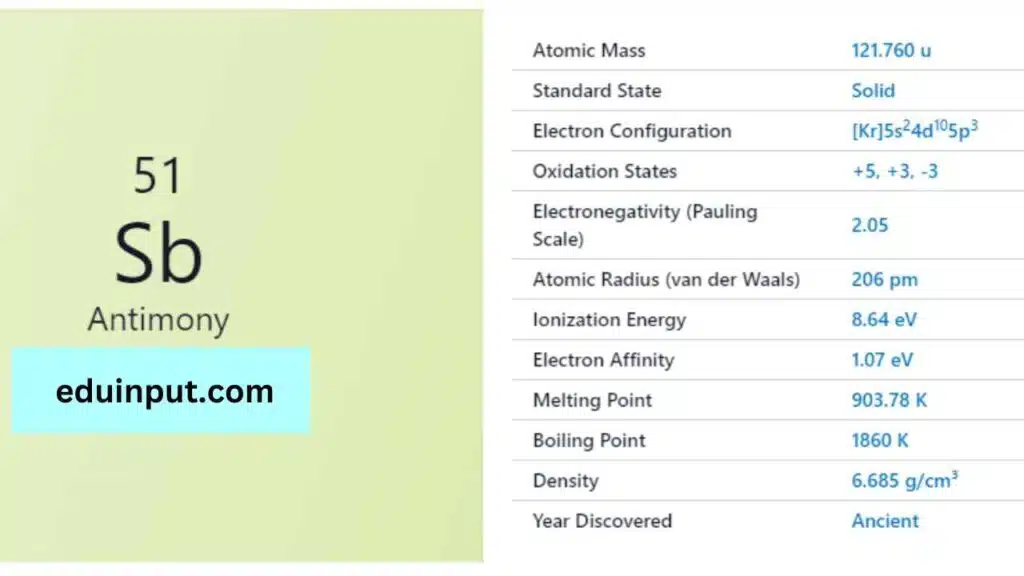
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol “Sb” and atomic number 51. It is a lustrous gray metalloid with a metallic appearance. Antimony is a relatively rare element, making up about 0.2 parts per million of the Earth’s crust.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Antimony |
| Symbol | Sb |
| Atomic number | 51 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Group in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery lustrous grey |
| Classification | Semi-metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | 15 |
| Group name | Pnictogen |
| Block in the periodic table | 5 |
| Block in periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.18.5 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-36-0 |
Discovery
Antimony has been known since ancient times. The first recorded use of antimony was in ancient Egypt, where it was used in cosmetics. The element was first isolated in the 16th century by the German chemist Andreas Libavius.
Physical Properties
Antimony is a brittle, silvery-white metalloid that has a crystalline structure. It has a melting point of 630.63 Kelvin and a boiling point of 1587 Kelvin. Antimony is a poor conductor of heat and electricity.
Chemical Properties
Antimony is a chemical element in the nitrogen group. It has five valence electrons and is a metalloid. It is not very reactive, but it does react with acids to form antimony salts. Antimony is also known for forming alloys with other metals, such as lead.
Facts
- Antimony has been used in the production of pottery and glassware for thousands of years.
- Antimony is used as a flame retardant in plastics, textiles, and other materials.
- Antimony is a toxic substance that can cause health problems if ingested or inhaled.
Applications
- Antimony is used in the production of flame retardants, alloys, and batteries.
- Antimony is also used as a semiconductor in electronic devices.
- Antimony has medical applications, including the treatment of parasitic infections.




Leave a Reply