Argon-Properties And Applications
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is a noble gas and the third-most abundant gas in Earth’s atmosphere, making up about 0.934% of the atmosphere. It was first isolated in 1894 by Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay.

| Property | Value |
| Name | Argon |
| Symbol | Ar |
| Atomic number | 18 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 39.948 g, r |
| Standard state | Gas at 298 K |
| Appearance | Colourless |
| Classification | Non-metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | 18 |
| Group name | Noble gas |
| Block in the periodic table | 3 |
| Block in periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.8 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-37-1 |
Physical Properties
Argon is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is denser than air. It has a boiling point of −185.848 °C (−302.526 °F) and a melting point of −189.344 °C (−308.852 °F). It is monatomic, which means it exists as single atoms instead of molecules.
Chemical Properties
Argon is a noble gas, which means it is non-reactive and does not easily form compounds with other elements. Its electron configuration makes it highly stable, and it has a full outer shell of electrons. As a result, argon is used in various applications where an inert atmosphere is required, such as welding and metal fabrication.
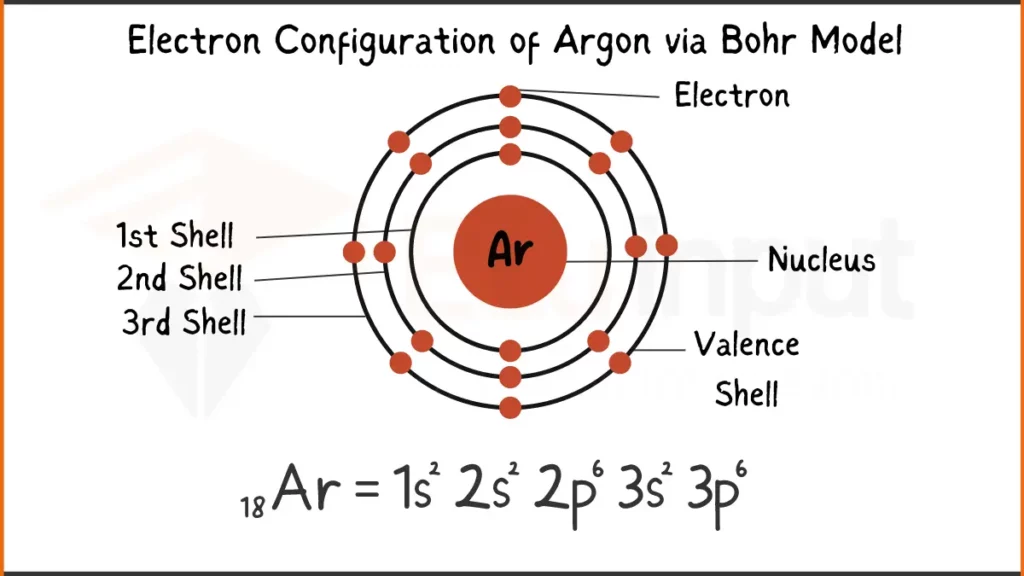
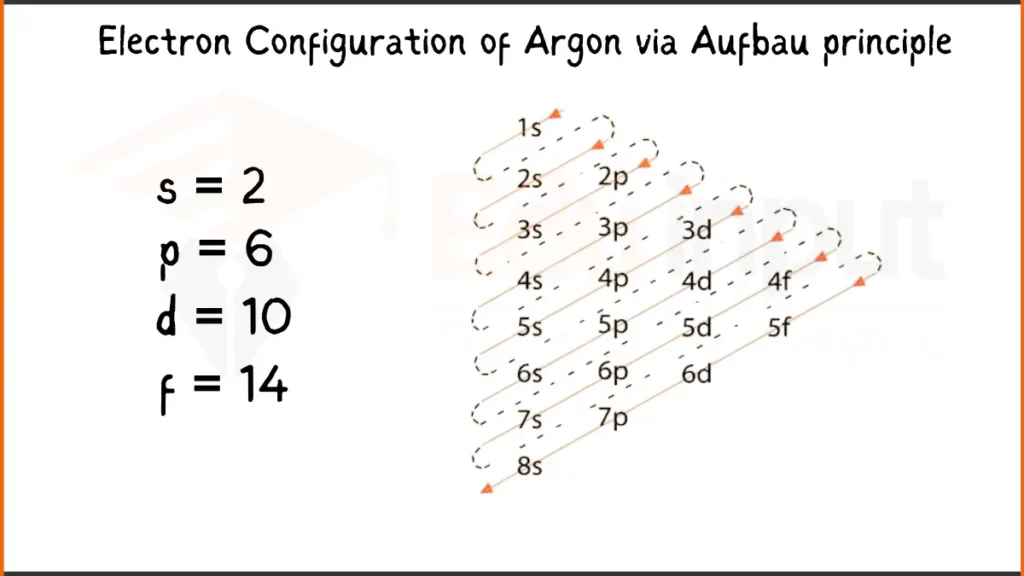
Electron Configuration of Argon
Argon (Ar), a noble gas known for its inertness, has 18 electrons. Its configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁶ showing how electrons fill the subshells.
Electron Configuration of Argon Via Bohr Model
Electron Configuration of Argon Via Aufbau Principle
Facts
Argon is named after the Greek word “argos,” which means “inactive.” It was the first noble gas to be discovered, and it has the symbol Ar on the periodic table. Argon is produced by the decay of potassium-40 in the Earth’s crust, and it is also present in the atmosphere of Mars.
Applications
Argon is used in various applications, including welding and metal fabrication, as an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation and other chemical reactions. It is also used in incandescent light bulbs to prevent the filament from oxidizing and in the production of semiconductors.
In the medical industry, argon is used in cryosurgery and laser eye surgery. Additionally, argon is used in the production of neon signs, as a coolant in gas chromatography, and in gas lasers.







Leave a Reply