Astatine-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Astatine is a highly radioactive element and a member of the halogen family. It has the atomic number 85 and is symbolized by the chemical symbol At.

| Property | Value |
| Name | Astatine |
| Symbol | At |
| Atomic number | 85 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | (longest-lived isotope) |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Metallic |
| Classification | Semi-metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | 17 |
| Group name | Halogen |
| Block in the periodic table | 6 |
| Block in periodic table | p |
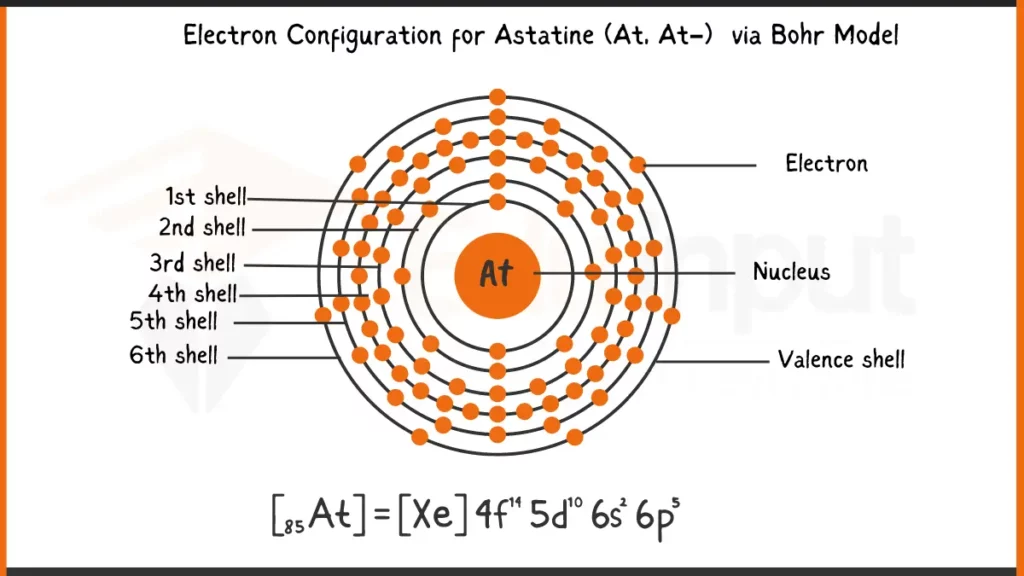
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.18.7 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-68-8 |
Discovery
Astatine was discovered in 1940 by Dale R. Corson, Kenneth Ross MacKenzie, and Emilio G. Segrè at the University of California, Berkeley. They produced the element by bombarding bismuth with alpha particles.
Physical Properties
Astatine is a rare and radioactive element that occurs naturally from the decay of heavier elements. It has no stable isotopes and its half-life ranges from milliseconds to a few hours. Astatine is a dark, crystalline solid that is similar in appearance to iodine.
Chemical Properties
Astatine is a halogen and thus has similar chemical properties to the other halogens, such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. It readily forms compounds with metals and nonmetals, such as astatine monofluoride (AtF), astatine monochloride (AtCl), and astatine oxide (At2O).
Electronic Configuration of Astatine
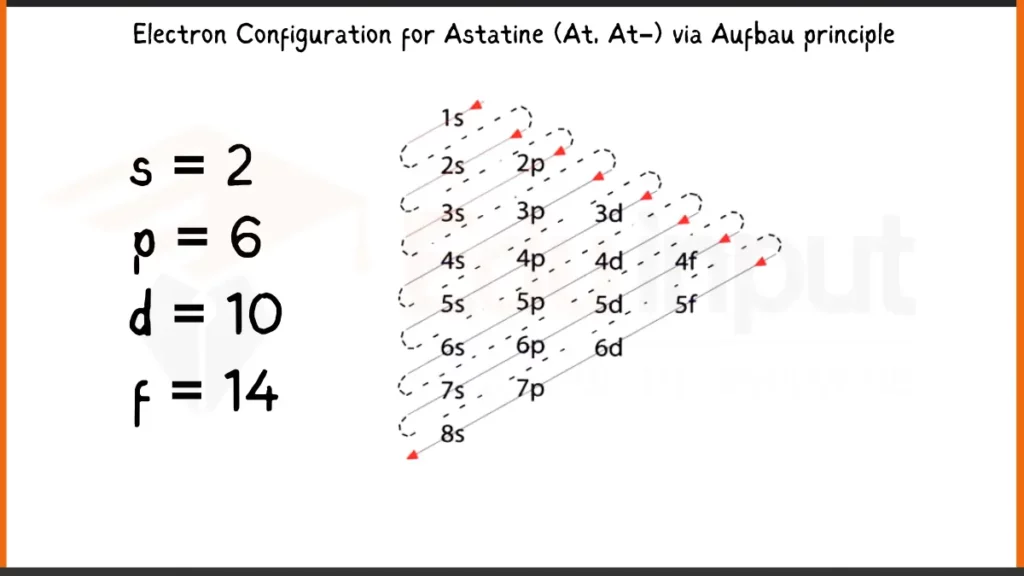
Astatine (At), with 85 electrons, follows the Aufbau principle for filling subshells. Its complete electron configuration is written as: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁶5s²4d¹⁰5p⁵6s². This configuration shows every subshell (1s, 2s, etc.) and the number of electrons residing in each.
Electronic Configuration of Astatine via Bohr Model
Electronic Configuration of Astatine via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Astatine is one of the rarest elements on Earth, with estimated total amounts of less than one gram.
- It is a highly unstable element, and its longest-lived isotope has a half-life of just over eight hours.
- Because of its short half-life and rarity, astatine has no significant commercial applications.
Applications
Astatine has no practical uses due to its rarity and radioactivity. However, researchers are studying its potential use in targeted alpha-particle therapy for cancer treatment. Astatine-211 has been used in preclinical and clinical trials to destroy cancer cells. Additionally, it is used as a tracer in biomedical research to study the behavior of cells and molecules.







Leave a Reply