Common Pronoun Errors With Examples
Common pronoun errors often involve issues such as incorrect pronoun case, or misuse. These errors can lead to confusion in understanding the intended meaning of a sentence.
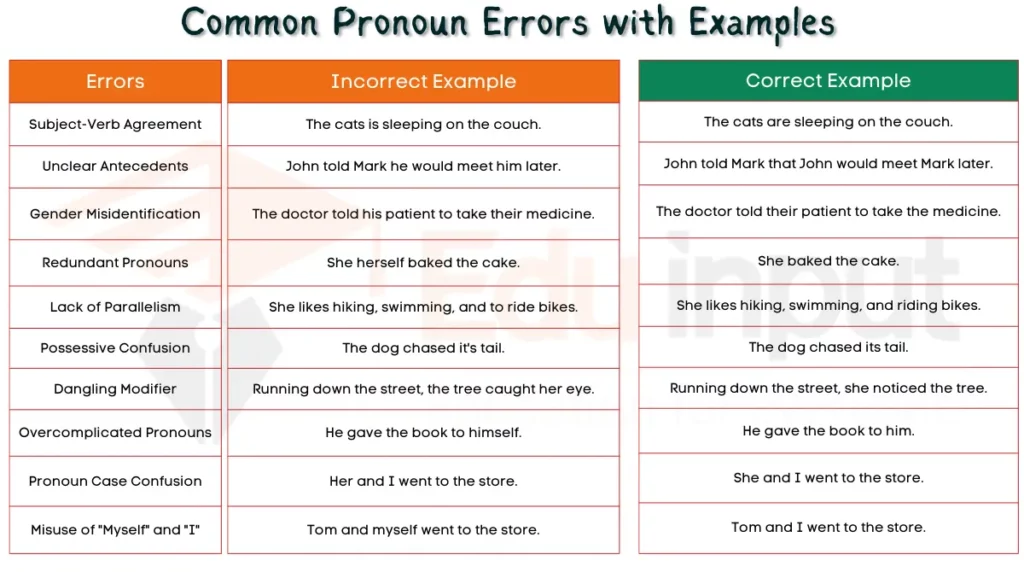
Common Pronoun Errors
Here are some common pronoun errors with examples:
1. Subject-Verb Agreement
Pronouns must agree with their antecedent in number (singular or plural). Use a singular pronoun with a singular antecedent and a plural pronoun with a plural antecedent.
Example 1
- Incorrect: The team is working on a new project. He is very excited about it.
- Correct: The team is working on a new project. It is very excited about it.
Example 2
- Incorrect: The children are playing outside. They needs to come in now.
- Correct: The children are playing outside. They need to come in now.
2. Pronoun Case Confusion
Pronouns have different forms for different grammatical cases (subject, object, possessive). Use the correct case based on the pronoun’s role in the sentence.
Example 1
- Incorrect: The teacher gave the book to her and I.
- Correct: The teacher gave the book to her and me.
Example 2
- Incorrect: Me and Sarah went to the movies.
- Correct: Sarah and I went to the movies.
3. Unclear Antecedents
Pronouns should refer clearly to their antecedents. Ensure the pronoun’s meaning is unambiguous by placing it close to its antecedent or using a specific noun or noun phrase.
Example 1
- Incorrect: The dog chased the cat, and it ran up the tree.
- Correct: The dog chased the cat, and the cat ran up the tree.
Example 2
- Incorrect: John talked to his friend about his new job.
- Correct: John talked to his friend David about David’s new job.
4. Gender Misidentification
Using incorrect pronouns based on someone’s assumed gender. Use the pronouns someone identifies with, or gender-neutral options like “they” or “their” if unsure.
Example 1
- Incorrect: The doctor asked the patient his symptoms.
- Correct: The doctor asked the patient their symptoms.
Example 2
- Incorrect: The teacher told the student he did a good job.
- Correct: The teacher told the student they did a good job.
5. Redundant Pronouns
Using pronouns unnecessarily when the noun or subject is already clear. Avoid unnecessary pronouns that repeat the meaning of the subject or noun.
Example 1
- Incorrect: I gave the book to myself.
- Correct: I gave the book to me.
Example 2
- Incorrect: Sarah and her went to the store.
- Correct: Sarah went to the store.
6. Vague Reference
Pronouns refer to unclear or unspecified nouns or noun phrases. Use specific nouns or noun phrases to establish clear antecedents for pronouns.
Example 1
- Incorrect: There is a new restaurant downtown that everyone is talking about. It is supposed to be very good.
- Correct: There is a new restaurant downtown called “The Spicy Mango” that everyone is talking about. It is supposed to be very good.
Example 2
- Incorrect: I read a book about a detective who solved a mystery. He was very clever.
- Correct: I read a book about Sherlock Holmes, a detective who solved a mystery. He was very clever.
7. Number Agreement
Singular pronouns cannot refer to plural nouns, and vice versa. Match the number of the pronoun to the number of its antecedent.
Example 1
- Incorrect: The committee is meeting tomorrow, and they will discuss the new proposal.
- Correct: The committee is meeting tomorrow, and it will discuss the new proposal.
Example 2
- Incorrect: My glasses are on the table. It needs cleaning.
- Correct: My glasses are on the table. They need cleaning.
8. Person Agreement
Pronouns must agree with the person of the noun they refer to (first person, second person, third person). Use the same person throughout the sentence for clarity.
Example 1
- Incorrect: You should have told me sooner.
- Correct: I should have told you sooner.
Example 2
- Incorrect: The teacher asked us if we understood the lesson. Then, he explained it further.
- Correct: The teacher asked us if we understood the lesson. Then, the teacher explained it further.
9. Possessive Pronoun Confusion
Mixing up possessive pronouns with object pronouns. Possessive pronouns show ownership, while object pronouns act as objects of verbs or prepositions.
Example 1
- Incorrect: The book is mine. Please give it to I.
- Correct: The book is my book. Please give it to me.
Example 2
- Incorrect: They gave the award to her and they.
- Correct: They gave the award to her and them.
10. Misuse of Reflexive Pronouns
Incorrect usage of reflexive pronouns, which refer back to the subject. Use reflexive pronouns only when the action reflects back on the subject.
Example 1
- Incorrect: I gave the book to my friend and myself.
- Correct: I gave the book to my friend and me.
Example 2
- Incorrect: Sarah hurt herself lifting the box.
- Correct: Sarah hurt her lifting the box.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply