Curium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
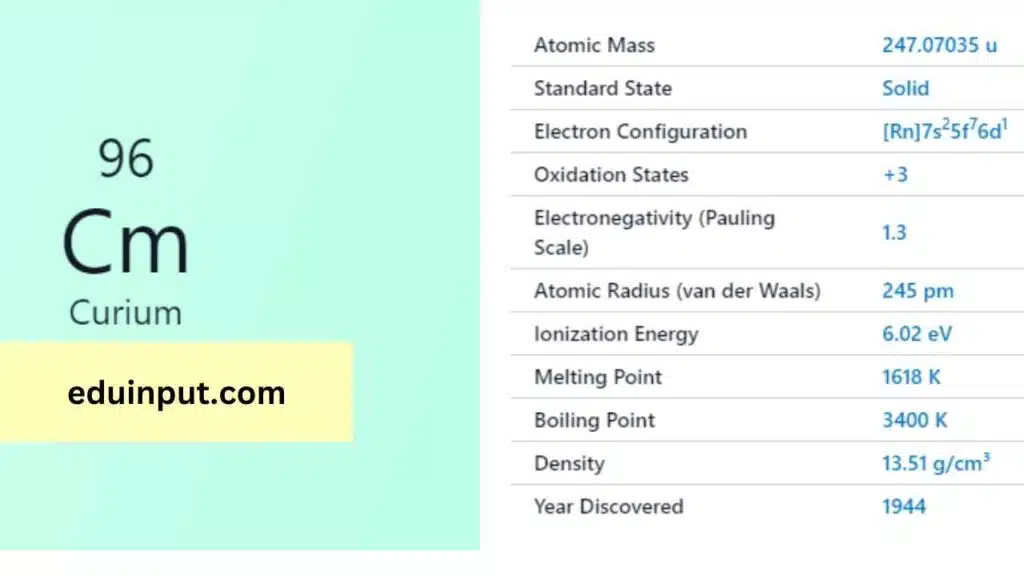
Curium is a synthetic, radioactive element with the atomic number 96 and symbol Cm. It is a member of the actinide series and is named after Marie and Pierre Curie, who discovered radium and polonium.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Curium |
| Symbol | Cm |
| Atomic number | 96 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | (longest-lived isotope) |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silver |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | |
| Group name | Actinoid |
| Period in periodic table | 7 (actinoid) |
| Block in periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.25.9.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-51-9 |
Discovery
Curium was first synthesized in 1944 by a group of scientists led by Glenn T. Seaborg, Ralph A. James, and Albert Ghiorso at the University of California, Berkeley. They created it by bombarding plutonium-239 with alpha particles.
Physical Properties
Curium is a dense, silvery-white metal that tarnishes in air. It has a melting point of 1,340°C and a boiling point of 3,110°C. Curium is highly radioactive and emits alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays.
Chemical Properties
Curium is a highly reactive metal that readily reacts with oxygen, water, and acids. It forms compounds in various oxidation states, with the +3 oxidation state being the most stable.
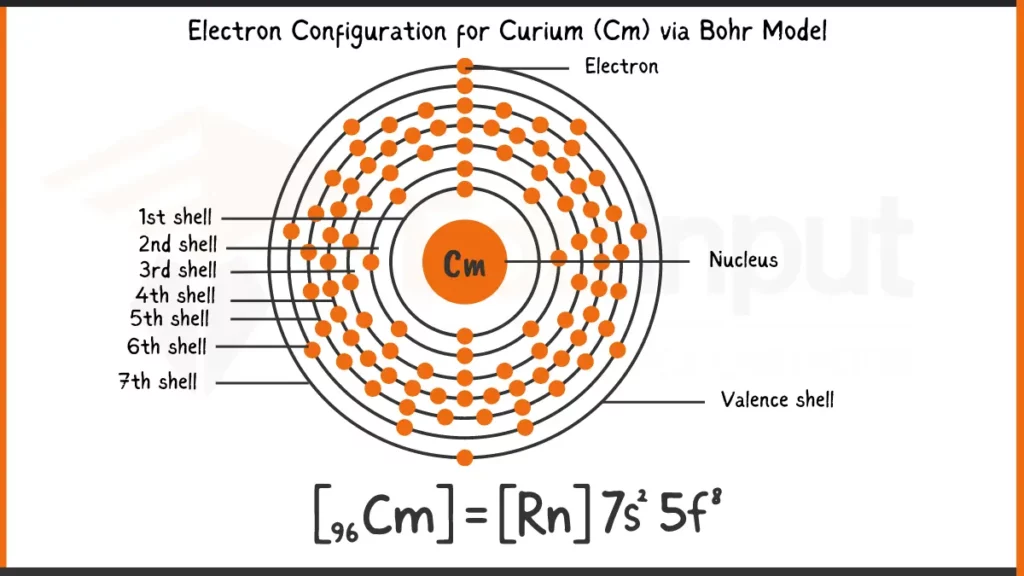
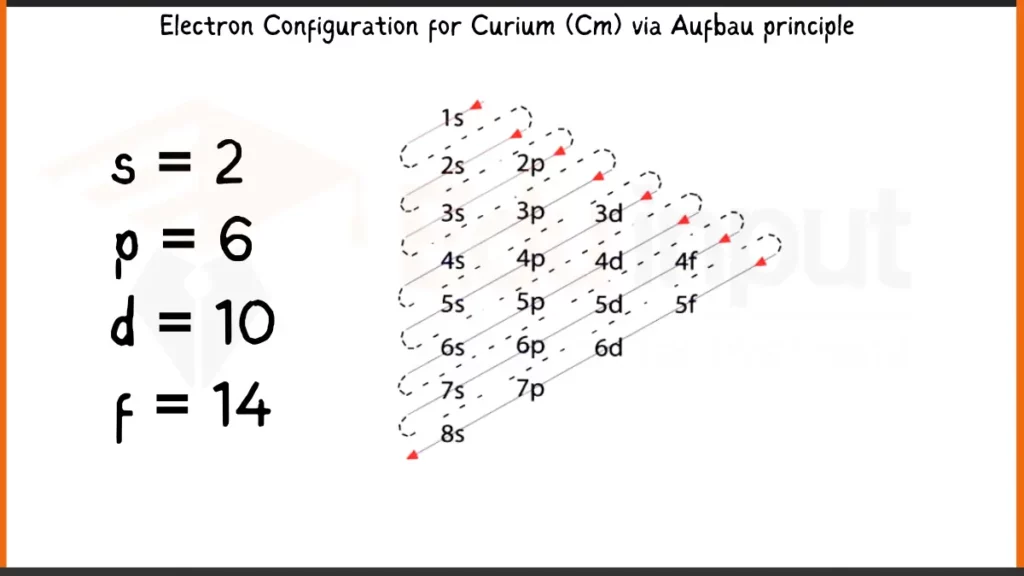
Electronic Configuration of Curium
Curium (Cm), with 96 electrons, follows the Aufbau principle to fill its orbitals. The full configuration reflects this, with 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁶5s²4d¹⁰5p⁶6s²4f⁷5d¹7s² showing the unique filling of the 5f subshell before 6d due to subtle energy level differences.
Electronic Configuration of Curium via Bohr Model
Electronic Configuration of Curium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Curium is used as a neutron source in certain types of nuclear reactors.
- It is also used in the production of other synthetic elements and in nuclear weapons research.
- Curium-244, a radioactive isotope of curium, has a half-life of 18.1 years and is used in space probes and satellites as a power source.
Applications
Curium has a limited number of applications due to its highly radioactive nature. It is mainly used in the research and development of nuclear technology and in space exploration.
Curium is a synthetic, radioactive element that was first synthesized in 1944. It has a silvery-white appearance and is highly reactive. Due to its radioactive properties, it has limited practical applications and is mainly used in research and development in nuclear technology and space exploration.





Leave a Reply