Darmstadtium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
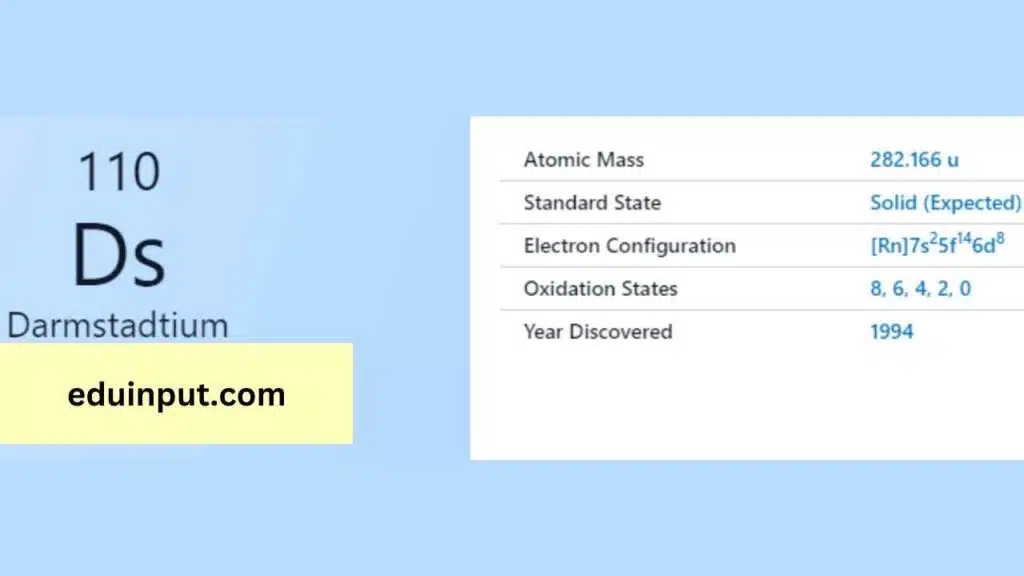
Darmstadtium, with the symbol Ds, is a synthetic element in the periodic table. It is a highly radioactive metal and a member of the transactinide elements. It is named after the German city of Darmstadt, where it was first synthesized in 1994.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Darmstadtium |
| Symbol | Ds |
| Atomic number | 110 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | (longest-lived isotope) |
| Standard state | Presumably a solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Unknown, probably metallic and silvery white or grey in appearance |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Block in the periodic table | 10 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Period in periodic table | 7 |
| Block in periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.32.17.1 |
| CAS Registry | 54083-77-1 |
Discovery
Darmstadtium was first created by a team of German scientists led by Sigurd Hofmann at the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany. The team used a heavy ion accelerator to bombard lead with nickel ions, which resulted in the creation of two atoms of darmstadtium. The discovery was officially confirmed in 2001.
Physical Properties
Darmstadtium is a highly radioactive metal with a silver-white appearance. It has a melting point of approximately 280 degrees Celsius and an estimated boiling point of 540 degrees Celsius. Due to its short half-life, the physical properties of darmstadtium are not well known.
Chemical Properties
Darmstadtium is a member of the transactinide series, which means it is highly reactive and unstable. It is predicted to have chemical properties similar to those of its neighboring elements on the periodic table, such as platinum and mercury. However, due to its short half-life, it is difficult to study the chemical properties of darmstadtium in detail.
Electronic Configuration of Darmstadtium
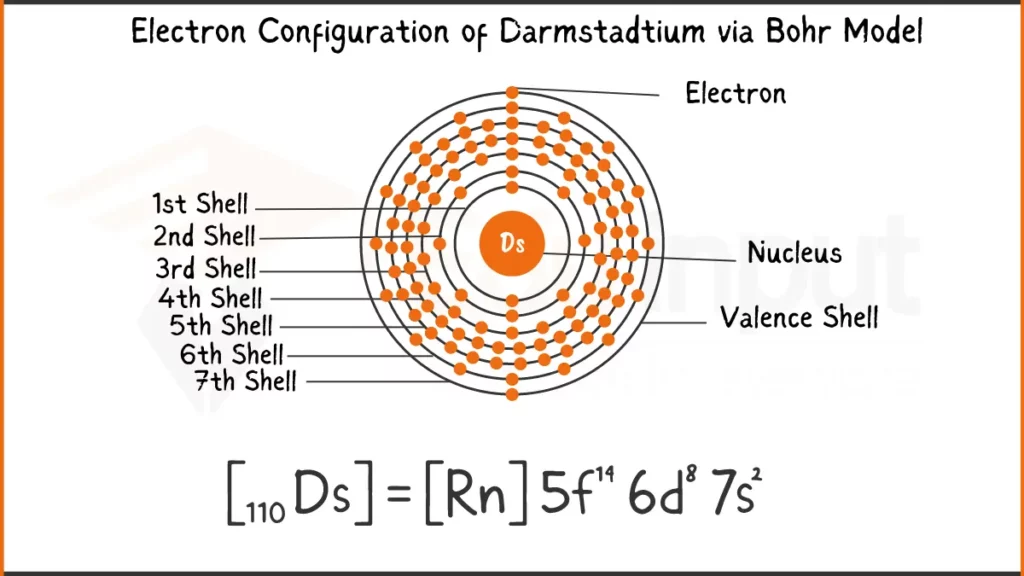
Darmstadtium (Ds) possess a complex configuration with 110 electrons ([Rn] 5f¹⁴ 7s² 6d⁸. The key lies in its outermost 6d subshell, holding an odd eight electrons (6d⁸). This unique arrangement is believed to influence how Darmstadtium bonds with other elements.
Electronic Configuration of Darmstadtium via Bohr Model
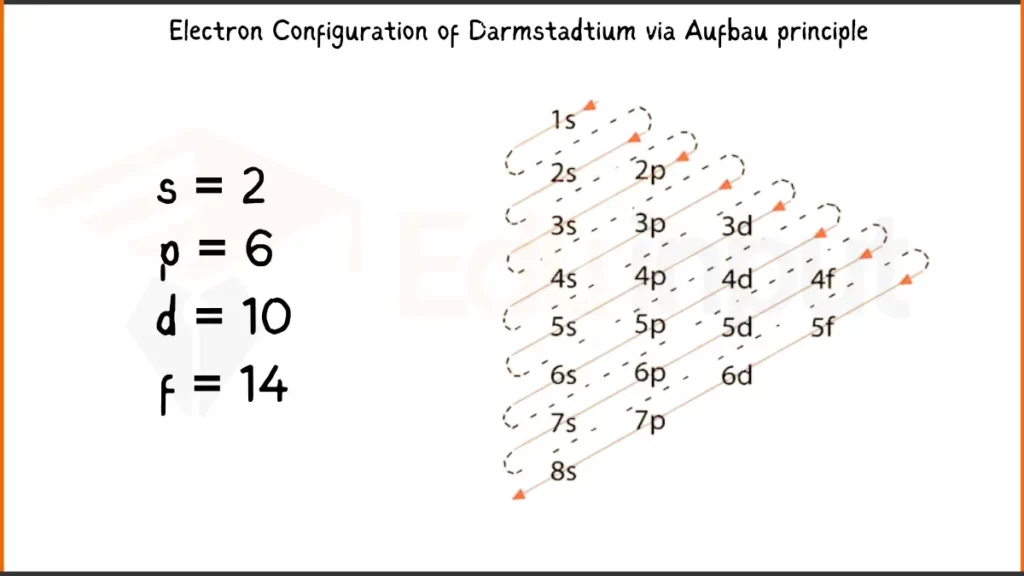
Electronic Configuration of Darmstadtium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Darmstadtium is a highly radioactive metal and is extremely difficult to produce.
- It has a half-life of less than a second and is not found naturally on Earth.
- Darmstadtium is the heaviest element that can be created by fusion of lighter elements, and cannot be created by neutron capture methods.
Applications
Due to its extremely short half-life and radioactive nature, darmstadtium currently has no known practical applications. However, it is used in scientific research to study the properties of the transactinide elements and to better understand the behavior of atomic nuclei.






Leave a Reply