Difference Between Hybridization and Cross-Breeding
Key Difference
Hybridization and cross-breeding are both methods of combining genetic material from different species or varieties, but they differ in technique and scope. Hybridization is a controlled process often conducted in a laboratory, focusing on creating a hybrid with specific traits from two different species or genetic lines.
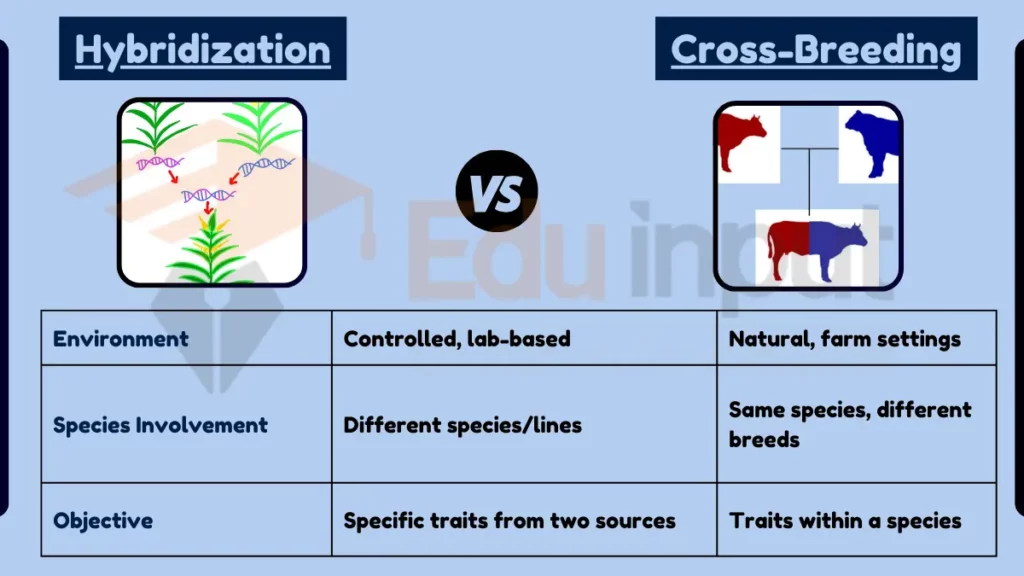
Cross-breeding, typically used in agriculture and animal breeding, involves mating individuals from different breeds or varieties to produce offspring with desired traits.
Comparative Analysis
- Control and Environment:
- Hybridization: More controlled, often in a lab.
- Cross-Breeding: Usually in natural or farm settings.
- Species or Varieties Involved:
- Hybridization: Different species or genetic lines.
- Cross-Breeding: Different breeds or varieties of the same species.
- Objective:
- Hybridization: Specific traits from two species.
- Cross-Breeding: Desired traits within a species.
Table Summary of Hybridization vs Cross-Breeding
| Feature | Hybridization | Cross-Breeding |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Controlled, lab-based | Natural, farm settings |
| Species Involvement | Different species/lines | Same species, different breeds |
| Objective | Specific traits from two sources | Traits within a species |
Hybridization and cross-breeding both aim to combine desirable traits, but differ in their methods, control levels, and the genetic diversity of the organisms involved.



Leave a Reply