Difference Between Myxomycota and Oomycota
Key Difference
Myxomycota and Oomycota are both groups of fungus-like organisms, but they differ significantly in their characteristics and life cycles. Myxomycota, commonly known as slime molds, are characterized by their amoeboid properties and life cycle that includes a plasmodial stage.
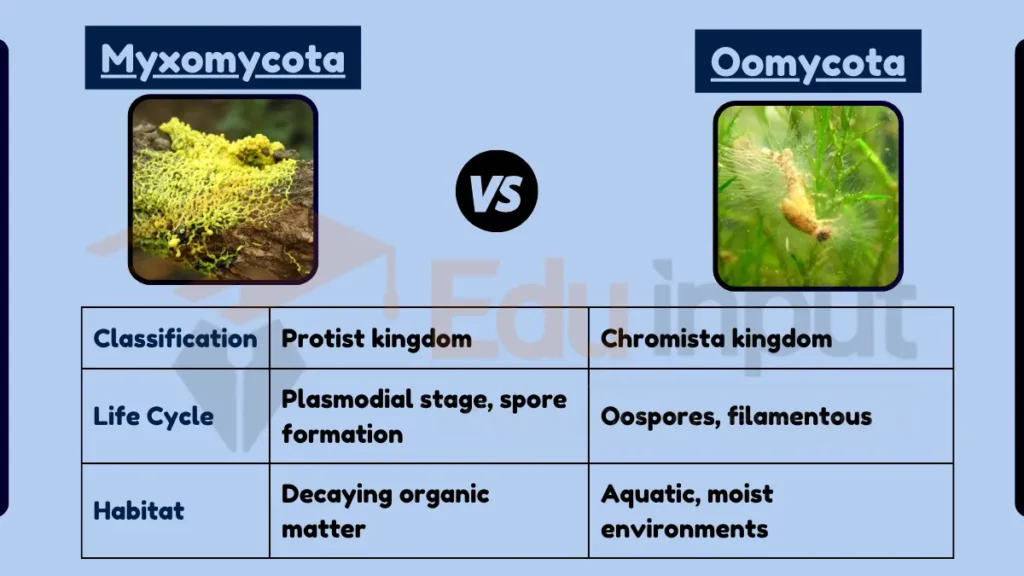
Oomycota, or water molds, are more closely related to algae and are known for their filamentous growth and oospores.
Comparative Analysis
- Biological Classification:
- Myxomycota: Considered a part of the protist kingdom.
- Oomycota: Classified under the Chromista kingdom, more related to algae.
- Life Cycle:
- Myxomycota: Has a plasmodial stage, forming spores.
- Oomycota: Produces oospores, filamentous growth.
- Habitat:
- Myxomycota: Often found on decaying wood and plant material.
- Oomycota: Aquatic or moist environments.
- Ecological Role:
- Myxomycota: Decomposers, feeding on microorganisms.
- Oomycota: Includes pathogens of plants and fish.
Table Summary Myxomycota vs Oomycota
| Feature | Myxomycota | Oomycota |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | Protist kingdom | Chromista kingdom |
| Life Cycle | Plasmodial stage, spore formation | Oospores, filamentous |
| Habitat | Decaying organic matter | Aquatic, moist environments |
| Role | Decomposers | Pathogens and decomposers |
Myxomycota and Oomycota, while both fungus-like, are distinguished by their classification, life cycles, habitats, and ecological roles, reflecting their unique evolutionary paths.



Leave a Reply