Difference between Spontaneous and Non-Spontaneous Reactions
The main difference between spontaneous and non-spontaneous reactions is their thermodynamic favorability.
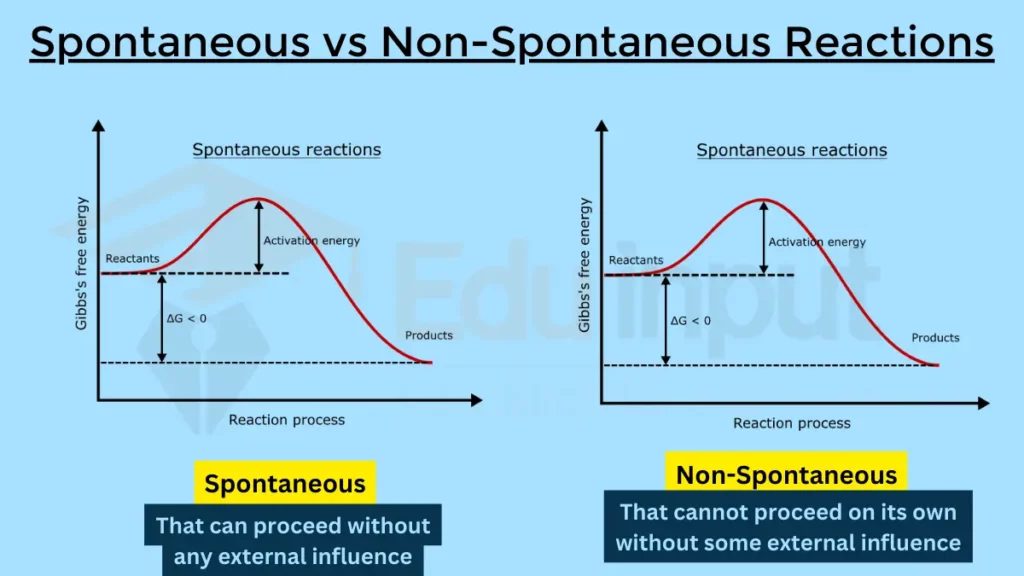
Spontaneous reactions are thermodynamically favorable, meaning they are exothermic reactions that can occur without any external input of energy. (Not all sponteneous reaction can occur without external energy, some of them might be endothermic)
Non-spontaneous reactions, on the other hand, are thermodynamically unfavorable, meaning they require an external input of energy to occur.
Also Read: Concept of Thermochemistry
Spontaneous vs. Non-Spontaneous Reactions
Here are the main difference between Spontaneous and Non-Spontaneous Reactions:
| Characteristic | Spontaneous Reactions | Non-Spontaneous Reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Occurrence | Occur naturally | Require external energy input |
| Energy Change | Often exothermic (release energy) | Often endothermic (absorb energy) |
| Direction | Proceed toward a lower free energy state | Proceed toward a higher free energy state |
| External Influence | Typically do not require external energy | Require external energy source |
| Thermodynamic Favorability | Thermodynamically favorable | Thermodynamically unfavorable |
| Standard Conditions | Can occur under standard conditions | Often require non-standard conditions |
| Reversibility | Typically irreversible | Typically reversible |
| Reaction Rate | Tend to be rapid | Tend to be slow |
| Observable Signs | May show signs such as heat, gas bubbles, or a color change | May not show noticeable signs |



Leave a Reply