Einsteinium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Einsteinium is a synthetic element that was discovered in 1952. It is a member of the actinide series and is denoted by the symbol Es. It is a radioactive metal and is difficult to study due to its short half-life.
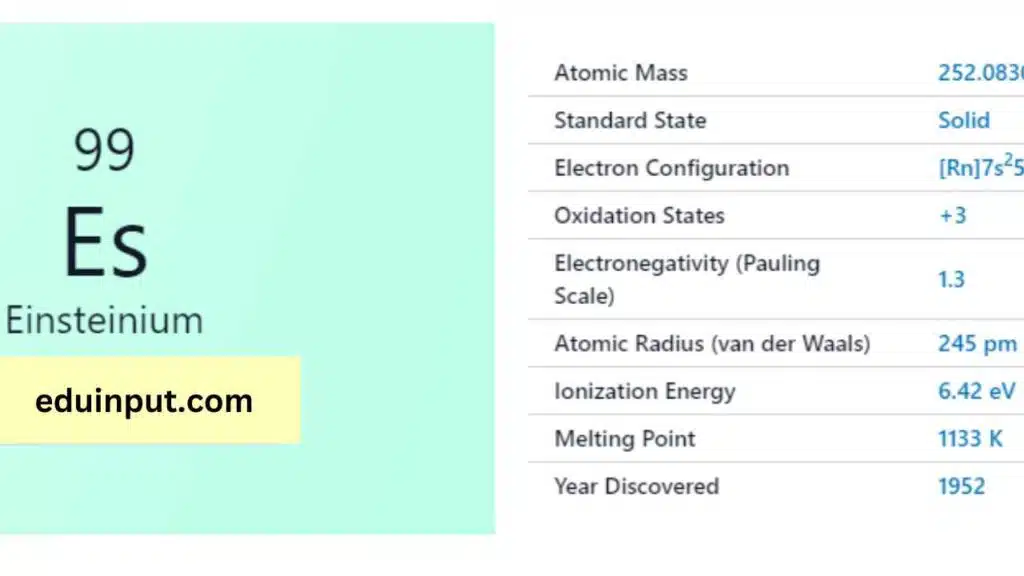
| Property | Value |
| Name | Einsteinium |
| Symbol | Es |
| Atomic number | 99 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | (longest-lived isotope) |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Unknown, but probably metallic and silvery white or grey in appearance |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | |
| Group name | Actinoid |
| Block in the periodic table | 7 (actinoid) |
| Block in periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.29.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7429-92-7 |
Discovery
Einsteinium was first discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion on November 1, 1952, by scientists at the University of California, Berkeley. The element was named after physicist Albert Einstein.
Physical Properties
Einsteinium is a soft, silvery-white, radioactive metal. It has a melting point of 860 °C and a boiling point of approximately 996 °C. It is also a paramagnetic metal, which means it is weakly attracted to magnetic fields.
Chemical Properties
Einsteinium is a highly reactive element and readily reacts with oxygen, steam, acids, and bases. Due to its radioactive nature, it is difficult to study its chemical properties.
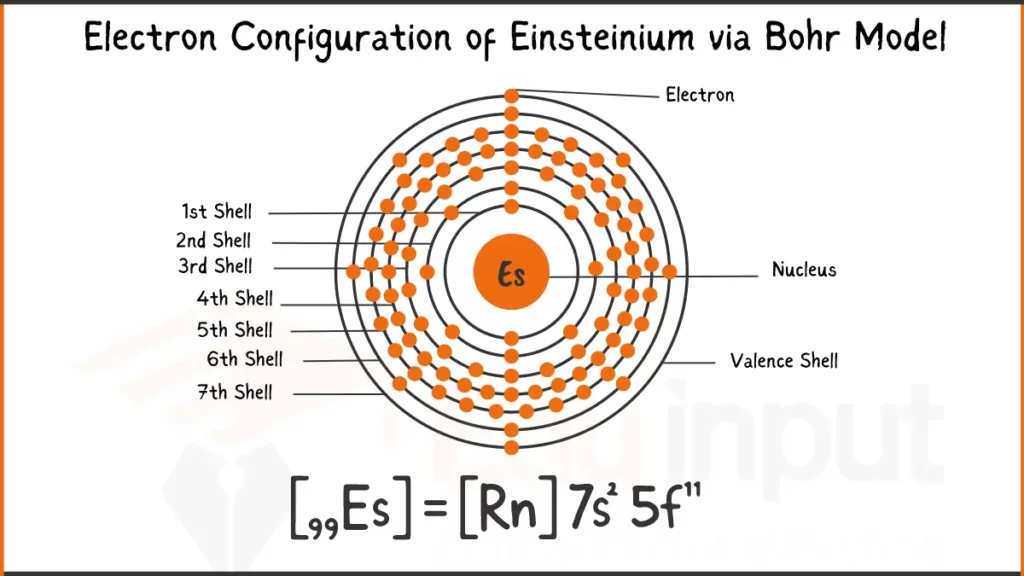
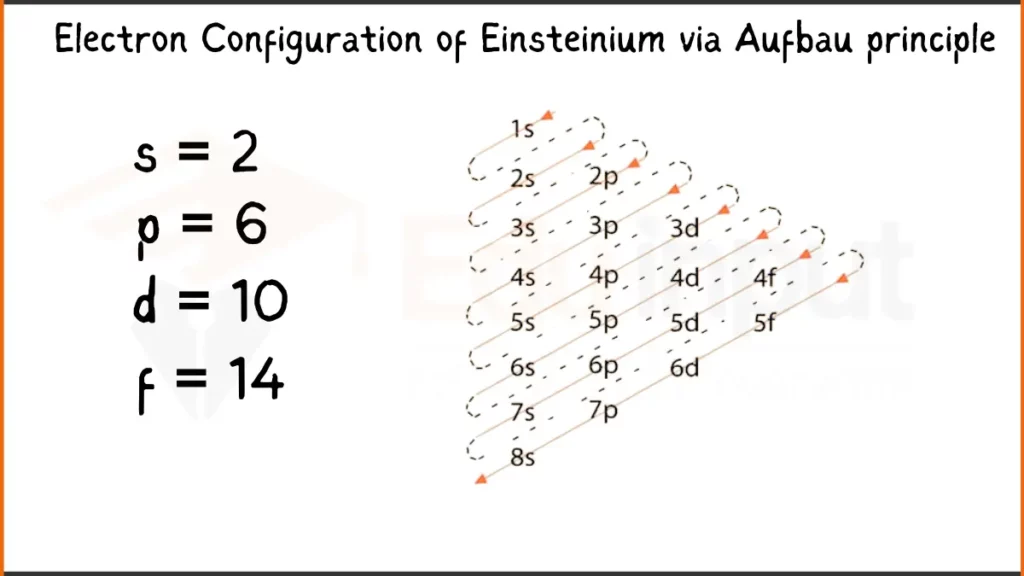
Electron Configuration of Einsteinium
Einsteinium (Es) has 99 electrons configured as [Rn]5f¹¹7s². This shows stable inner electron shell structure of Radon (Rn), with the remaining electrons filling the 5f subshell (11) and the outermost 7s subshell (2).
Electron Configuration of Einsteinium Via Bohr Model
Electron Configuration of Einsteinium Via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Einsteinium is one of the rarest elements on Earth, with only a few grams of it produced each year.
- It is used in research to study the properties of other elements and to study the effects of radiation on materials.
Applications
Einsteinium does not have any practical applications outside of scientific research. It is used primarily as a tool for studying the properties of other elements and materials.
Einsteinium is a fascinating element that is difficult to study due to its radioactive nature and short half-life. While it does not have any practical applications, it is an important tool for scientists studying the properties of other elements and materials.






Leave a Reply