Empirical Formula from Combustion Analysis
Those organic compounds which simply consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen can be analyzed by combustion.
Sole product
CO2 and H2O are the sole products.
What is combustion analysis?
Combustion analysis is a standard method of determining a chemical formula of a substance that contains hydrogen and carbon.
History of Combustion
In the 1780s, a chemist was the first to analyze organic compounds with combustion, practice Associate in nursing particularly big and expensive instrumentation that required over fifty g of the organic sample and a team of operators.
Procedure
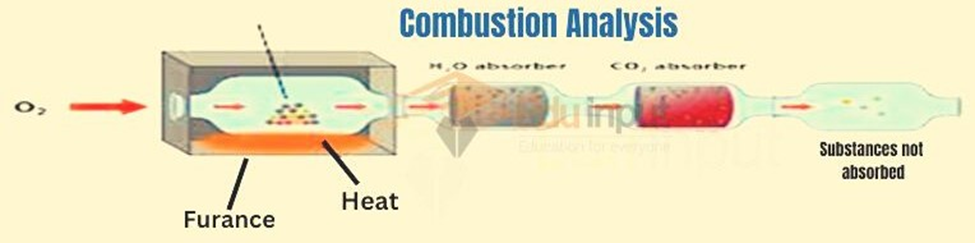
First, a sample of organic compound is weighed and then places in the combustion tube. This combustion tube is fitted in a furnace. An organic compound is burned in a furnace in the presence of excess oxygen.
All of the carbon is converted to carbon dioxide, and the hydrogen is converted to water. Water and Carbon dioxide are absorbed in Mg (ClO4) and 50% KOH respectively.
The difference in the masses of these absorbers gives us the amounts of H2O and CO2 produced. The amount of oxygen is determined by the method of difference.
Diagram for Combustion analysis
Formula used in combustion analysis
The following formulas are used to get the percentages of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, respectively.
% of Carbon = mass of CO2 / mass of organic compound x 12/44 x 100
% of Hydrogen = mass of H2O/ mass of organic compound x 2.016/18 x 100
The percentage of oxygen is obtained by the method of difference.
% of oxygen = 100 – (% of carbon + % of hydrogen)
Example
A sample of liquid consisting of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen was subjected to combustion analysis. 0.5439 g of the compound gave 1.039 g of CO2, 0.6369 g of H2O. Determine the empirical formula of that compound.
Solution
Mass of organic compound = 0.5439 g
Mass of carbon dioxide = 1.039 g
Mass of water = 0.6369 g
% of Carbon = 1.039 / 0.5439 x 12/44 x 100 = 52.098 %
% of Hydrogen = 0.6369 / 0.5439 x 2.016/18 x 100 = 13.11%
% of oxygen = 100 – (52.098 +13.11) = 34.79
No. of gram atoms of C = 52.108/12 = 4.34
No. of gram atoms of H = 13.11/1.008 = 13.01
No. of gram atoms of O = 34.77/16 = 2.17
Atomic ratio of C = 4.34/2.17 = 2
Atomic ratio of H = 13.01/ 2.17 = 6
Atomic ratio of O = 2.17/2.17 = 1
Empirical formula C2H6O
FAQs
Why do we use combustion analysis?
Combustion analysis is a vital component of the management and operation of combustion processes. This study analyzes the combustion parameters of different fuels, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to use each type of fuel more efficiently.
What is combustion in chemistry?
Combustion analysis is important for the right management and operation of combustion processes. Through studying the parameters of combustion, you will know what causes blessing to occur, so that you can obtain greater efficiency, which reduces costs and emissions.




Leave a Reply