Examples of Digital Quantities
Digital quantities refer to numerical values expressed using binary digits, i.e., 0s and 1s. These values are used to represent and store information in a computer system.
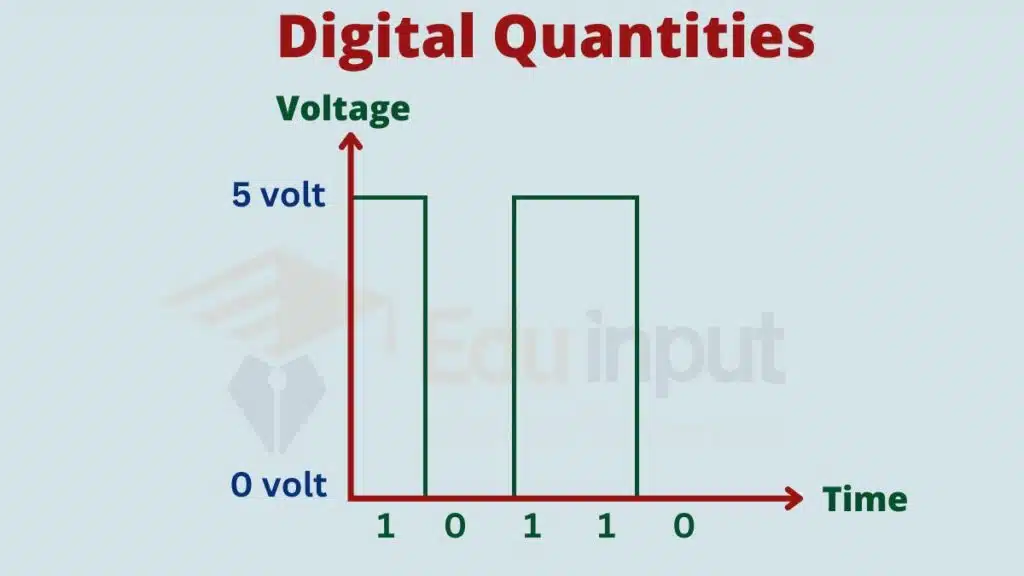
The binary nature of digital quantities stems from electronic devices being in one of two states: off (represented by 0) or on (represented by 1). By arranging these bits in specific sequences, computers can represent and process a wide range of data.
Understanding digital quantities is crucial in computer science, as they form the foundation for various concepts and operations. From simple calculations to complex algorithms, digital quantities are vital in executing computer programs and functioning digital devices.
Examples of Digital Quantities
Let’s explore some popular examples of digital quantities that students should be familiar with:
Binary Numbers
Binary numbers are a fundamental example of digital quantities. They consist of only two digits: 0 and 1. Unlike the decimal number system, which uses ten digits (0-9), the binary system operates on a base of 2.
This means each digit in a binary number represents a power of 2. Computer systems widely use binary numbers for various purposes, such as representing memory addresses, performing arithmetic operations, and encoding instructions.
To convert a decimal number to binary, you can use a simple process of division and remainders.
Let’s consider an example
Decimal Number: 25
Binary Representation: 11001
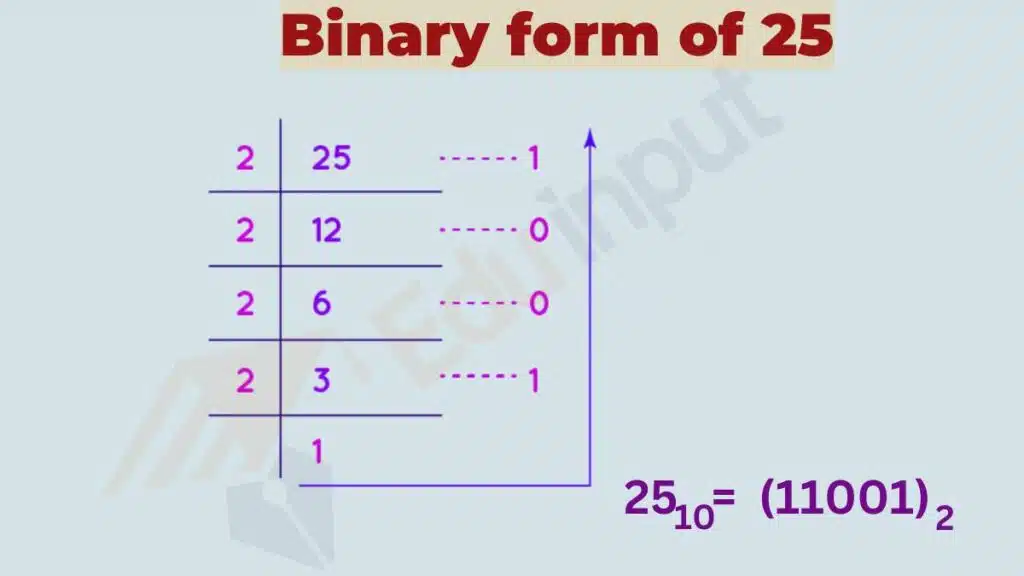
To convert 25 to binary, divide it successively by 2 and note down the remainder until the quotient becomes zero. Reading the remainder from bottom to top gives us the binary representation: 11001.
ASCII Characters
Another example of digital quantities is ASCII characters. ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a character encoding scheme that assigns unique numeric codes to characters. These codes are represented using digital quantities, specifically 7-bit binary numbers.
For example
The ASCII code for the letter ‘A’ is 65. In binary, it is represented as 01000001. Similarly, each character has a corresponding ASCII code that can be represented using digital quantities. ASCII codes are essential for computer communication, ensuring consistent representation and interpretation of characters.
Pixels in Digital Images
Digital images are made up of pixels, which are small units of visual information. Each pixel represents a specific colour or shade. The digital quantity associated with each pixel determines its colour or intensity level. The number of bits used to represent a pixel determines the colour depth or the number of distinct colours that can be displayed.

For example
An 8-bit digital quantity can represent 256 different colours, while a 24-bit digital quantity can represent millions of colours. Digital images are composed of millions of pixels, each represented by a digital quantity, allowing for the creation of intricate and detailed visuals.
Audio Samples in Digital Audio
In digital audio, sound is converted into a series of discrete samples. Each sample represents the amplitude of the sound wave at a specific point in time. These samples are represented using digital quantities, typically 16-bit or 24-bit values.
The digital quantities associated with audio samples determine the resolution and fidelity of the sound. Higher bit depths allow for a more accurate representation of sound, resulting in better audio quality. Computers can store, manipulate, and reproduce audio precisely by converting analogue sound waves into digital quantities.
Memory Addresses
In computer systems, memory addresses are used to locate and access data stored in memory. Memory addresses are represented using digital quantities, usually in binary form. Each memory address corresponds to a specific location in the computer’s memory hierarchy, such as RAM (Random Access Memory) or secondary storage devices like hard drives.
Computers efficiently store and retrieve data from memory by using digital quantities to represent memory addresses. Understanding how memory addresses are represented and manipulated is crucial for tasks such as data storage, memory management, and program execution.
Network Addresses
In computer networks, IP (Internet Protocol) addresses are used to identify and communicate with devices connected to the network. IP addresses are represented using digital quantities, specifically 32-bit or 128-bit binary numbers.
The binary representation of IP addresses enables computers to route network traffic accurately. By analyzing the digital quantities associated with IP addresses, routers, and other network devices can determine the appropriate path for data packets to reach their destinations. Understanding network addresses is essential for network administration, troubleshooting, and security tasks.
FAQs
What are digital quantities?
Digital quantities are discrete values represented using numbers, typically in binary form (0s and 1s), and are used in digital systems like computers and electronics.
How are digital quantities represented?
Digital quantities are usually represented in binary format, with two states: 0 (OFF) and 1 (ON).
What is the difference between digital and analogue quantities?
Digital quantities are discrete and have fixed steps or values.
Analogue quantities are continuous and can take any value within a range.
Why are digital quantities reliable?
Digital quantities are less affected by noise or distortion, ensuring accurate data processing and communication.





Leave a Reply