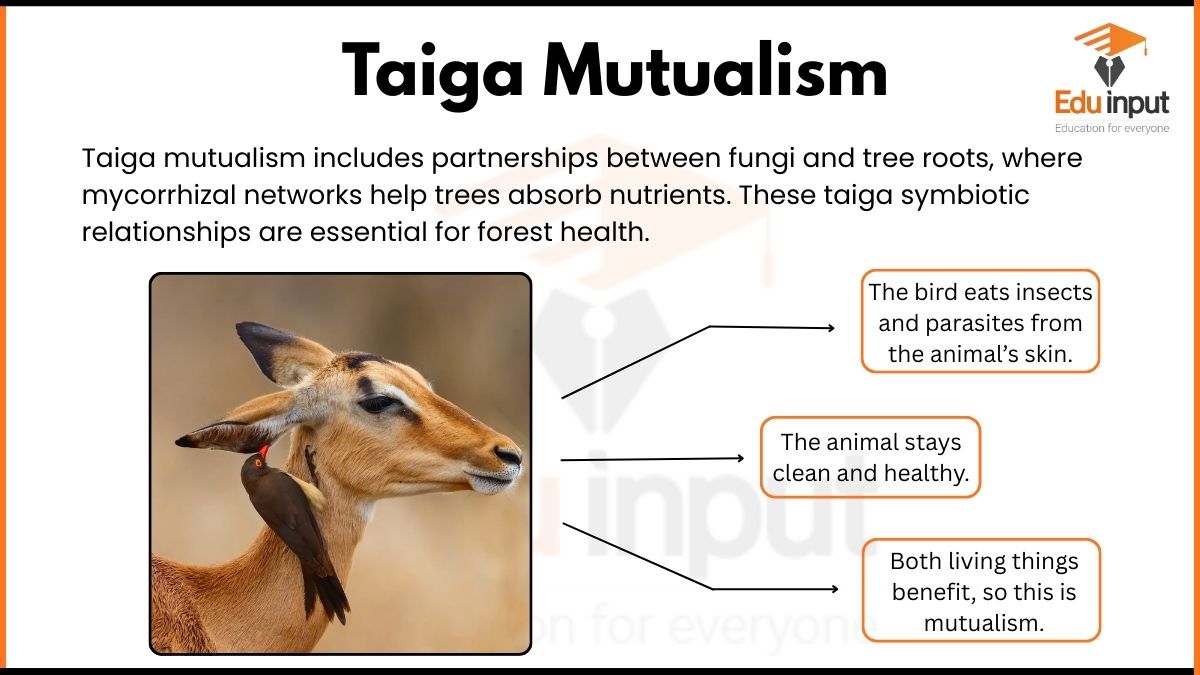
20 Examples of Genotypes
Homozygous dominant (e.g., TT), homozygous recessive (e.g., tt), heterozygous (e.g., Tt), XX, and XY are some examples of genotypes in genetics.
Examples of Genotypes
Genotypes are the genetic compositions of individuals, representing the specific combinations of alleles for particular genes. They play a crucial role in determining an organism’s traits and characteristics. Here are 20 examples of genotypes:
1: Homozygous Dominant (AA)
In this genotype, an individual carries two dominant alleles for a specific gene, resulting in the expression of the dominant trait.
2: Homozygous Recessive (aa)
Homozygous recessive individuals have two recessive alleles for a gene, leading to the expression of the recessive trait.
3: Heterozygous (Aa)
Heterozygous individuals have one dominant and one recessive allele for a gene, expressing the dominant trait while carrying the recessive allele.
4: XX
The genotype XX represents the typical sex chromosomes of a female in mammals.
5: XY
The genotype XY is characteristic of males in mammals, determining male sex.
6: AABB
This genotype represents an individual with two dominant alleles for two different genes.
7: AaBb
- AaBb indicates an individual heterozygous for two different genes, exhibiting the dominant traits for both.
8: DdEe
In this genotype, an individual is heterozygous for two genes, expressing the dominant traits for both genes.
9: PP
This genotype denotes an individual with two dominant alleles for a specific gene.
10: pp
Individuals with the genotype pp have two recessive alleles for a particular gene.
11: I^A I^A
This genotype represents a person with two dominant alleles for the ABO blood group system, resulting in type A blood.
12: I^A i
An individual with this genotype has one dominant allele for the ABO blood group (I^A) and one recessive allele (i), resulting in type A blood.
13: I^B I^B
This genotype indicates a person with two dominant alleles for the ABO blood group system, resulting in type B blood.
14: I^B i
I^B i represents an individual with one dominant allele for the ABO blood group (I^B) and one recessive allele (i), resulting in type B blood.
15: I^A I^B
Individuals with this genotype have both dominant alleles (I^A and I^B) for the ABO blood group system, resulting in type AB blood.
16: i i
This genotype signifies an individual with two recessive alleles for the ABO blood group, resulting in type O blood.
17: HbAHbA
Individuals with this genotype have two normal hemoglobin alleles and are unaffected by sickle cell disease.
18: HbSHbS
This genotype represents an individual with two mutated hemoglobin alleles, causing sickle cell disease.
19: Tt
In this genotype, an individual carries one dominant allele (T) and one recessive allele (t) for a specific gene.
20: CC
This genotype denotes an individual with two dominant alleles for a specific gene.




Leave a Reply