10 Examples of Habitat
A habitat in an ecosystem is the physical environment in which an organism or population of organisms lives and functions. It includes all of the biotic and abiotic factors that affect the organism’s survival and reproduction.
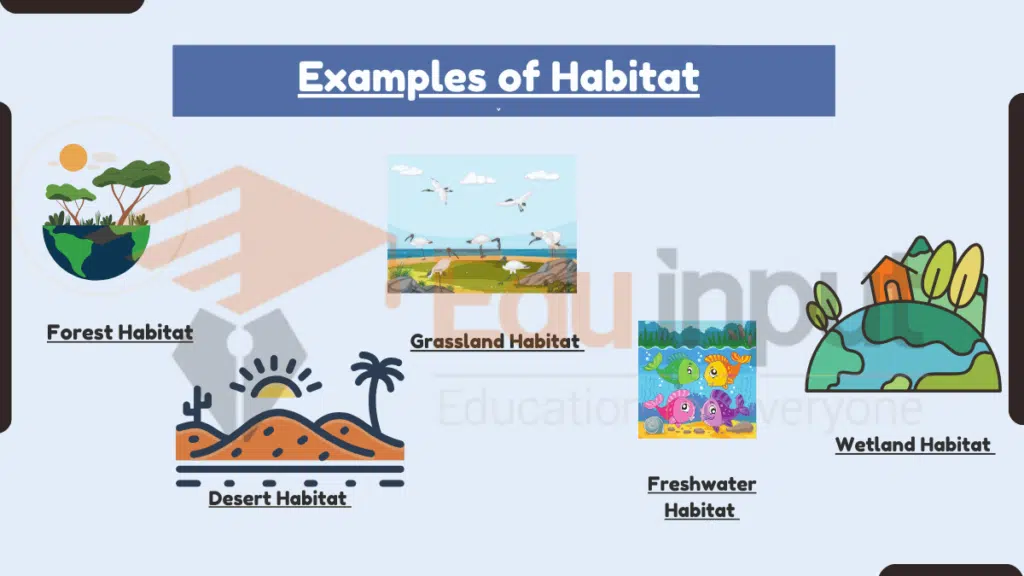
Examples of Habitat
Here are 10 examples of habitat in different ecosystems:
1. Forest Habitat
Forest habitats are examples of habitat that are home to many species of birds, mammals, insects, and fungi. Examples include tropical rainforests, temperate deciduous forests, and coniferous forests.
2. Desert Habitat
Desert habitats are arid environments with low precipitation levels. Organisms in desert habitats are adapted to conserve water, and they include animals like camels, rattlesnakes, and plants like cacti.
3. Grassland Habitat
Grassland habitats are characterized by vast expanses of grasses and herbaceous plants. Examples include prairies, savannas, and steppes. Animals such as bison, zebras, and pronghorn antelope are commonly found in grasslands.
4. Freshwater Habitat
Freshwater habitats include bodies of water like lakes, rivers, ponds, and streams. These habitats support a wide range of aquatic life, including fish, amphibians, aquatic plants, and various invertebrates.
5. Marine Habitat
Marine habitats the world’s oceans and seas, including coral reefs, kelp forests, and deep-sea environments. They host diverse marine life, such as fish, sharks, corals, and marine mammals like dolphins and whales.
6. Wetland Habitat
Wetland habitats are characterized by saturated or inundated soil conditions. Examples include swamps, marshes, and bogs. Wetlands are critical for water filtration, flood control, and habitat for birds, amphibians, and insects.
7. Tundra Habitat
Tundra habitats are found in cold, high-latitude regions and are characterized by permafrost and a short growing season. Organisms adapted to tundra environments include caribou, Arctic foxes, and lichens.
8. Urban Habitat
Urban habitats are human-made environments found in cities and towns. They include parks, gardens, and even pockets of nature within urban areas. Common urban wildlife includes squirrels, pigeons, and various plant species.
9. Mountain Habitat
Mountain habitats are characterized by steep terrain and often extreme weather conditions. They are home to species adapted to high altitudes, such as mountain goats, snow leopards, and alpine plants.
10. Cave Habitat
Cave habitats are found underground and can host unique ecosystems adapted to complete darkness. Organisms like bats, cave crickets, and blind fish are common inhabitants of cave environments.




Leave a Reply