6 Examples of User Interfaces (UIs)
User interfaces (UIs) are how humans interact with machines, devices, and computer systems.
User interfaces can be broadly categorized into graphical user interfaces (GUIs), command-line interfaces (CLIs), speech user interfaces (SUIs), tactile user interfaces (TUIs), haptic user interfaces (HUIs), and mixed reality user interfaces (MRUIs), as exemplified by Microsoft Word, macOS Terminal, Siri, ATM touchscreens, iPhone vibration feedback, and HoloLens augmented reality.
Find out what is icons in computer and their role in graphical user interfaces.
Examples of User Interfaces
Here are a few examples of user interfaces:
1. Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are the most common UI type. They provide visual elements like windows, icons, menus, and pointer cursors. GUIs are common in desktop applications like Microsoft Word and Photoshop, web apps like Gmail and Facebook, and mobile apps like Instagram and Uber.

Their graphical approach makes complex programs intuitive and user-friendly.
Examples of GUI applications
Here are a few examples of Graphical User Interfaces:
- Desktop applications – Microsoft Word, Adobe Photoshop, Spotify
- Web applications – Google Docs, Gmail, Facebook
- Mobile apps – Instagram, Twitter, Uber
- Video game interfaces – The Sims, Minecraft, Zelda – Breath of the Wild
2. Command-Line Interface (CLI)
In contrast to GUIs, command-line interfaces (CLIs) are text-based systems where users type in commands. CLIs are commonly found in terminal emulators like the macOS Terminal, in text editors like Vim and Notepad++, and in version control systems like Git Bash. CLIs require memorizing commands but allow greater control and automation via scripting.

Examples of CLI applications
Here are a few examples of Command-Line User Interfaces:
- Terminal emulators – macOS Terminal, Windows Command Prompt, Linux Terminal
- Text editors – Vim, Emacs, Notepad++
- Version control systems – Git Bash, TortoiseGit
3. Speech User Interface (SUI)
Speech user interfaces (SUIs) have emerged with the rise of virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. Voice control offers hands-free convenience for tasks like requesting information, playing music, or controlling smart home devices. SUIs are also used for voice dialing in cars or phones.
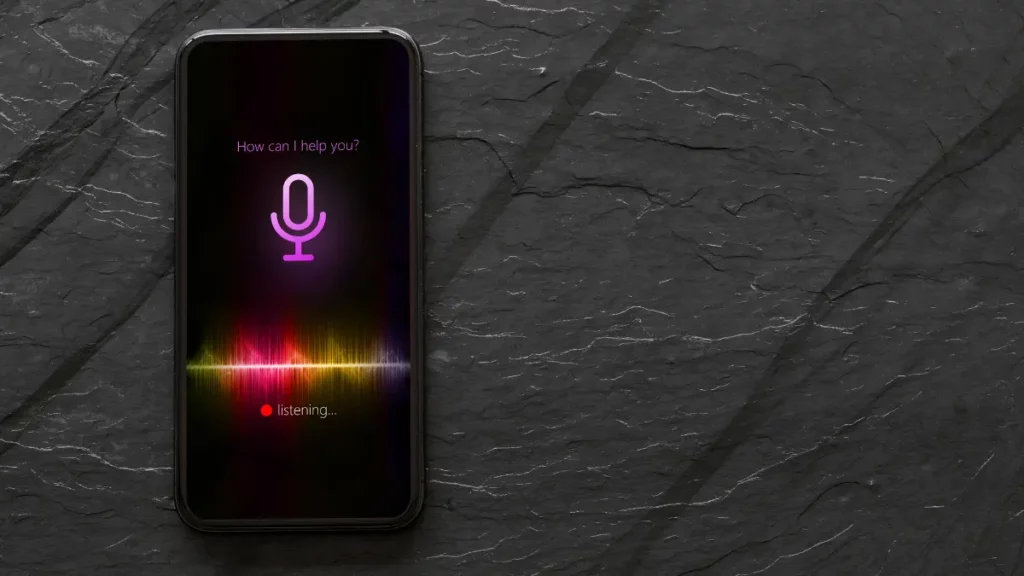
Examples of SUI applications
Here are a few examples of Speech User Interfaces:
- Virtual assistants – Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant
- Voice dialing – Car navigation systems, phone call management
- Hands-free control – Smart home devices, wearable technology
4. Tactile User Interface (TUI)
Tactile user interfaces (TUIs) employ tactile controls for direct physical manipulation. Examples include the buttons on a microwave, touchscreens on ATMs, and interactive museum exhibits. TUIs provide intuitive interactions that are well-suited for kiosks and installations.

Examples of TUI applications
Here are a few examples of Tactile User Interfaces:
- Physical buttons – Toaster controls, microwave buttons
- Touchscreen interfaces – ATMs, self-checkout kiosks
- Interactive sculptures – Museum exhibits, art installations
5. Haptic User Interface (HUI)
Haptic user interfaces (HUIs) add touch feedback, such as vibrations or force feedback. Haptics are found in phones and game controllers and can be combined with virtual reality to simulate immersive touch sensations. This expanded tactile vocabulary increases usability.
Examples of HUI applications
Here are a few examples of Haptic User Interfaces:
- Vibration feedback – Mobile game controls, haptic feedback keyboards
- Force feedback – Steering wheels, haptic feedback controllers
- Virtual reality haptics – Gloves, vests, suits that simulate touch
6. Mixed Reality User Interface (MRUI)
Mixed reality user interfaces (MRUIs) overlay digital information onto the real world. Examples include the HoloLens augmented reality headset, Meta Quest 2 virtual reality with passthrough cameras, and Magic Leap One which mixes real and virtual objects. These experiences represent the cutting edge of natural UI.
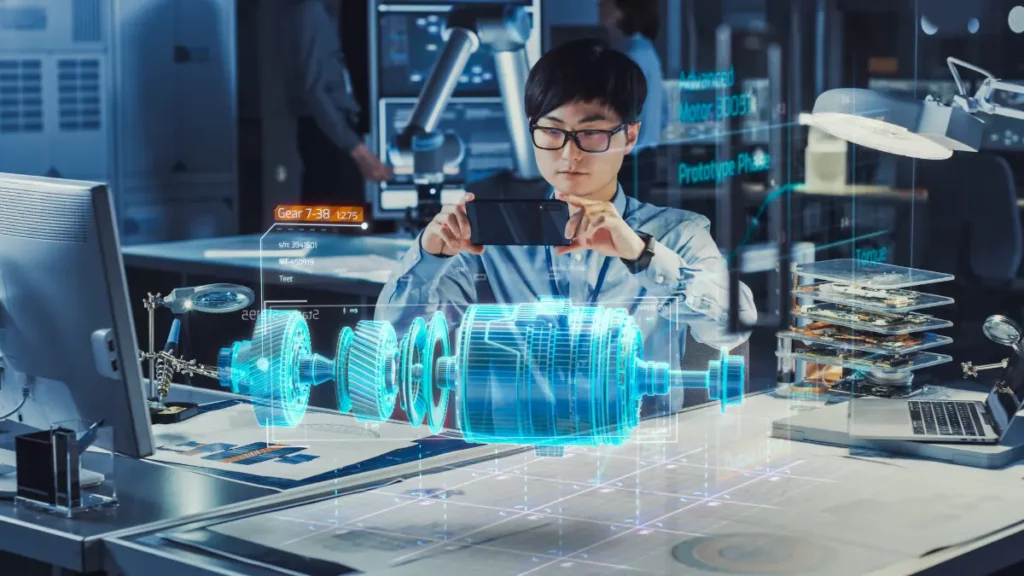

Examples of MRUI applications
- HoloLens – Overlaying digital holograms onto the physical world
- Magic Leap One – Combining real-world objects with augmented reality overlays
- Meta Quest 2 – Virtual reality headsets with pass-through cameras for real-world visibility
FAQs
What does UI mean?
UI stands for User Interface. It refers to the visual layout and elements (like buttons, menus, and icons) that users interact with on a device, app, or website.
What is a GUI?
GUI (Graphical User Interface) is a visual interface with icons, buttons, and menus that lets users interact with devices easily.
What is the 5-user interface?
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Touchscreen Interface
Voice User Interface (VUI)
Menu-Driven Interface






Leave a Reply