Fermium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Fermium is a radioactive metal element with the atomic number 100 and the symbol Fm. It belongs to the actinide series of the periodic table and is named after Enrico Fermi, a physicist who made significant contributions to nuclear physics and the development of the first nuclear reactor. It was first synthesized in 1952 by a team of scientists led by Glenn T. Seaborg.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Fermium |
| Symbol | Fm |
| Atomic number | 100 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Period in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Presumably a solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Unknown, but probably metallic and silvery white or grey in appearance |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | |
| Group name | Actinoid |
| Block in the periodic table | 7 (actinoid) |
| Group in the periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.30.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-72-4 |
Discovery
Fermium was first synthesized by bombarding plutonium-239 with neutrons in a nuclear reactor. The team of scientists led by Glenn T. Seaborg at the University of California, Berkeley, first identified the element in the debris of the nuclear explosion in the Nevada desert in 1952. Fermium is one of the heaviest elements that has been synthesized and is difficult to produce in large quantities.
Physical Properties
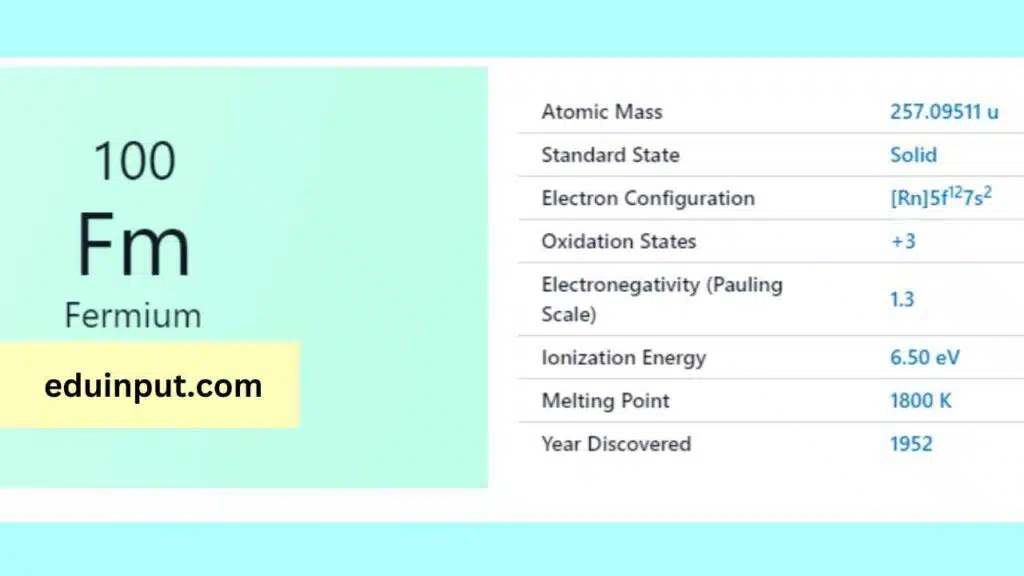
Fermium is a silvery-white metal that is radioactive and highly reactive. It has a melting point of 1527 °C and a boiling point of 1950 °C. Its density is around 20.84 g/cm3. It has no stable isotopes, and all of its isotopes are radioactive.
Chemical Properties
Fermium is a highly reactive element and is prone to oxidation. It is mainly produced in nuclear reactors and is usually found in trace amounts in uranium ores. Due to its high radioactivity, it poses a significant health hazard and requires strict handling and disposal measures.
Electron Configuration of Fermium
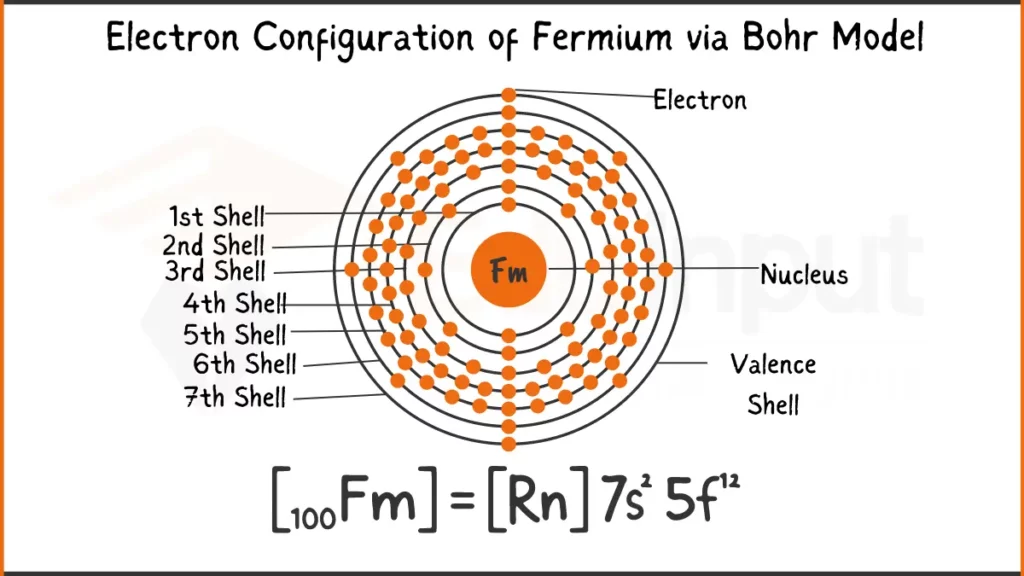
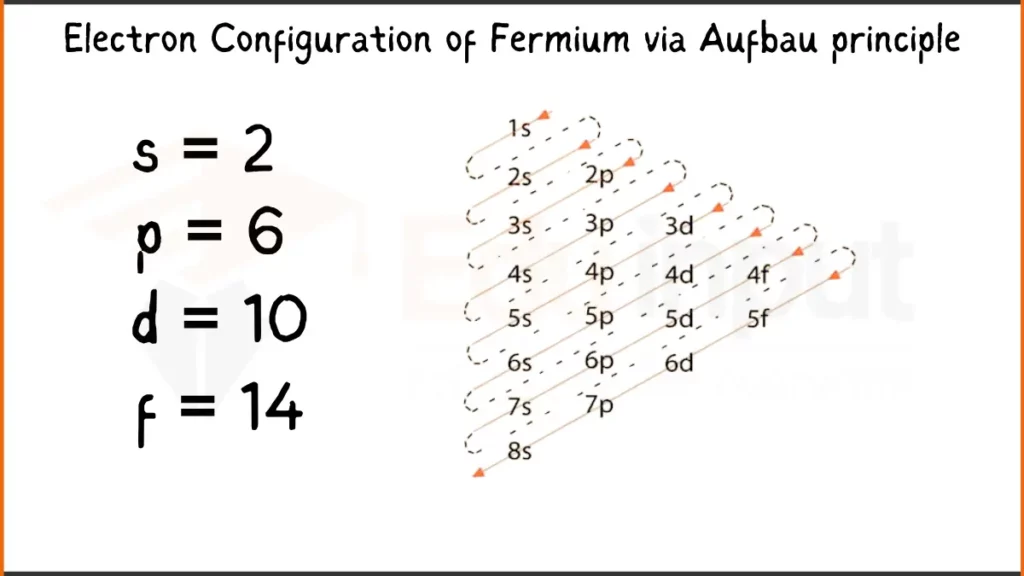
Fermium (Fm) possesses 100 electrons arranged as [Rn]5f¹²7s². This signifies it shares the stable electron configuration of Radon (Rn) for inner shells, while the remaining electrons occupy the specialized 5f subshell (12 electrons) and the outermost 7s subshell (2 electrons).
Electron Configuration of Fermium Via Bohr Model
Electron Configuration of Fermium Via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Fermium is named after Enrico Fermi, a physicist who made significant contributions to nuclear physics and the development of the first nuclear reactor.
- Fermium is one of the heaviest elements that has been synthesized.
- Fermium is highly reactive and radioactive, and all of its isotopes are unstable.
- Due to its high radioactivity, fermium poses a significant health hazard and requires strict handling and disposal measures.
Applications
Fermium has no practical applications due to its highly radioactive nature and difficulty in producing large quantities. It is mainly used for research purposes in nuclear physics, and its properties are studied to better understand the behavior of heavy elements and their isotopes.
Fermium is a highly reactive and radioactive metal element that was first synthesized in 1952 by a team of scientists led by Glenn T. Seaborg. It is mainly used for research purposes in nuclear physics and has no practical applications due to its highly radioactive nature and difficulty in producing large quantities.






Leave a Reply