Gadolinium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a rare earth metal and belongs to the lanthanide series. The element was named after the Finnish chemist Johan Gadolin, who discovered the first rare earth metal, yttrium, in 1794. Gadolinium is soft and silvery-white in appearance and is relatively stable in air.
It has a high melting and boiling point, and it is one of the few elements that can absorb neutrons without becoming radioactive.
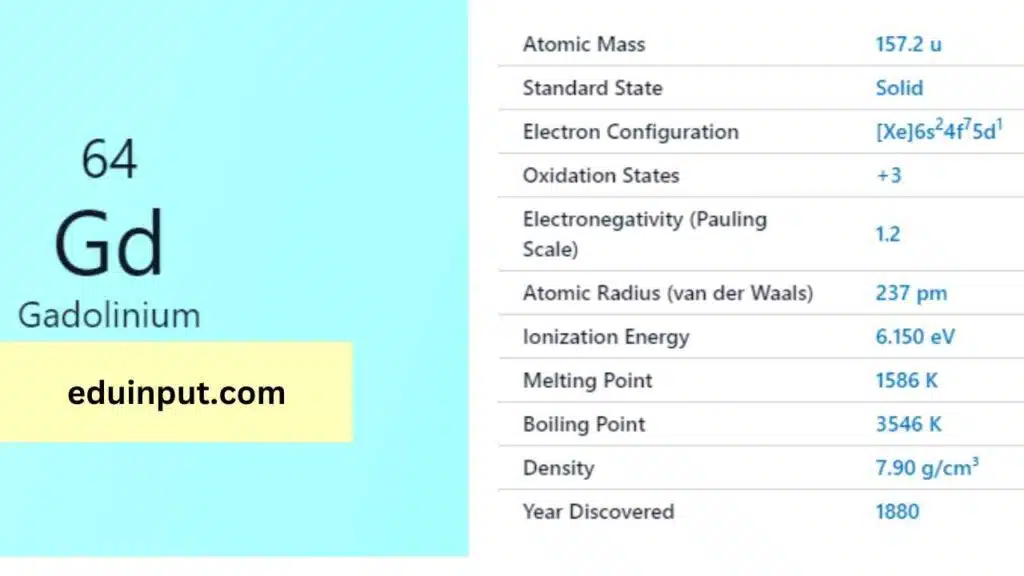
| Property | Value |
| Name | Gadolinium |
| Symbol | Gd |
| Atomic number | 64 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 157.25 g |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Block in the periodic table | |
| Group name | Lanthanoid |
| Period in periodic table | 6 (lanthanoid) |
| Period in the periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.25.9.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-54-2 |
Discovery
Gadolinium was discovered in 1880 by the Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac. He was analyzing the mineral gadolinite when he found a new oxide, which he named “gadolinite”. Later, this oxide was shown to contain a new element, which was named “gadolinium” after Johan Gadolin.
Physical Properties
Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal that is relatively soft and ductile. It has a density of 7.90 g/cm³, which is higher than that of water. It has a melting point of 1313 °C and a boiling point of 3273 °C. Gadolinium is paramagnetic, meaning that it is attracted by a magnetic field, and it has a Curie temperature of 292 °C.
Chemical Properties
Gadolinium is a reactive metal that reacts slowly with oxygen in the air to form a layer of gadolinium oxide on its surface. It is soluble in acids, and it reacts with water to form gadolinium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Gadolinium also has the ability to absorb neutrons, making it useful in nuclear reactors.
Facts
- Gadolinium is used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a contrast agent.
- Gadolinium is used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of nuclear reactions.
- Gadolinium has the highest neutron capture cross-section of any stable isotope.
- Gadolinium is named after the Finnish chemist Johan Gadolin.
Applications
Gadolinium has a few applications due to its unique properties. It is commonly used as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to enhance the contrast between different tissues. It is also used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of nuclear reactions. Gadolinium has a high neutron capture cross-section, which makes it useful in the production of nuclear fuels.
Gadolinium is a rare earth metal with unique physical and chemical properties. It is useful in a few applications, including MRI contrast agents and nuclear reactors. The element was named after the Finnish chemist Johan Gadolin, who discovered the first rare earth metal, yttrium, in 1794. Despite its relative rarity, gadolinium plays an important role in modern technology and scientific research.





Leave a Reply