Integer Factorization
Integers are whole numbers, both positive and negative, including zero. Examples of integers are -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. Integer factorization is the process of expressing a composite number as the product of its prime factors
In this article, we’ll discuss the concept of integer factorization.
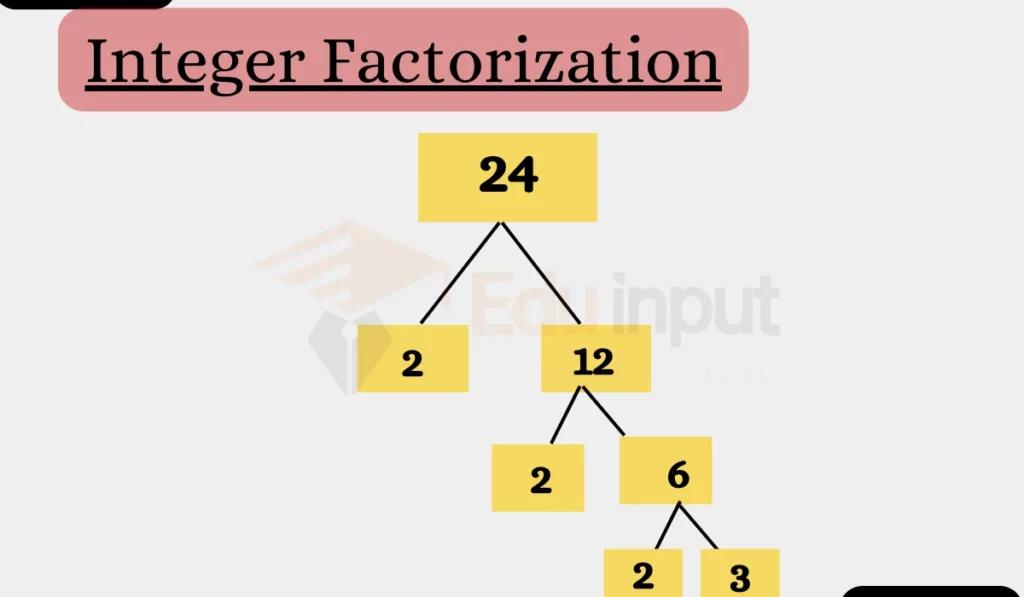
How to Factorize Integers
Step 1: Identify the Integer
Factorize this number 24.
Step 2: Find the Prime Factors
Now, we break down 24 into its prime factors. For 24, the prime factors are 2, 2, 2, and 3.
Step 3: Express as a Product
Combine these prime factors: 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 24.
So, the prime factorization of 24 is 2^3 * 3.
Solved Examples
Example
Factorizing 36
Identify the Integer 36
Find the Prime Factors 2, 2, 3, 3
Express as a Product 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 36
Therefore, the prime factorization of 36 is 2^2 * 3^2.
Example
Factorizing -48
Identify the Integer (-48)
Find the Prime Factors 2, 2, 2, 2, 3
Express as a Product -1 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = -48
So, the prime factorization of -48 is -1 x 2^4 x 3.
Also Read:
FAQs
Why is Prime Factorization Important?
Prime factorization is crucial for understanding the building blocks of numbers. It helps in simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and is fundamental in various mathematical applications.
Can Negative Numbers be Factorized?
Yes, negative numbers can be factorized. The process is similar to positive numbers, but one factor will always be -1.
What is the Significance of Prime Numbers in Factorization?
Prime numbers are the elementary components of factorization. They are the indivisible numbers that, when multiplied together, form the original integer.




Leave a Reply