Lithium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Lithium symbolized as ‘Li’ and bearing the atomic number 3, is a unique and lightweight chemical element known for its diverse properties and applications.
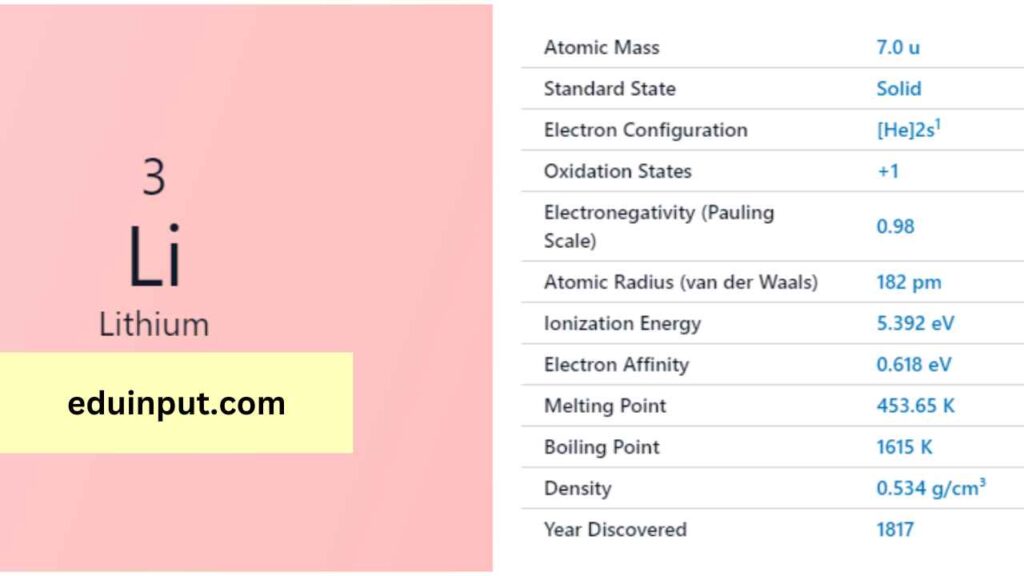
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Lithium |
| Symbol | Li |
| Atomic number | 3 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 6.94 |
| Period in the periodic table | 2 |
| Group in the periodic table | 1 (Alkali metal) |
| Block in the periodic table | s |
| Shell structure | 2.1 |
Discovery
Lithium’s discovery is credited to the Swedish chemist Johan August Arfwedson, who identified it in 1817. Lithium’s name originates from the Greek word “lithos,” meaning stone, due to its presence in mineral sources.
Physical Properties
Lithium is the lightest metal, a silver-white solid at room temperature. It is exceptionally lightweight, with a density of approximately 0.534 g/cm³. Lithium has a melting point of 180.54°C and a boiling point of 1,342°C. It is highly reactive, especially when exposed to moisture.
Chemical Properties
Lithium is highly reactive and readily forms compounds with elements like oxygen and nitrogen. It has the lowest density of all solid elements. Lithium’s most common oxidation state is +1.
Facts
- Lithium has only two stable isotopes, Li-6 and Li-7, with Li-7 being the more abundant isotope.
- Lithium plays a crucial role in the field of psychiatry and is used to treat bipolar disorder and depression.
- It is an essential component in lithium-ion batteries, powering a wide range of portable electronic devices.
Applications
Lithium has a wide array of applications across different industries:
- Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries are the cornerstone of modern portable electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems.
- Pharmaceuticals: Lithium salts are used in psychiatric medications to stabilize mood and treat bipolar disorder.
- Aerospace: Lithium’s lightweight properties make it valuable in the aerospace industry for aircraft and spacecraft components.
- Nuclear Applications: Lithium compounds are used in nuclear reactors for cooling and neutron moderation.





Leave a Reply